Java排序算法-Java入门|Java基础课程
2021-07-01 11:04
标签:stat 课程 下界 分治 应用 计算机 数组 指针 大量数据 十种常见排序算法可以分为两大类: 线性时间非比较类排序:不通过比较来决定元素间的相对次序,它可以突破基于比较排序的时间下界,以线性时间运行,因此称为线性时间非比较类排序。 稳定:如果a原本在b前面,而a=b,排序之后a仍然在b的前面。 不稳定:如果a原本在b的前面,而a=b,排序之后 a 可能会出现在 b 的后面。 时间复杂度:对排序数据的总的操作次数。反映当n变化时,操作次数呈现什么规律。 空间复杂度:是指算法在计算机内执行时所需存储空间的度量,它也是数据规模n的函数。 n个记录的直接选择排序可经过n-1趟直接选择排序得到有序结果。具体算法描述如下: 动图来源 实现步骤(分而治之) 欢迎进×××流学习,更多不定期福利、免费课程等你来~ QQ群号:560819979 敲门砖(验证信息):浪淘沙 Java排序算法-Java入门|Java基础课程 标签:stat 课程 下界 分治 应用 计算机 数组 指针 大量数据 原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/13477015/21743301、 课程目标
2、适用对象
3、相关概念
3.1 排序概念
3.2 排序算法
4、算法介绍
4.1 算法分类
非线性时间比较类排序:通过比较来决定元素间的相对次序,由于其时间复杂度不能突破O(nlogn),因此称为非线性时间比较类排序。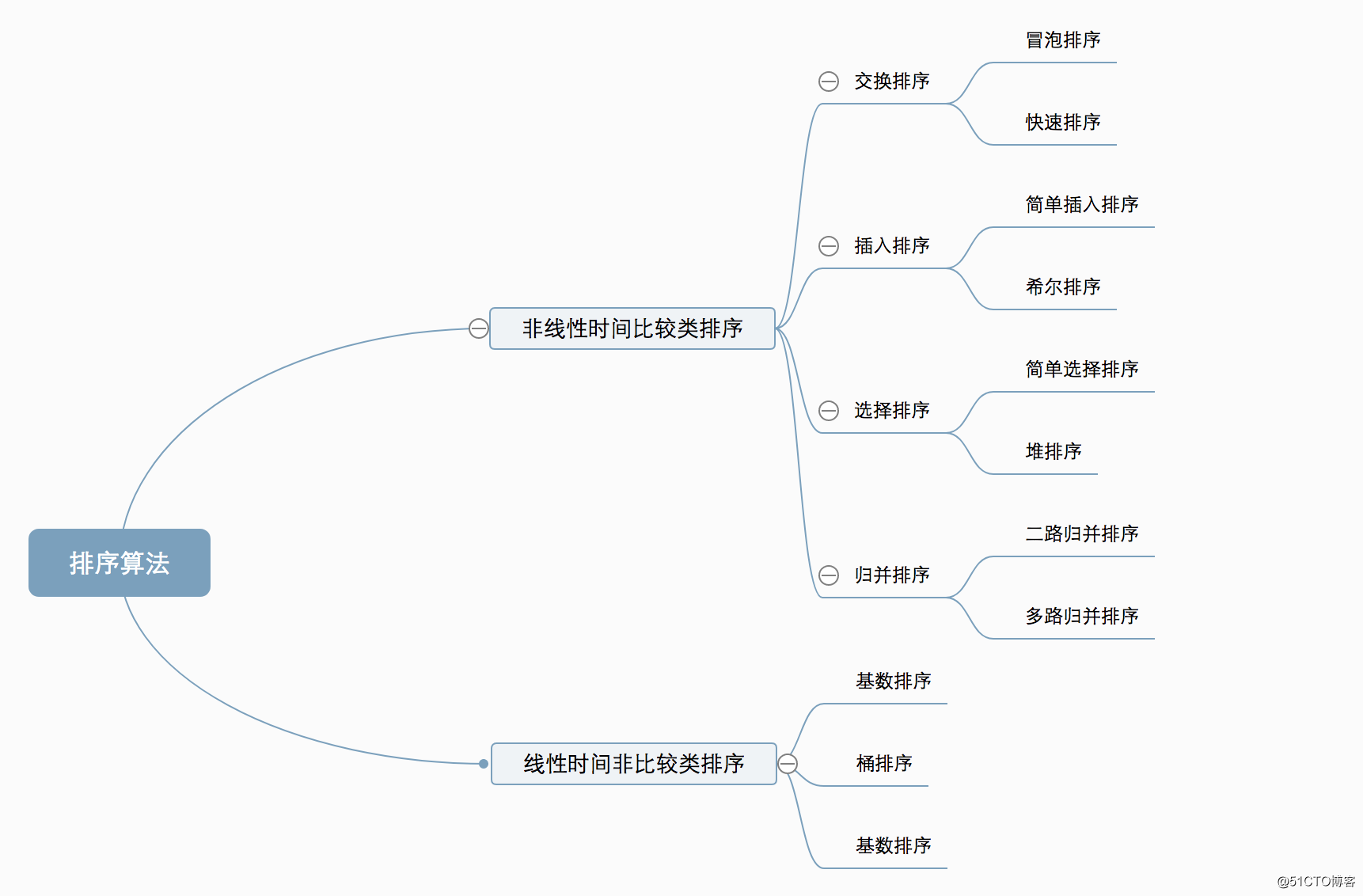
4.2 算法复杂度
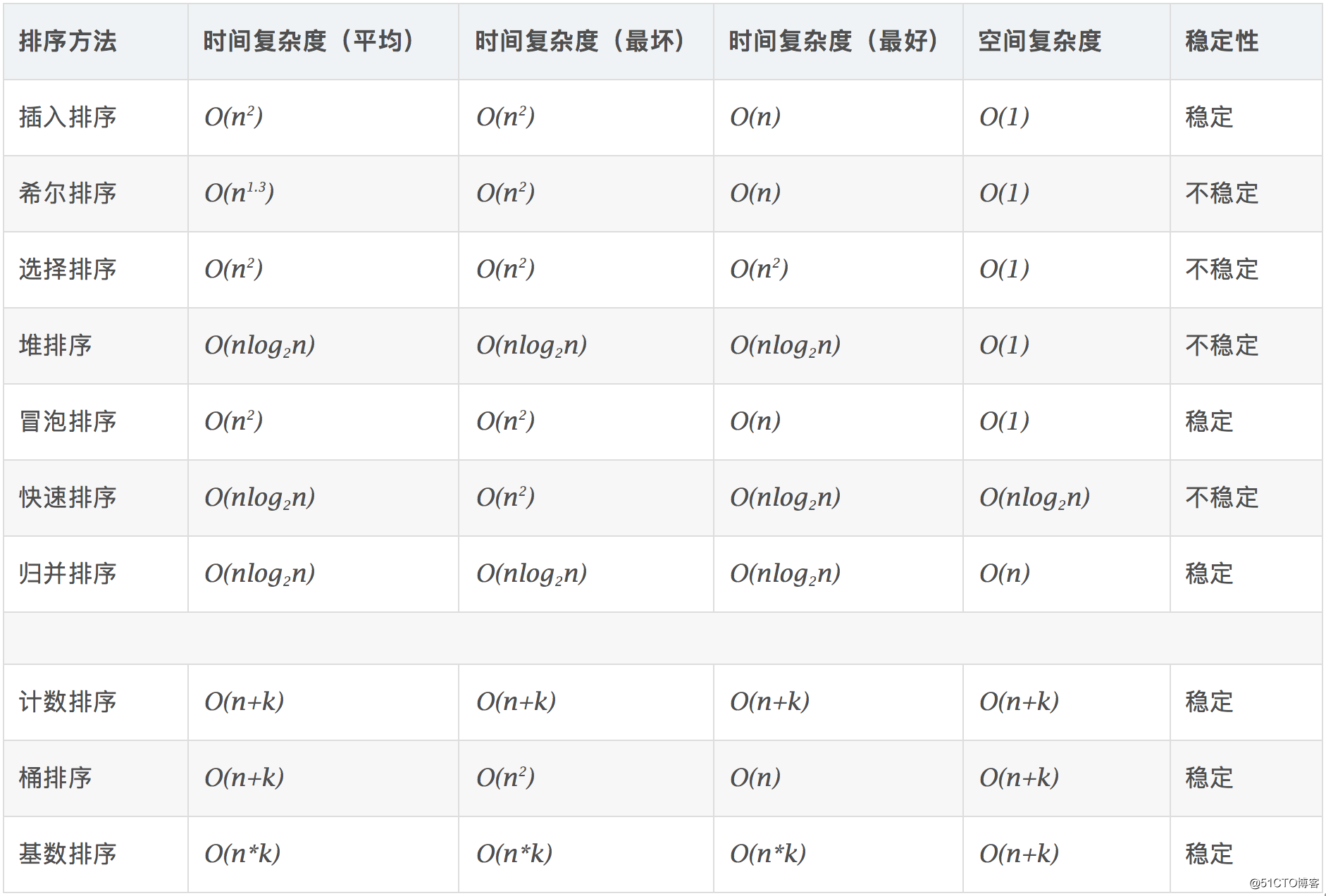
4.3 名词解释
5、冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
5.1 原理
5.2 算法描述
5.3 动图演示
5.4 代码实现
/**
* 冒泡排序
* 分类 -------------- 内部比较排序
