机器学习算法及代码实现–神经网络
2021-01-18 20:12
阅读:737
机器学习算法及代码实现–神经网络
1、神经网络
神经网络是一种运算模型,由大量的节点(或称神经元)之间相互联接构成。每个节点代表一种特定的输出函数,称为激励函数(activation function)。每两个节点间的连接都代表一个对于通过该连接信号的加权值,称之为权重,这相当于人工神经网络的记忆。网络的输出则依网络的连接方式,权重值和激励函数的不同而不同。而网络自身通常都是对自然界某种算法或者函数的逼近,也可能是对一种逻辑策略的表达。 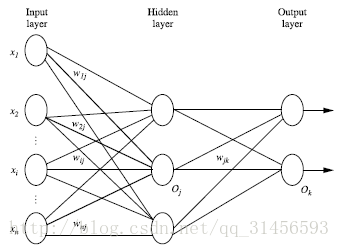
2、多层向前神经网络
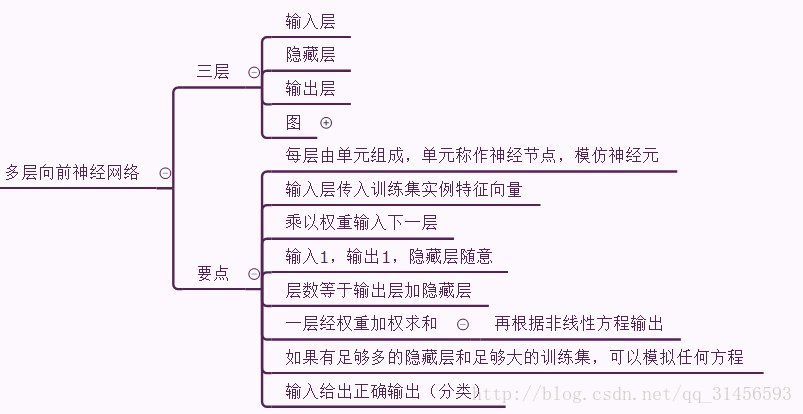
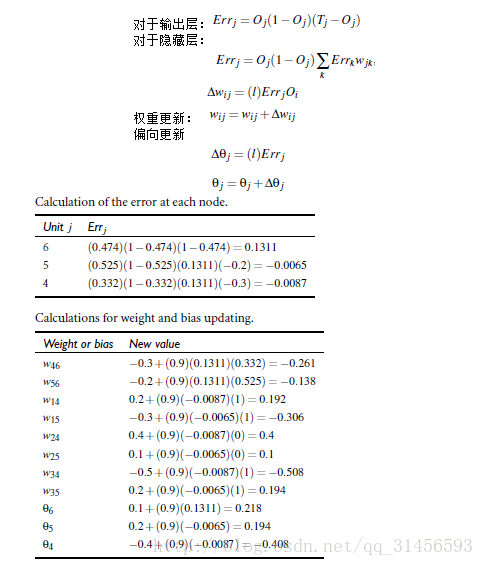
3、设计神经网络结构

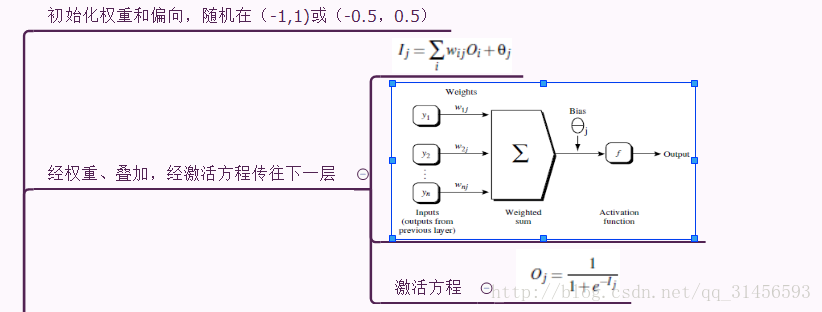
4、反向回馈算法

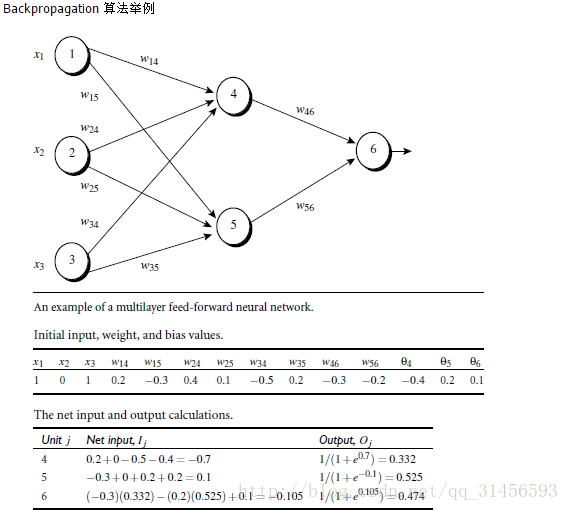
5、实例
代码
import numpy as np def tanh(x): return np.tanh(x) def tanh_deriv(x): return 1.0 - np.tanh(x)*np.tanh(x) def logistic(x): return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x)) def logistic_derivative(x): return logistic(x)*(1-logistic(x)) class NeuralNetwork: def __init__(self, layers, activation=‘tanh‘): """ :param layers: A list containing the number of units in each layer. Should be at least two values :param activation: The activation function to be used. Can be "logistic" or "tanh" """ if activation == ‘logistic‘: self.activation = logistic self.activation_deriv = logistic_derivative elif activation == ‘tanh‘: self.activation = tanh self.activation_deriv = tanh_deriv self.weights = [] for i in range(1, len(layers) - 1): self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1, layers[i] + 1))-1)*0.25) self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i] + 1, layers[i + 1]))-1)*0.25) def fit(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000): X = np.atleast_2d(X) temp = np.ones([X.shape[0], X.shape[1]+1]) temp[:, 0:-1] = X # adding the bias unit to the input layer X = temp y = np.array(y) for k in range(epochs): i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0]) a = [X[i]] for l in range(len(self.weights)): #going forward network, for each layer a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[l]))) #Computer the node value for each layer (O_i) using activation function error = y[i] - a[-1] #Computer the error at the top layer deltas = [error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])] #For