Vue.js起手式+Vue小作品实战
2021-04-01 10:25
本文是小羊根据Vue.js文档进行解读的第一篇文章,主要内容涵盖Vue.js的基础部分的知识的,文章顺序基本按照官方文档的顺序,每个知识点现附上代码,然后根据代码给予个人的一些理解,最后还放上在线编辑的代码以供练习和测试之用;
在最后,我参考SegmentFault上的一篇技博,对Vue进行初入的实战,目的是将新鲜学到的知识立即派上用场;
如果你还是前端的小白,相信这篇文章可能会对产生一些帮助和引起思想的碰撞,因为大家的学习历程是相似的,遇到的困惑也有一定的共通性,如果文章出现谬误之处,欢迎各位童鞋及时指正;

1. Vue.js是什么
Vue.js(读音 /vju?/, 类似于?view) 是一套构建用户界面的?渐进式框架。与其他重量级框架不同的是Vue 的核心库只关注视图层。
Vue.js 的目标是通过尽可能简单的 API 实现响应的数据绑定和组合的视图组件。
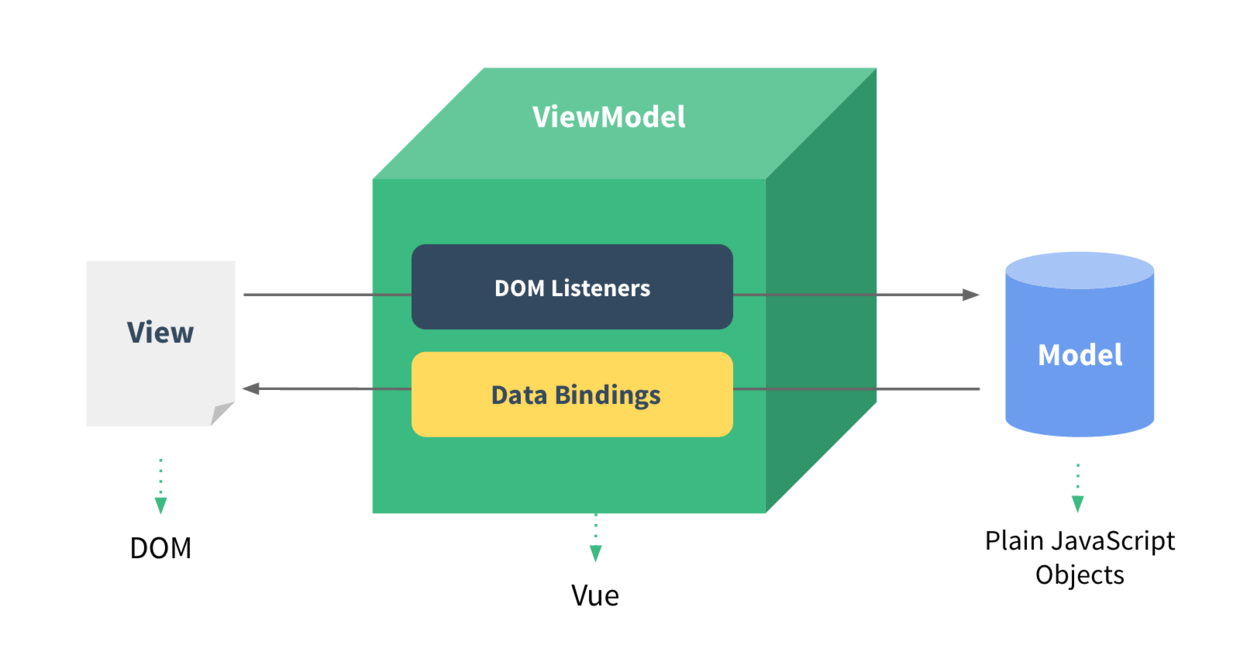
Vue.js是一种MVVM框架,其中html是view层,js是model层,通过vue.js(使用v-model这个指令)完成中间的底层逻辑,实现绑定的效果。改变其中的任何一层,另外一层都会改变;
2.Vue的基本语法
2.1 Vue构造函数开启Vue之旅
通过构造函数Vue创建一个Vue的根实例
---
var vm = new Vue({
//options
el:‘#el‘,
data:{},
methods:{}
})
---
//扩展Vue构造器
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
//扩展选项
})
var vm = new MyComponent({})解读:
使用Vue构造函数创建一个Vue实例,然后通过Vue实例的
el接口实现和HTML元素的挂载;构造函数Vue需要传入一个选项对象,可包含挂载元素、数据、方法和生命周期钩子等;
构造函数Vue可以通过
extend方法实现扩展,从而可以用预定义的选项创建可复用的组件构造函数,但是构建组件的常用方法是使用Vue.component()接口去实现;
2.2 Vue实例的属性和方法
Vue实例将代理data对象的所有属性,也就是说部署在data对象上的所有属性和方法都将直接成为Vue实例的属性和方法
{{message}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el:‘#app‘,
data:{
message:‘hello world!‘,
sayHello:function(){
console.log(1)
}
}
})
---
//如果想要获取到app这一实例中选项的对象,Vue提供$进行获取
app.$el === document.getElementById(‘app‘)//true
app.$data.message//hello world
【demo】
【TIP】
Vue实例所代理data对象上的属性只有在实例创建的同时进行初始化才具有响应式更新,若在实例创建之后添加是不会触发视图更新的;
2.3数据绑定操作
绑定文本和HTML
{{msg}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
msg: ‘hello world!‘,
hi:‘hi
‘
}
})解读:
HTML部分实现数据的动态绑定,这个数据是vue实例的属性值;
JS部分的语法可以从jQuery角度去理解,相当于创建一个Vue实例,这个实例指向#app,并在Vue提供的固定接口data上定义Vue实例的属性;
使用
{{message}}的mustache语法只能将数据解释为纯文本,为了输出HTML,可以使用v-html指令;
绑定数据在元素的属性
{{message}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
message: ‘hello world!‘,
red: ‘color:red‘
}
})解读:
定义在Vue实例的data接口上的数据的绑定灵活的,可以绑定在DOM节点内部,也可以绑在属性上;
绑定数据到节点属性上时,需要使用
v-bind指令,这个元素节点的?title属性和 Vue 实例的?message属性绑定到一起,从而建立数据与该属性值的绑定,也可以使用v-bind:href="http://www.soscw.com/url"的缩写方式:href="http://www.soscw.com/url";v-once指令能够让你执行一次性的插值,当数据改变时,插值处的内容不会更新;
【demo】
使用JS表达式处理数据
{{num + 10 }}
{{message + ‘jirengu‘}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
num:10,
message: ‘hello world!‘,
seen:true
}
})
【demo】
使用过滤器来格式化数据
{{message | capitalize}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
message: ‘hello world!‘,
seen:true,
},
filters:{
capitalize:function(value){
if(!value) return ‘‘
value = value.toString()