* 数据结构 ---------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- O(n^2)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- 如果能在内部循环第一次运行时,使用一个旗标来表示有无需要交换的可能,可以把最优时间复杂度降低到O(n)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(n^2)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(1)
* 稳定性 ------------ 稳定
*/
public void bubble (int []array){
int temp;//交换数据
System.out.println("冒泡排序:");
for(int i=0;i6、选择排序(Selection Sort)
6.1 原理
6.2 算法描述
6.3 动图演示
6.4 代码实现
/**
* 选择排序
* 分类 -------------- 内部比较排序
* 数据结构 ---------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- O(n^2)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- O(n^2)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(n^2)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(1)
* 稳定性 ------------ 不稳定
*/
public void selection (int []arr){
int len = arr.length;
int minIndex, temp;
for (int i = 0; i 7、插入排序(Insertion Sort)
7.1 原理
7.2 算法描述
7.3 动图演示
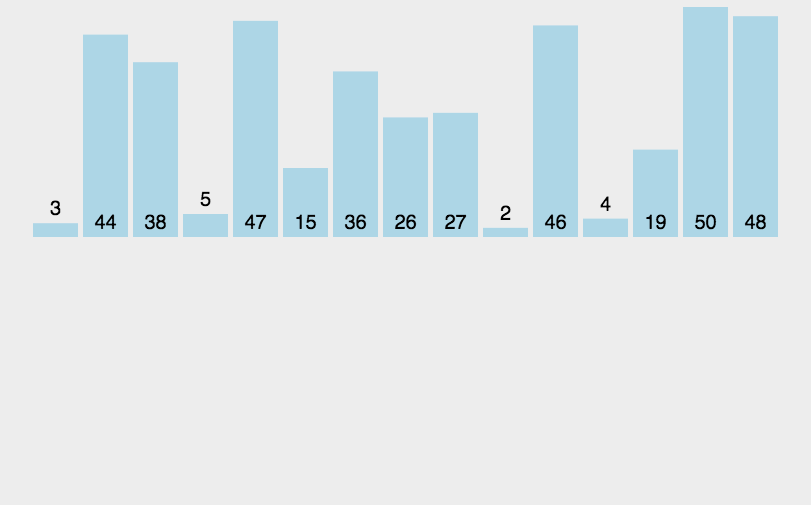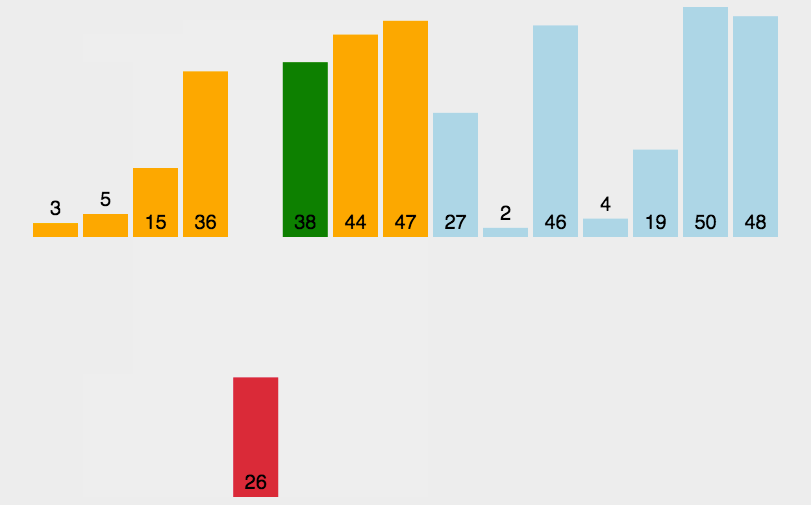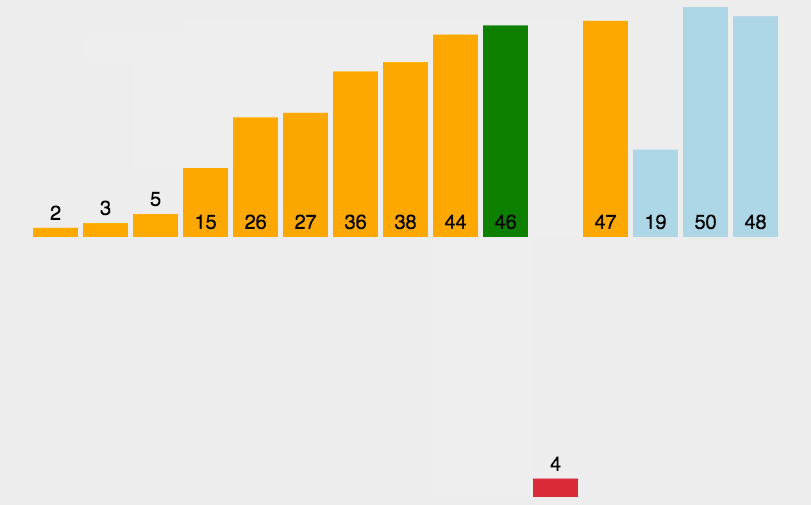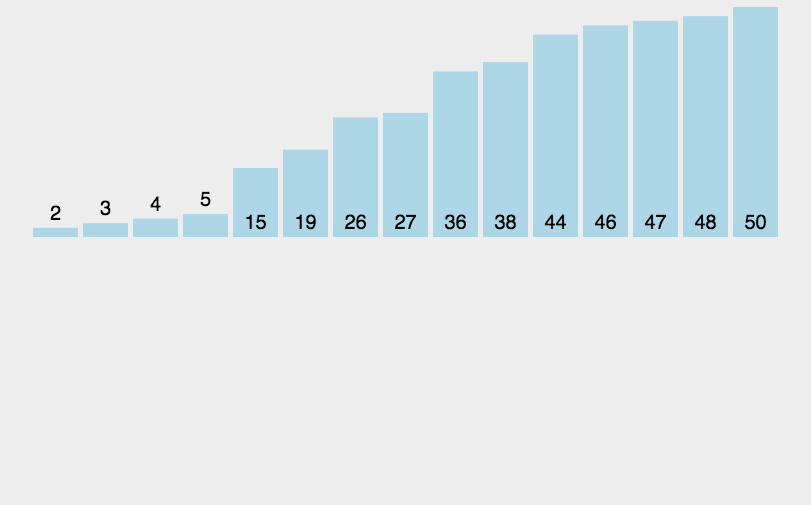
7.4 代码实现
/**
* 插入排序
* 分类 ------------- 内部比较排序