output layer, Err calculation (delta is updated error) #Staring backprobagation for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1): # we need to begin at the second to last layer #Compute the updated error (i,e, deltas) for each node going from top layer to input layer deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T)*self.activation_deriv(a[l])) deltas.reverse() for i in range(len(self.weights)): layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i]) delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i]) self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta) def predict(self, x): x = np.array(x) temp = np.ones(x.shape[0]+1) temp[0:-1] = x a = temp for l in range(0, len(self.weights)): a = self.activation(np.dot(a, self.weights[l])) return
简单非线性关系数据集测试(XOR):
from NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork import numpy as np nn = NeuralNetwork([2,2,1], ‘tanh‘) X = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]) y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0]) nn.fit(X, y) for i in [[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1,1]]: print(i, nn.predict(i))
手写数字识别:
每个图片8x8
识别数字:0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_digits from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer from NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split digits = load_digits() X = digits.data y = digits.target X -= X.min() # normalize the values to bring them into the range 0-1 X /= X.max() nn = NeuralNetwork([64,100,10],‘logistic‘) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y) labels_train = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_train) labels_test = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_test) print "start fitting" nn.fit(X_train,labels_train,epochs=3000) predictions = [] for i in range(X_test.shape[0]): o = nn.predict(X_test[i] ) predictions.append(np.argmax(o)) print confusion_matrix(y_test,predictions) print classification_report(y_test,predictions)
下一篇:流批一体机器学习算法平台
评论
亲,登录后才可以留言!