Java IO(八) PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream
2021-01-16 04:16
标签:mes alt print api connect cte 定义 通过 xtend PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream 是管道输入流和管道输出流。它们的作用就是让多线程通过管道进行线程间的通讯。在使用管道通讯时,必须 PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream 配套使用。 使用管道通信时,大致的流程是:我们在线程A中向 PipedOutputStream 中写入数据,这些数据会自动的发送到与 PipedOutputStream 对应的 PipedInputStream 中,进而存储在 PipedInputStream 的缓冲中;此时,线程B通过读取 PipedInputStream 中的数据,这样就可以实现,线程A和线程B的通信。 多线程通过 PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream 进行线程间同通讯,下面例子分别定义三个类:PipedDemo(主线程main类),PipedSender(发送者对象)、PipedReceiver(接收者对象)。实例中只贴出主要代码。 管道输入流 PipedInputStream 与管道输出流 PipedOutputStream 建立连接 建立连接一般使用 connect() ,如:out.connect(in) 和 in.connect(out) 是等价的,开发时只能选择其中的一个而不能两个 connect 同时调用,否则会抛出 java.io.IOException: Already connected 异常。 创建流对象,如:PipedOutputStream out = new PipedOutputStream(in),in 为 PipedInputStream 对象,必须先实例化使用,否则会报 java.lang.NullPointerException 异常。PipedOutputStream out = new PipedOutputStream(in) 与 PipedInputStream in = new PipedInputStream(out) 是等价的,开发时传递的流对象作为参数必须实例化,然后进行传递。 Java IO(八) PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream 标签:mes alt print api connect cte 定义 通过 xtend 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lingq/p/12920208.htmlJava IO(八) PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream
一、介绍
二、构造方法
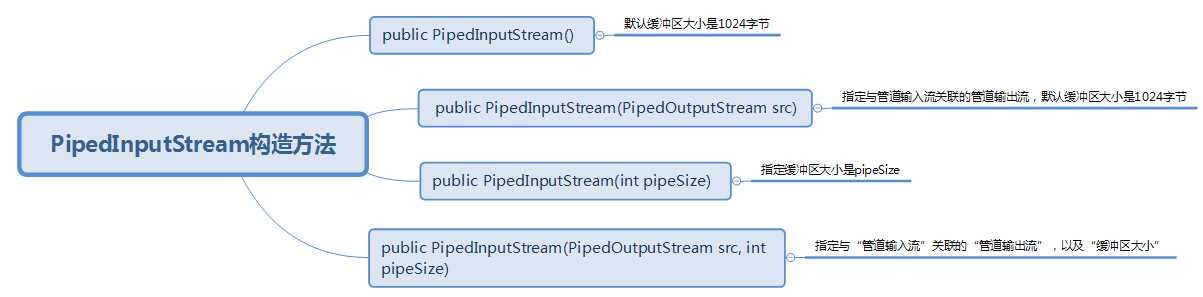
(一)、PipedInputStream
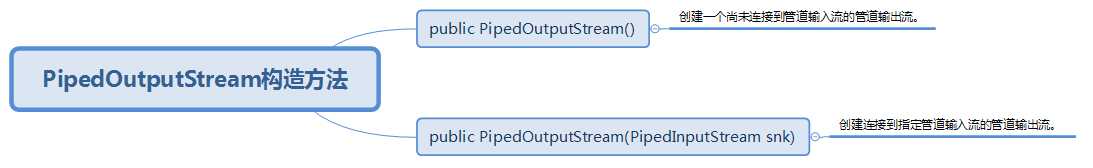
(二)、PipedOutputStream
三、常用API
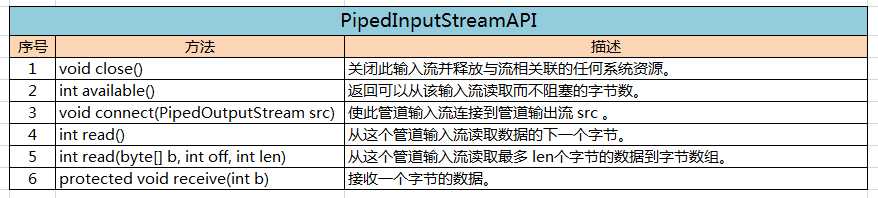
(一)、PipedInputStream
(二)、PipedOutputStream

四、实例
注意点:
connect() 方法连接或在创建输入流对象时,传递连接该管道的输出流对象。(一)、PipedSender(发送者对象)
public class PipedSender extends Thread{
// 定义私有PipedOutputStream 对象
private PipedOutputStream out = new PipedOutputStream();
public PipedOutputStream getOutputStream() {
return out;
}
// 线程执行的方法
@Override
public void run() {
//writeOne();
writeMove();
}
/**
* 写入一段短数据
*/
private void writeOne() {
byte[] buffer = "this is a message".getBytes();
try {
out.write(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 写入较长数据
*/
public void writeMove() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0;i ) {
sb.append("12345678790");
}
sb.append("abcdefghijklmnopqrstvuwxyz");
String str = sb.toString();
try {
out.write(str.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
(二)、PipedReceiver(接收者对象)
public class PipedReceiver extends Thread{
// 私有PipedInputStream 对象
private PipedInputStream in = new PipedInputStream();
public PipedInputStream getInputStream() {
return in;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//readOne();
readMove();
}
/**
* 读取一次
*/
public void readOne() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
int len = 0;
try {
len = in.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 读取多次
*/
private void readMove() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
try {
while(true) {
len = in.read(buffer);
// 一值读取,直到结束
if(len == -1)
break;
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
(三)、PipedDemo(main方法类)
public class PipedDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PipedSender sender = new PipedSender();
PipedReceiver receiver = new PipedReceiver();
PipedOutputStream out = sender.getOutputStream();
PipedInputStream in = receiver.getInputStream();
try {
// 下面两条语句是一样的,但只能允许存在一条语句
//in.connect(out);
out.connect(in);
// 分别开启两个线程
sender.start();
receiver.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
下一篇:java新学者(二)
文章标题:Java IO(八) PipedInputStream 和 PipedOutputStream
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/42549.html