* 数据结构 ---------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- 最坏情况为输入序列是降序排列的,此时时间复杂度O(n^2)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- 最好情况为输入序列是升序排列的,此时时间复杂度O(n)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(n^2)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(1)
* 稳定性 ------------ 稳定
*/
public void insertion (int []arr){
int len = arr.length;
int preIndex, current;
for (int i = 1; i = 0 && arr[preIndex] > current) {
arr[preIndex + 1] = arr[preIndex];
preIndex--;
}
arr[preIndex + 1] = current;
}
}8、希尔排序(Shell Sort)
8.1 原理
8.2 算法描述
8.3 动图演示
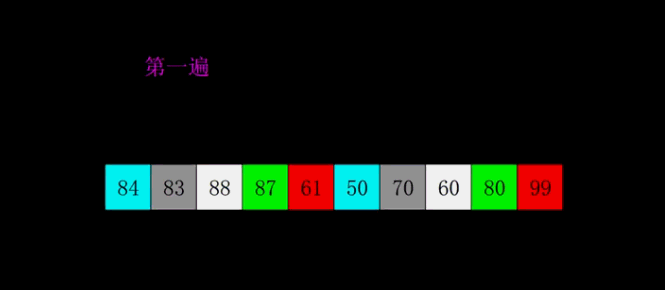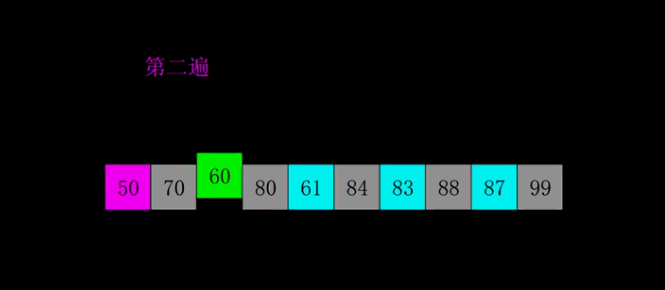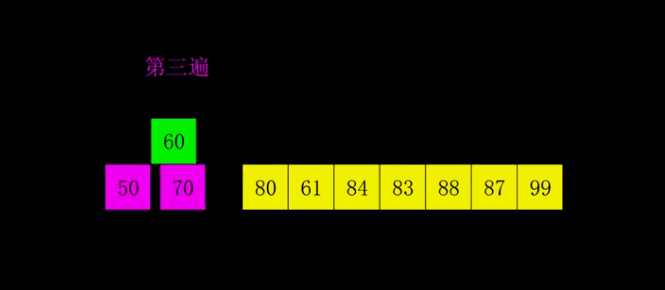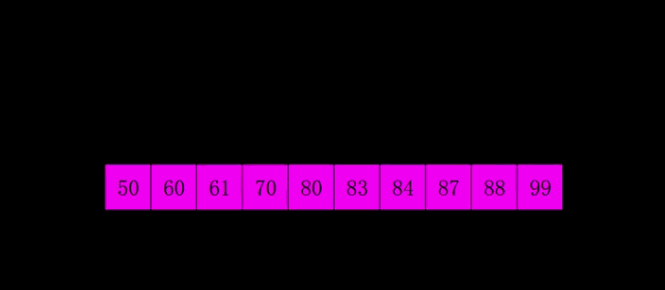
8.4 代码实现
/**
* 希尔排序
* 分类 -------------- 内部比较排序
* 数据结构 ---------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- 根据步长序列的不同而不同。已知最好的为O(n(logn)^2)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- O(n)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- 根据步长序列的不同而不同。
