CSS:定位(静态、相对、绝对、固定、粘性)
2021-02-01 23:13
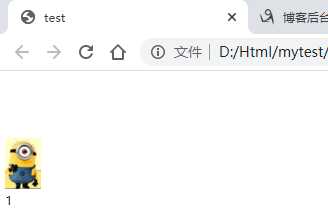
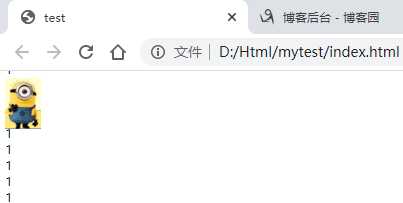
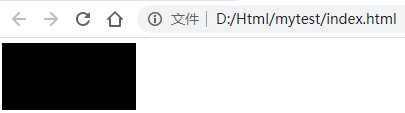
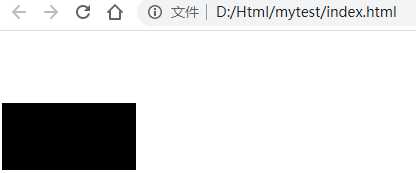
标签:title image test position mic pre width htm top 1、定位 (1)定位 将盒子定在某一个位置,所以定位也是在摆放盒子,按照定位的方式移动盒子 (2)定位的作用 某一个元素可以自由的在一个盒子内部移动,并且压住其他盒子(使用标准流或者浮动很难实现) 定位可以让元素固定屏幕中的某个位置,并且可以压住其他盒子 (3)定位的组成 定位=定位模式+边偏移 定位模式用于指定一个元素在文档中的定位方式,边偏移则决定了该元素的最终位置 (4)定位模式 定位模式决定元素的定位方式,它通过CSS的position属性来设置,它的值可以分为四个:static(静态定位),relative(相对定位),absolute(绝对定位),fixed(固定定位) (5)边偏移 有top、bottom、left、right四个属性 2、 (1)静态定位 静态定位是元素的默认定位方式,无定位的意思。静态定位按照标准流特征摆放位置,他没有边偏移,很少使用 (2)相对定位 元素在移动位置的时候,是相对于它原来的位置来说的 定义相对定位之前: 长方形是紧贴上边缘显示的 定义相对定位: 长方形的位置相对于原来的位置发生了变化,但是他依旧是标准流。 (3)绝对定位 元素在移动位置的时候是相对于祖先元素来说的,如果没有祖先元素或者祖先元素没有定位,则以浏览器为准 没有父元素: 有父元素,但是该父元素没有定位: 有父元素,并且该父元素有定位: 如果祖先元素有定位(不包括绝对定位),则以最近一级的定位为参考点来移动位置: 如果最近的一级父元素没有,则再向上一级去查找,如果都没有定位,就以浏览器为准。 绝对定位是脱离标准流的,不再占有原来的位置。这也就意味着,父元素不能加绝对定位,如果加了绝对定位父元素下的布局就会占用父元素的位置,页面的结构就会乱掉。因此,父元素的布局需要占有位置,要使用绝对定位,而子元素可以使用相对定位,就可以在父元素内部自由移动了。 (4)固定定位 元素固定于浏览器的可视区的位置,在浏览页面的时候元素的位置不变。 在翻阅浏览器的时候,图片是固定不动的,文字随着浏览器的滚动而滚动 固定定位的特点,以浏览器的可视化窗口为参考点移动元素,跟父元素没有任何关系,不随滚动条滚动,固定定位不再占有原来的位置 (5)粘性定位 在滚动浏览器的,滚动到距离上边沿10px的时候图片就不动了,而在这之前会随着浏览器的滚动而滚动。 粘性定位的特点:以浏览器的可视化窗口为参考点移动元素;占有原来的位置;必须加上top、left、right、bottom中的一个才有效;IE不支持 CSS:定位(静态、相对、绝对、固定、粘性) 标签:title image test position mic pre width htm top 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhai1997/p/13170772.htmlDOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 200px;
background-color: black;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="test">div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 200px;
background-color: black;
position: relative;
top:100px;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="test">div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 200px;
background-color: black;
position: absolute;
top:100px;
left: 200px;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="test">div>
body>
html>
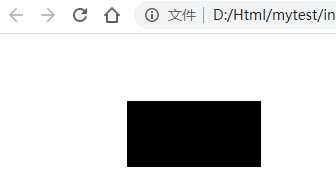
DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 200px;
background-color: black;
position: absolute;
top:100px;
left: 200px;
}
.big{
height: 400px;
width: 400px;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0 auto;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="big">
div class="test">div>
div>
body>
html>
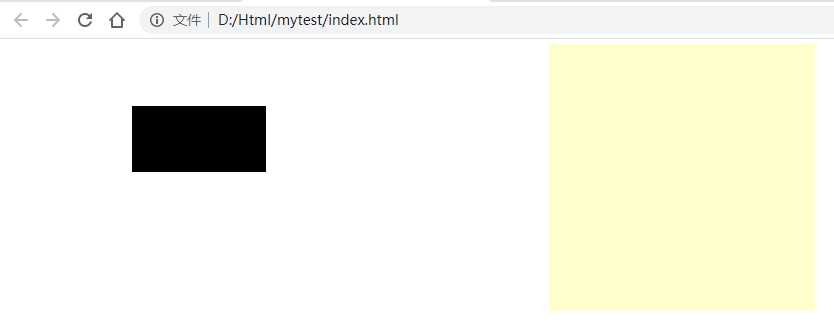
DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 200px;
background-color: black;
position: absolute;
top:100px;
left: 200px;
}
.big{
height: 400px;
width: 400px;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0 auto;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="big">
div class="test">div>
div>
body>
html>

DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test {
height: 100px;
width: 200px;
background-color: black;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 200px;
}
.big {
height: 400px;
width: 400px;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0 auto;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
}
.biggest {
height: 500px;
width: 600px;
position: absolute;
margin: 0 auto;
top: 100px;
background-color: #fffcf5;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="biggest">
div class="big">
div class="test">div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
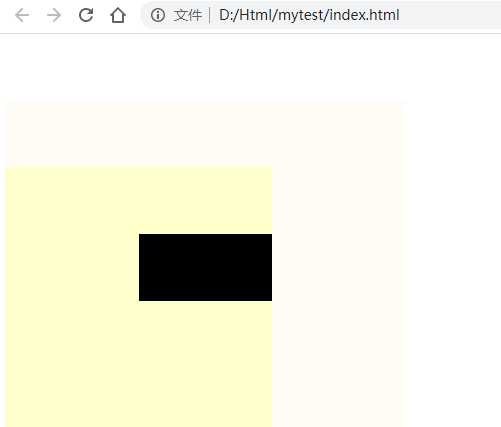
DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test {
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
left: 200px;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="test">
img src="img/1.png" />
div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
body>
html>
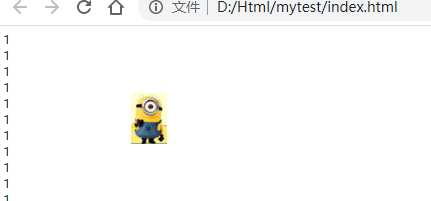
DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta charset="utf-8" />
title>testtitle>
style type="text/css">
.test {
position: sticky;
margin-top: 100px;
top: 10px;
}
style>
head>
body>
div class="test">
img src="img/1.png" />
div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
div>1div>
body>
html>