python tips:类的动态绑定
2020-12-07 06:35
标签:print == __name__ self 千万 style limited mamicode ted 使用实例引用类的属性时,会发生动态绑定。即python会在实例每次引用类属性时,将对应的类属性绑定到实例上。 从上述代码中可以看到,类方法的变化是实时影响实例对方法的调用的,这说明python是在实例调用方法的过程中动态地查找类方法。 上图两个循环中,一个调用a.test(),不断进行动态绑定,另一个则先把a.test赋值给f,只有一次动态绑定,通过对两个循环计时,测试动态绑定的代价。 折线图中横坐标为log10(循环次数),纵坐标为秒数。 输出数据中,第一行为动态绑定和一次绑定耗费时间的差值,第二行为差值占动态绑定总时间的比例。 可以看出,在次数很小的时候,两者基本没有差距,或者说差距忽略不计。 在10^7次循环,即千万次循环的时候,动态绑定与静态绑定的耗费时间才出现了明显差异,当循环次数达到十亿级的时候,耗费时间相差15秒之多,约占总时间的15%。 由上可知,动态绑定效率低于静态绑定,但由于绑定代价耗时很少,在次数很少的时候基本没有影响。 类方法的变动能够实时反应在动态绑定上,而提前绑定则无法感知到类方法的变动。 1. 一次动态绑定代价很小,当绑定次数少的时候基本不影响效率,当绑定次数达到千万级时影响才会很显著。 2. 动态绑定实时跟踪类方法的变动,更具灵活性。 python tips:类的动态绑定 标签:print == __name__ self 千万 style limited mamicode ted 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/luoheng23/p/10989435.html动态绑定的例子:
1 class A:
2 def test1(self):
3 print("hello")
4
5 def test2(self):
6 print("world")
7
8 def bound():
9 a = A()
10 a.test1()
11 A.test1 = A.test2
12 a.test1()
13
14 if __name__ == "__main__":
15 bound()
输出结果:
1 hello
2 world
动态绑定的代价:
1 class A:
2 def test(self):
3 pass
4
5 def one_loop(limited_time):
6 a = A()
7 for i in range(limited_time):
8 a.test()
9 f = a.test
10 for i in range(limited_time):
11 f()
输出结果:
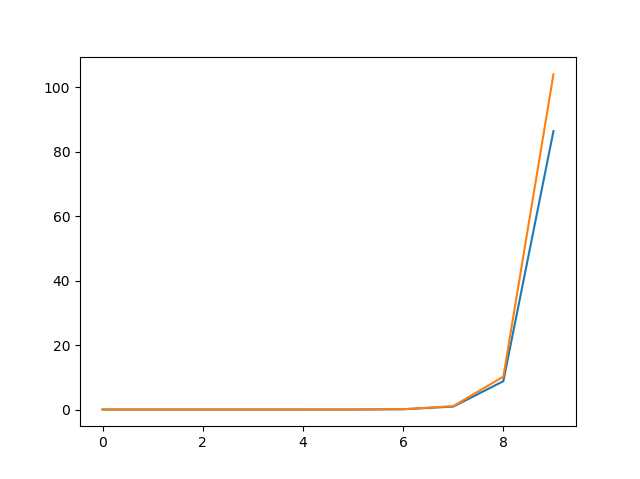
1 [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0009999275207519531, 0.008995771408081055, 0.19991111755371094, 1.2715933322906494, 15.831915855407715]
2 [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.12503726671039295, 0.09472344399590288, 0.1999776288967874, 0.131608969147562, 0.1553209370384522]
动态绑定的优点:
1 class A:
2 def test_hello(self):
3 print("hello")
4
5 def test_world(self):
6 print("world")
7
8 def main():
9 s = A()
10 # 提前绑定
11 f = s.test_hello
12 # 改变方法
13 A.test_hello = test_world
14 f()
15 # 动态绑定
16 s.test_hello()
17
18 if __name__ == "__main__":
19 main()
输出结果:
1 hello
2 world
总结:
上一篇:.net多线程 Parallel