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(1)
* 稳定性 ------------ 不稳定
*/
public void shellSort(int[] arrays) {
if (arrays == null || arrays.length = 1) {
for (int i = 0; i arrays[j + incrementNum]) {
int temple = arrays[j];
arrays[j] = arrays[j + incrementNum];
arrays[j + incrementNum] = temple;
}
}
}
//设置新的增量
incrementNum = incrementNum / 2;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrays));
}9、归并排序(Merge Sort)
9.1 原理
9.2 算法描述
9.3 动图演示
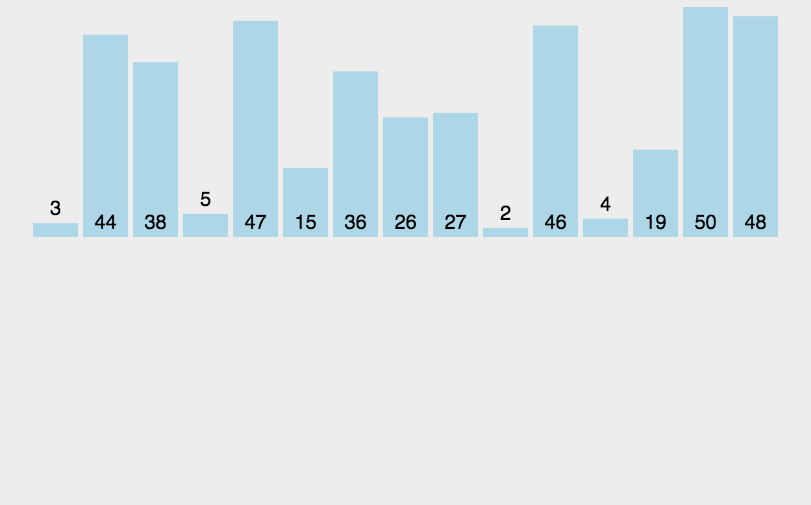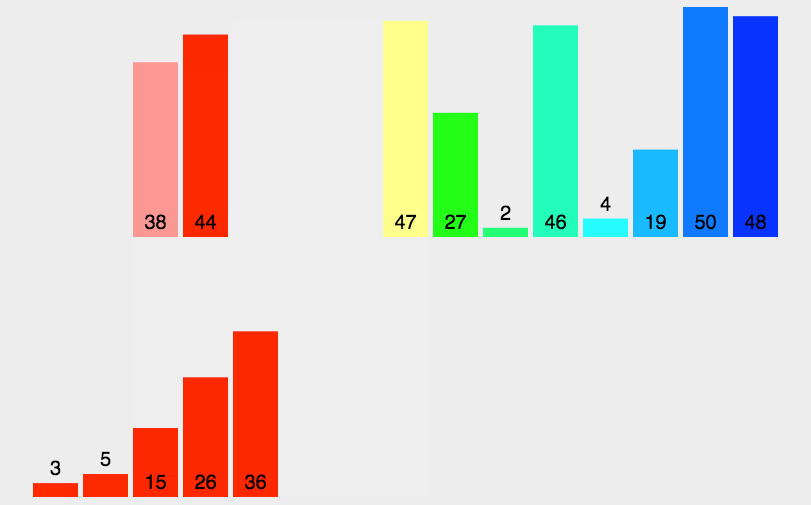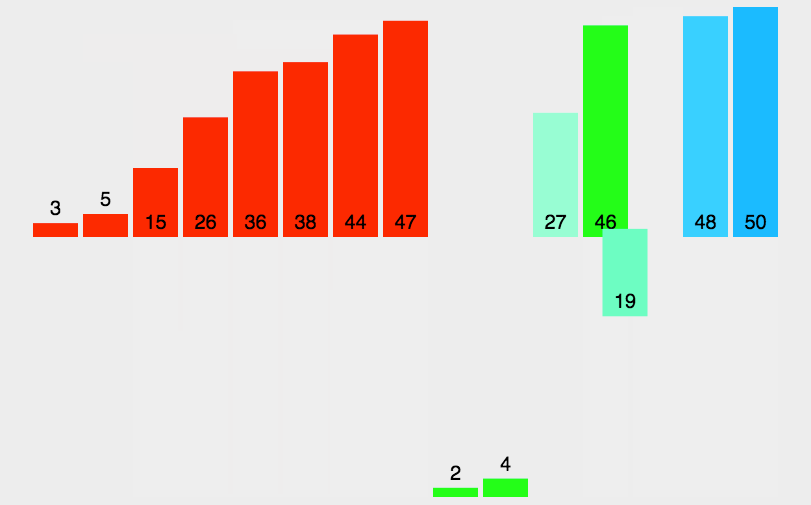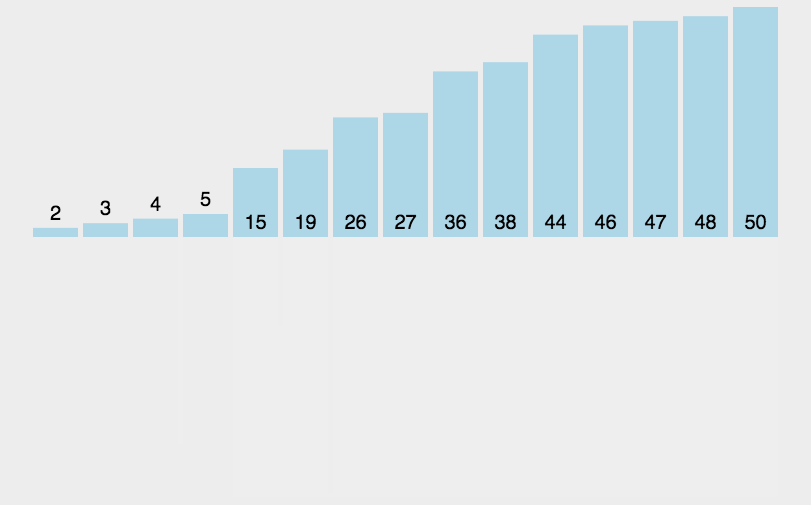
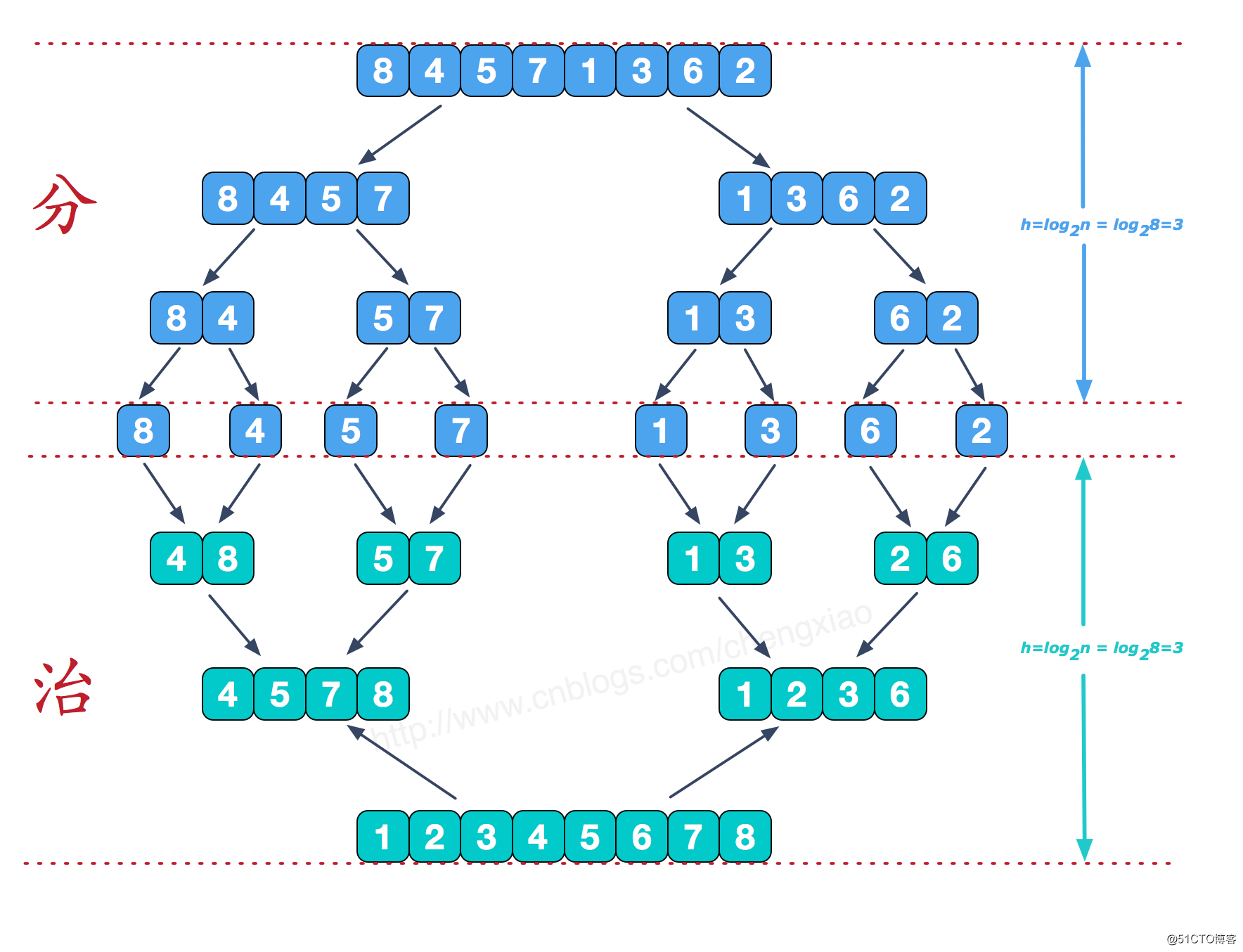
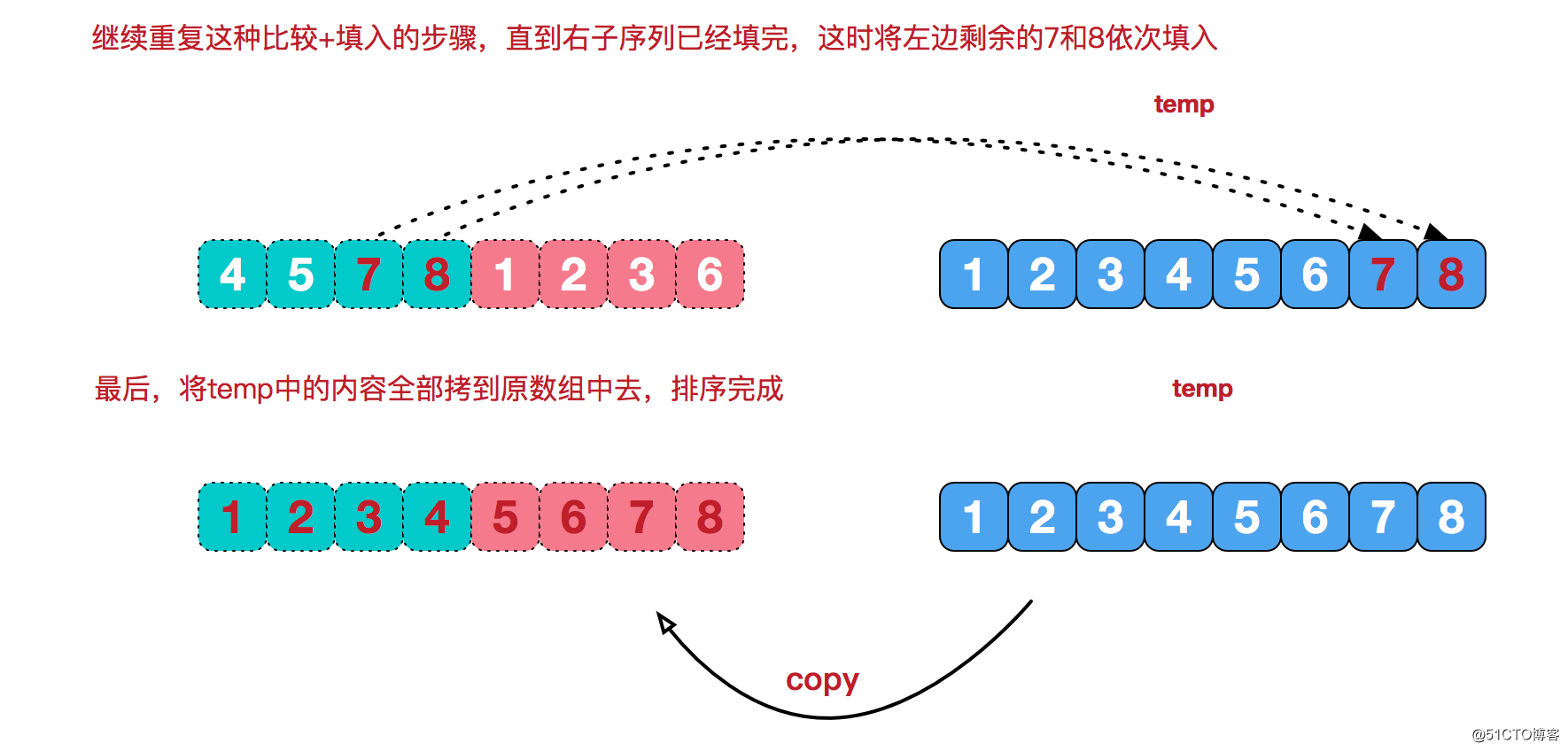
9.4 代码实现
/**
* 归并排序
* 分类 -------------- 内部比较排序
* 数据结构 ---------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(n)
* 稳定性 ------------ 稳定
*/
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];//在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间
sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, temp);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left 10、快速排序(Quick Sort)
10.1 原理
10.2 算法描述
10.3 动图演示
10.4 代码实现
/**
* 快速排序
* 分类 ------------ 内部比较排序
* 数据结构 --------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- 每次选取的基准都是最大(或最小)的元素,导致每次只划分出了一个分区,需要进行n-1次划分才能结束递归,时间复杂度为O(n^2)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- 每次选取的基准都是中位数,这样每次都均匀的划分出两个分区,只需要logn次划分就能结束递归,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ 主要是递归造成的栈空间的使用(用来保存left和right等局部变量),取决于递归树的深度,一般为O(logn),最差为O(n)
* 稳定性 ---------- 不稳定
*/
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 4, 5, 3, 9, 0};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
quickSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void quickSort(int[] a) {
if (a.length > 0) {
quickSort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
}
private static void quickSort(int[] a, int low, int high) {
//1,找到递归算法的出口
if (low > high) {
return;
}
//2, 存
int i = low;
int j = high;
//3,key
int key = a[low];
//4,完成一趟排序
while (i key) {
j--;
}
// 4.2 从左往右找到第一个大于key的数
while (i 11、堆排序(Heap Sort)
11.1 原理
11.2 算法描述
11.3 动图演示
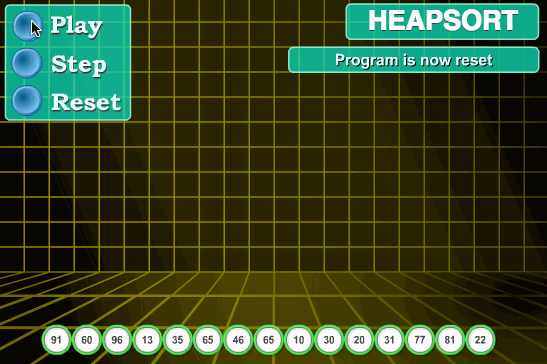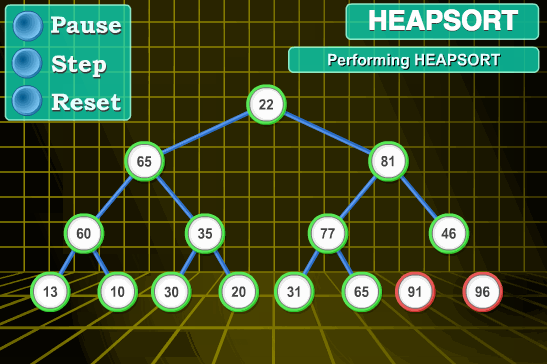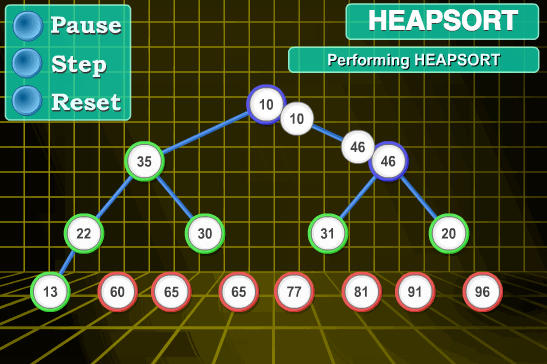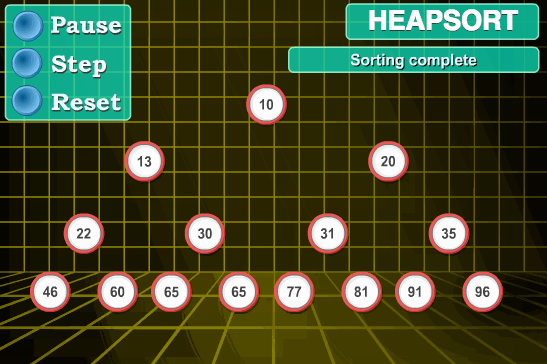
11.4 代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 堆排序
* 分类 -------------- 内部比较排序
* 数据结构 ---------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(1)
* 稳定性 ------------ 不稳定
*/
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = { 51, 46, 20, 18, 65, 97, 82, 30, 77, 50 };
heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
/**
* 构建大顶堆
*/
public static void adjustHeap(int[] a, int i, int len) {
int temp, j;
temp = a[i];
for (j = 2 * i; j = a[j])
break;
a[i] = a[j];
i = j;
}
a[i] = temp;
}
public static void heapSort(int[] a) {
int i;
for (i = a.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {// 构建一个大顶堆
adjustHeap(a, i, a.length - 1);
}
for (i = a.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {// 将堆顶记录和当前未经排序子序列的最后一个记录交换
