Asp .Net Core 2.0 登录授权以及多用户登录
2021-03-06 03:27
标签:场景 msi return sni err tco 使用方法 color password
用户登录是一个非常常见的应用场景 .net core 2.0 的登录方式发生了点变化,应该是属于是良性的变化,变得更方便,更容易扩展。 打开项目中的Startup.cs文件,找到ConfigureServices方法,我们通常在这个方法里面做依赖注入的相关配置。添加如下代码: 这段代码的大概意思就是,添加授权支持,并添加使用Cookie的方式,配置登录页面和没有权限时的跳转页面。 再找到Configure方法,添加 app.UseAuthentication(),使用授权: 这样基本的配置就完成了。 添加一个Controller,如AccountController,再添加一个Action,如 Login,所配置的路由,要与上面的配置对应,不然跳转登录时会跳错页面。 用户提交用户名和密码,登录代码大致如下: 这里要注意的是 AuthenticationType 所设置的Scheme一定要与前面的配置一样,这样对应的登录授权才会生效。 登录的目录,就是希望有些页面或者资源只有登录以后才可访问。使用AuthorizeAttribute来做限制。在需要做限制的Controller上加上[Authorize]特性来做限制。 这样这个Controller下的所有的Action都必需要登录后才可访问。如果希望其中某些Action可以不用登录也可访问,可以添加例外: 到这里一个最基础的登录就完成了。 在Web项目中,通常会遇到一个问题,后端管理员和前台用户。这两个用户都是可登录的,在 .net core 2.0,这个将很容易实现。 CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme,这是系统已经定义好的一个默认的登录方案,添加一个新的来实现一个不同的身份登录。代码如下: 添加使用这个新的方案,在Startup.cs文件下: 添加新的登录方案,并配置一个新的登录页面,登录的方法和刚才是一样,只是AuthenticationType使用了新的方案。 使用方法和之前的差不多,换成新的CustomerAuthorizeAttribute就行了: CustomerAuthorizeAttribute这个类,不是必需的,只是为了方便使用而写,其实完全可以只定义一个新的方案(Scheme)就行了。 登录了多个用户,那么谁才是HttpContext.User呢?如果你的Controller或者Action上有使用AuthorizeAttribute,那这个Attribute使用的登录方案是哪个,则这个HttpContext.User对应的就是那个方案的登录用户。如果没有使用,则AddAuthentication()方法默认指它的方案(Scheme)所登录的用户,就是这个HttpContext.User了。 如何获取对应方案的登录用户呢?使用HttpContext.AuthenticateAsync 这个就简单了,指定方案退出就可以了。 原文地址:http://www.zkea.net/codesnippet/detail/post-60 Asp .Net Core 2.0 登录授权以及多用户登录 标签:场景 msi return sni err tco 使用方法 color password 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lonelyxmas/p/12900740.html配置
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddCookie(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, o =>
{
o.LoginPath = new PathString("/Account/Login");
o.AccessDeniedPath = new PathString("/Error/Forbidden");
});
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
app.UseAuthentication();
}
登录
[HttpPost]
public async Task
使用登录身份
[Authorize]
public class ThemeController
{
}
[AllowAnonymous]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
多用户登录
添加一个登录方案(Scheme)
public class CustomerAuthorizeAttribute : AuthorizeAttribute
{
public const string CustomerAuthenticationScheme = "CustomerAuthenticationScheme";
public CustomerAuthorizeAttribute()
{
this.AuthenticationSchemes = CustomerAuthenticationScheme;
}
}
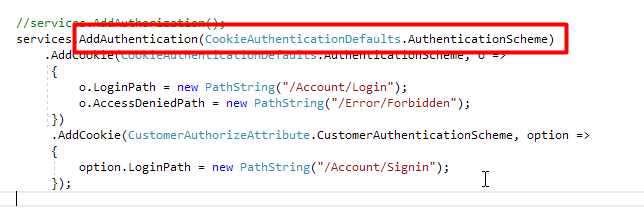
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddCookie(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, o =>
{
o.LoginPath = new PathString("/Account/Login");
o.AccessDeniedPath = new PathString("/Error/Forbidden");
})
.AddCookie(CustomerAuthorizeAttribute.CustomerAuthenticationScheme, option =>
{
option.LoginPath = new PathString("/Account/Signin");
option.AccessDeniedPath = new PathString("/Error/Forbidden");
});
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task
验证登录状态
[CustomerAuthorize]
public class CustomerController
{
}
谁才是HttpContext.User?
var auth = await HttpContext.AuthenticateAsync(CustomerAuthorizeAttribute.CustomerAuthenticationScheme);
if (auth.Succeeded)
{
auth.Principal.Identity...
}
退出登录
public async Task Logout(string returnurl)
{
await HttpContext.SignOutAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
return Redirect(returnurl ?? "~/");
}
文章标题:Asp .Net Core 2.0 登录授权以及多用户登录
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/60677.html