深度分析:java设计模式中的原型模式,看完就没有说不懂的
2021-03-30 00:28
标签:ali 实现 ddr zab final 引用 erp com 注意 形象的理解:孙大圣拔出猴毛,变出其他孙大圣 Sheep类实现Cloneable接口重写clone方法 Client类测试创建多个Sheep的实例,查看是否状态一致。 beans.xml配置文件 追踪 applicationContext.getBean(“id01”):进入AbstractApplicationContext类的getBean方法 追踪getBeanFactory():进入AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext类的getBeanFactory()方法 追踪getBean():进入AbstractBeanFactory类的getBean()方法 追踪doGetBean():进入doGetBean()方法 在原有的Sheep类基础上添加 public Sheep friend; 编写Client的测试用例,打印sheep.friend的hashCode值,观察它是否产生了新的对象。 DeepCloneableTarget类 DeepProtoType类 测试用例:Client DeepCloneableTarget类 DeepProtoType 类 Client 测试用例 感谢你看到这里,看完有什么的不懂的可以在评论区问我,觉得文章对你有帮助的话记得给我点个赞,每天都会分享java相关技术文章或行业资讯,欢迎大家关注和转发文章! 深度分析:java设计模式中的原型模式,看完就没有说不懂的 标签:ali 实现 ddr zab final 引用 erp com 注意 原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/14801695/2526163
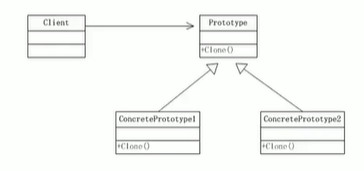
原型模式类图实例
原型模式java代码实例
public class Sheep implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
private String color;
public Sheep(String name, int age, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sheep{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
", color=‘" + color + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
//克隆该实例,使用默认的clone方法来完成
@Override
protected Object clone() {
Sheep sheep = null;
try {
sheep = (Sheep) super.clone();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return sheep;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("原型模式完成对象的创建");
Sheep sheep=new Sheep("tom",1,"白色");
Sheep sheep2=(Sheep)sheep.clone();
Sheep sheep3=(Sheep)sheep.clone();
Sheep sheep4=(Sheep)sheep.clone();
System.out.println("sheep2: "+sheep2);
System.out.println("sheep3: "+sheep3);
System.out.println("sheep4: "+sheep4);
}
}
原型模式在Spirng框架中源码分析
ProtoType类的测试用例public class ProtoType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Object bean = applicationContext.getBean("id01");
System.out.println("bean" + bean);
Object bean2 = applicationContext.getBean("id01");
System.out.println(bean==bean2);
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of BeanFactory interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(name);
}
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - " +
"call ‘refresh‘ before accessing beans via the ApplicationContext");
}
return this.beanFactory;
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
通过if (mbd.isSingleton()) 和else if (mbd.isPrototype())判断scope的作用域,
通过createBean()创建一个原型模型,返回一个bean。/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
* not for actual use
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected 浅拷贝
浅拷贝代码实例:
public class Sheep implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
private String color;
private String address="蒙古羊";
public Sheep friend;
public Sheep(String name, int age, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sheep{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
", color=‘" + color + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
//克隆该实例,使用默认的clone方法来完成
@Override
protected Object clone() {
Sheep sheep = null;
try {
sheep = (Sheep) super.clone();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return sheep;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("原型模式完成对象的创建");
Sheep sheep = new Sheep("tom", 1, "白色");
sheep.friend=new Sheep("jack",2,"黑色");
Sheep sheep2 = (Sheep) sheep.clone();
Sheep sheep3 = (Sheep) sheep.clone();
Sheep sheep4 = (Sheep) sheep.clone();
System.out.println("sheep2: " + sheep2+"sheep.friend2="+sheep2.friend.hashCode());
System.out.println("sheep3: " + sheep3+"sheep.friend3="+sheep3.friend.hashCode());
System.out.println("sheep4: " + sheep4+"sheep.friend4="+sheep4.friend.hashCode());
}
}
基本介绍
深拷贝代码实例:
方式一:重写clone方法
public class DeepCloneableTarget implements Serializable, Cloneable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String cloneName;
private String cloneClass;
public DeepCloneableTarget(String cloneName, String cloneClass) {
this.cloneName = cloneName;
this.cloneClass = cloneClass;
}
//因为该类的属性,都是String,因此我们这里使用默认的clone完成即可.
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class DeepProtoType implements Serializable, Cloneable {
public String name;
public DeepCloneableTarget deepCloneableTarget;
public DeepProtoType() {
super();
}
//深拷贝 - 方式1 使用clone 方法
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Object deep = null;
//完成对基本数据类型(属性)和String的克隆
deep = super.clone();
//对引用类型的属性,进行单独的处理。
DeepProtoType deepProtoType = (DeepProtoType) deep;
deepProtoType.deepCloneableTarget = (DeepCloneableTarget) deepCloneableTarget.clone();
return deep;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DeepProtoType p = new DeepProtoType();
p.name="宋江";
p.deepCloneableTarget=new DeepCloneableTarget("大牛","小牛的");
//方式1 完成深拷贝
DeepProtoType p2=(DeepProtoType)p.clone();
System.out.println("p.name="+p.name+"p.deepCloneableTarget="+p.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
System.out.println("p2.name="+p2.name+"p.deepCloneableTarget="+p2.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
}
}
方式二:通过对象序列化来实现深拷贝(推荐使用)
public class DeepCloneableTarget implements Serializable, Cloneable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String cloneName;
private String cloneClass;
public DeepCloneableTarget(String cloneName, String cloneClass) {
this.cloneName = cloneName;
this.cloneClass = cloneClass;
}
//因为该类的属性,都是String,因此我们这里使用默认的clone完成即可.
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class DeepProtoType implements Serializable, Cloneable {
public String name;
public DeepCloneableTarget deepCloneableTarget;
public DeepProtoType() {
super();
}
//深拷贝 - 方式2 通过对象序列化实现(推荐使用)
public Object deepClone() {
//创建流对象
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bis = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
//序列化
bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);//当前这个对象以对象流的方式输出
//反序列化
bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
DeepProtoType copyObj = (DeepProtoType) ois.readObject();
return copyObj;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} finally {
try {
bos.close();
oos.close();
bis.close();
ois.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DeepProtoType p = new DeepProtoType();
p.name = "宋江";
p.deepCloneableTarget = new DeepCloneableTarget("大牛", "小牛的");
//方式2 完成深拷贝
DeepProtoType p3=(DeepProtoType) p.deepClone();
System.out.println("p.name=" + p.name + "p.deepCloneableTarget=" + p.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
System.out.println("p3.name=" + p3.name + "p.deepCloneableTarget=" + p3.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode());
}
}
原型模式的注意事项和细节
最后
文章标题:深度分析:java设计模式中的原型模式,看完就没有说不懂的
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/69754.html