int temp = a[0];
a[0] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
adjustHeap(a, 0, i - 1);// 将a中前i-1个记录重新调整为大顶堆
}
}
}12、计数排序(Counting Sort)
12.1 原理
12.2 算法描述
12.3 动图演示
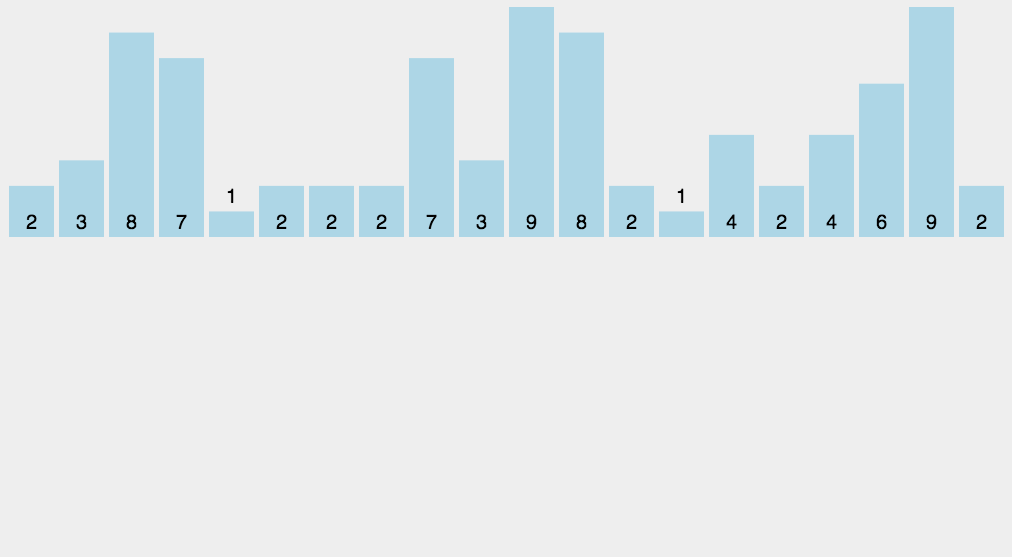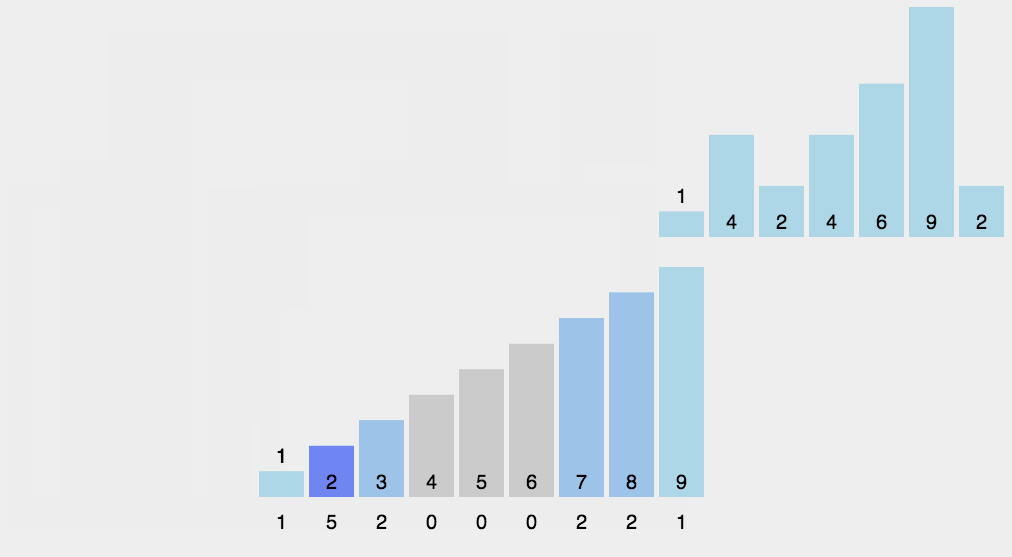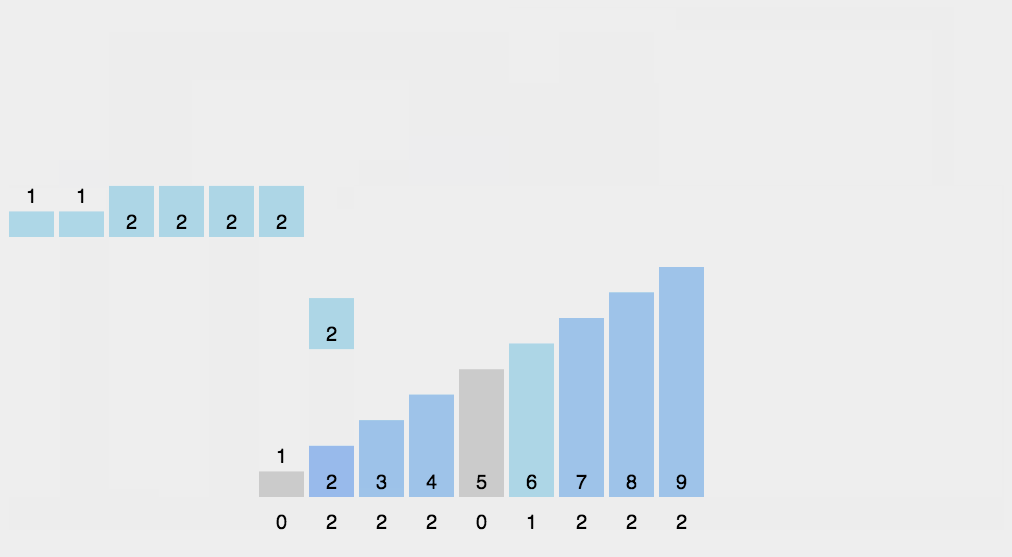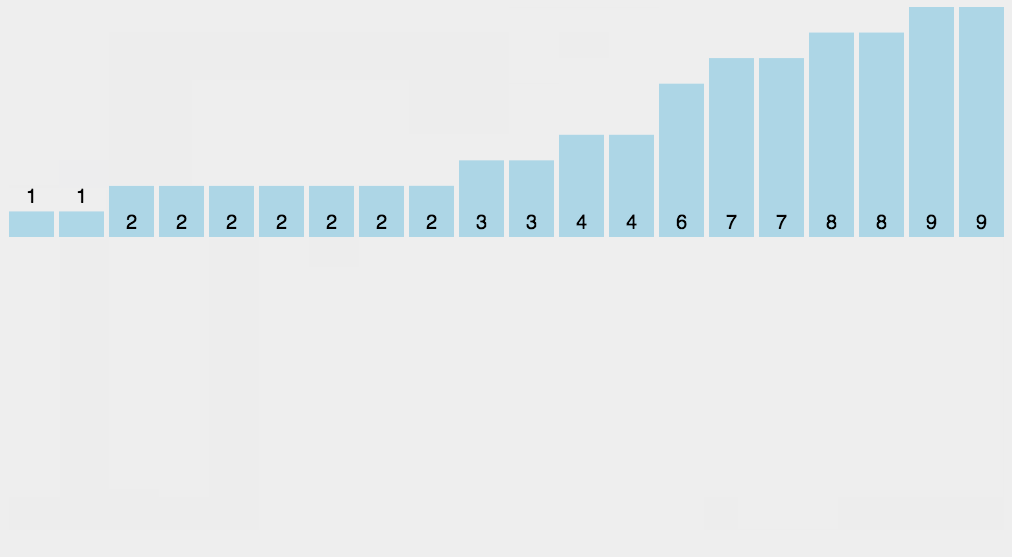
12.4 代码实现
/**
* 计数排序
* 分类 ------------ 内部非比较排序
* 数据结构 --------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- O(n + k)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- O(n + k)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(n + k)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(n + k)
* 稳定性 ----------- 稳定
*/
public class CountSort {
private static int[] countSort(int[] array,int k)
{
int[] C=new int[k+1];//构造C数组
int length=array.length,sum=0;//获取A数组大小用于构造B数组
int[] B=new int[length];//构造B数组
for(int i=0;i13、桶排序(Bucket Sort)
13.1 原理
13.2 算法描述
13.3 动图演示
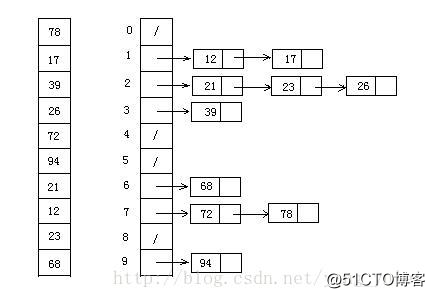
13.4 代码实现
/**
* 桶排序
* * 分类 ------------- 内部非比较排序