return value.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + value.slice(1)
}
}
})【demo】
条件指令控制DOM元素的显示操作
{{message}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
message: ‘hello world!‘,
seen:true
}
})解读:
v-if指令可以绑定一个属性值为布尔型的属性,当值为真时,元素将显示,反之则消失;
循环指令实现数据的遍历
-
{{ item.text }}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
items:[
{text:‘Vue‘},
{text:‘React‘},
{text:‘Angular‘}
]
}
})解读:
v-for可以绑定数组型数据进行绑定,并使用item in items形式,从而数据的遍历操作;
【demo】
事件绑定指令可以实现事件监听
{{message}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
message: ‘hello world!‘
},
methods:{
reverseMessage:function(){
this.message = this.message.split(‘‘).reverse().join(‘‘)
}
}
})解读:
v-on指令用于监听事件操作,click="reverseMessage"定义点击事件后执行的回调函数;v-on指令也可以采用缩写方式:@click="method"在Vue实例中,提供methods接口用于统一定义函数;
【demo】
小结
本章涉及Vue的基础的数据绑定操作,内容包括:
{{message}}实现文本数据的绑定,并且文本数据可以使用JS表达式和过滤器进行进一步处理;
-v-html="hi"实现HTML数据的绑定;v-bind:href="http://www.soscw.com/url"实现属性数据的绑定;v-if="seen"和v-for="item in items"指令实现流程控制;v-on:click="method"指令实现事件监听
2.4计算属性
使用计算属性完成一些数据计算操作
Original message : {{message}}
Reversed message : {{ReversedMessage}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
message: ‘hello world!‘,
},
computed:{
ReversedMessage:function(){
return this.message.split(‘‘).reverse().join(‘‘)
}
}
})解读:
Vue实例提供
computed对象,我们可以在对象内部定义需要进行计算的属性ReverseMessage,而提供的函数将作为属性的getter,即获取器;上述的代码使得
app.ReverseMessage依赖于app.message;与先前直接在
{{message.split(‘‘).reverse().join(‘‘) }}使用表达式相比,它让模板过重并且难以维护代码;
计算属性 VS Methods
Original message : {{message}}
Reversed message : {{ReversedMessage}}
Reversed message:{{reversedMessage()}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
message: ‘hello world!‘,
},
computed:{
ReversedMessage:function(){
return this.message.split(‘‘).reverse().join(‘‘)
}
},
methods:{
reversedMessage:function(){
return this.message.split(‘‘).reverse().join(‘‘)
}
}
})解读:
通过Vue实例的methods接口,我们在模板中调用
reversedMessage函数同样实现需求;methods与computed方法的区别在于:computed的数据依赖于
app.message,只要message未变,则访问ReverseMessage计算属性将立即返回之前的计算结果,而methods则每次重新渲染时总是执行函数;如果有缓存需要,请使用computed方法,否则使用methods替代;
计算属性的setter
Vue实例的computed对象默认只有getter,如果你要设置数据,可以提供一个setter,即设置器;
Hi,I‘m{{fullName}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
message: ‘hello world!‘,
name:‘Teren‘
},
computed:{
fullName:{
get:function(){
return this.name
},
set:function(value){
this.name = value
}
}
}
})2.5Class与Style的绑定
绑定Class
Hello world!