* 数据结构 --------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- O(nlogn)或O(n^2),只有一个桶,取决于桶内排序方式
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- O(n),每个元素占一个桶
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(n),保证各个桶内元素个数均匀即可
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(n + bn)
* 稳定性 ----------- 稳定
*/
public static void bucketSort(int[] arr){
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i > bucketArr = new ArrayList(bucketNum);
for(int i = 0; i ());
}
//将每个元素放入桶
for(int i = 0; i 14、基数排序(Radix Sort)
14.1 原理
14.2 算法描述
14.3 动图演示

14.4 代码实现
/**
* 基数排序
* 分类 ------------- 内部非比较排序
* 数据结构 ---------- 数组
* 最差时间复杂度 ---- O(n * dn)
* 最优时间复杂度 ---- O(n * dn)
* 平均时间复杂度 ---- O(n * dn)
* 所需辅助空间 ------ O(n * dn)
* 稳定性 ----------- 稳定
*/
private static void radixSort(int[] array,int d)
{
int n=1;//代表位数对应的数:1,10,100...
int k=0;//保存每一位排序后的结果用于下一位的排序输入
int length=array.length;
int[][] bucket=new int[10][length];//排序桶用于保存每次排序后的结果,这一位上排序结果相同的数字放在同一个桶里
int[] order=new int[length];//用于保存每个桶里有多少个数字
while(n