こんにちは
你好
Olá
---
//css
.static{
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: #ccc;
}
.active{
color:red;
}
.error{
font-weight: 800;
}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
isActive:true,
hasError:true,
classObj:{
static:true,
active:true,
error:true,
},
staticClass:‘static‘,
activeClass:‘active‘,
errorClass:‘error‘,
},
computed:{
style:function(){
return {
active: this.isActive,
static:true,
error:this.hasError
}
}
},
methods:{
changeColor:function(){
this.isActive = !this.isActive
}
}
})解读:
通过
v-bind:class="{}"或v-bind:class=[]方式为模板绑定class通过
v-bind:class="{active:isActive,error:hasError}"绑定class,首先要在css中设置.active和,error,然后在Vue实例的data对象中设置isActive和hasError的布尔值;也可以直接传一个对象给class,即v-bind:class="classObj,再在data对象上直接赋值:
data:{
classObj:{
static:true,
active:true,
error:true,
}你也可以通过传递数组的方式为class赋值
v-bind:class="[staticClass,activeClass,errorClass]",此时你要在data对象上为数组的元素的属性赋值:
data:{
staticClass:‘static‘,
activeClass:‘active‘,
errorClass:‘error‘,
}【TIP】无论是哪种方式,前提都是css中的class要先设定
【demo】
绑定style
Hello World!
你好
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
styleObj:{
fontWeight:800,
color:‘red‘
},
bgObj:{
width:‘100px‘,
height:‘80px‘,
background:‘#ccc‘
}
},
})解读:
绑定style到模板的方法有两种,一是
v-bind:style="styleObj",然后在data对象上定义styleObj;而是可以通过数组方式为style传入多个样式对象
【demo】
2.6条件渲染和列表渲染
前面简单介绍了一下v-if、v-for和v-on指令,下面的部分将详细介绍以上3个指令;
条件渲染
Hello World!
Hello Universal
Steve Jobs
motto:stay hungry ! stay foolish
Show Me
---
var app = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data:{
ok:true,
motto:true,
},
})解读:
通过
v-if和v-else指令实现条件渲染,其中v-if="value"的valuey
要在data对象中赋布尔值,v-if支持语法v-show="value"是另一种条件渲染的方法;
【TIP】 v-if和v-show的区别
v-if是真实的条件渲染,当进行条件切换时,它会销毁和重建条件块的内容,并且它支持
语法;v-show的条件切换时基于css的display属性,所以不会销毁和重建条件块的内容;
当你频繁需要切换条件时,推荐使用v-show;否则使用v-if;
【demo】
列表渲染
-
{{car.name}}
-
{{index}}---{{food}}---{{delicious}}
-
{{index}}.{{key}}.{{value}}
{{n}}
{{n}}
解读:
v-for指令能够让我们循环渲染列表型数据,数据放在data对象中,类型可以如下:
data:{
//数字数组
numbers:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],
counts:[1,2,3,4,5]
//字符串数组
foods:[
‘tomato‘,
‘potato‘,
‘ice cream‘
],
//对象数组
cars:[
{name:‘Benz‘},
{name:‘BMW‘}
],
//对象
object :{
name:‘Benz‘,
age:‘18‘
},
}根据不同类型的数据,
v-for指令在模板中具体采用的语法如下:
//数据为数字数组
{{n}}
---
//数据为字符数组
{{food}}
---
//数据为对象
{{value}}
//或者
{{index}}.{{key}}.{{value}}
---
//数据为对象数组
{{car.name}}
在?v-for块中,我们拥有对父作用域属性的完全访问权限;
【demo】
2.7 事件监听
简单的事件监听——直接在指令上处理数据
{{counter}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data:{
counter: 0,
}
})复杂的事件监听——在methods对象定义回调函数
{{vue}
---
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data:{
vue:"hello Vue.js"
},
methods:{
greet:function(event){
console.log(this.vue)
}
}
})事件修饰符——调用事件对象函数的快捷方式
1//等价于event.preventDefault()
2//等价于event.stopPropagation()
3//等价于事件回调函数采用捕获阶段监听事件
4//等价于event.target按键修饰符——按键事件的快捷方式
常见按键别名包括:
- enter
- tab
- delete
- esc
- space
- up
- down
- left
- right【demo】
2.8 表单控件绑定
文本控件
{{message}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el:‘#app‘,
data:{
message:‘Hello World!‘
},
})解读:
通过
v-model指令可以实现数据的双向绑定,即View层的数据变化可以直接改变Model层的数据,而Model层的数据改变也可以直接反映在View层;上述代码
v-model="message"使得input的value属性和message属性绑定,在输入框输入值,即改变value同时也改变message;
单选控件
{{picked}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el:‘#app‘,
data:{
message:‘Hello World!‘,
picked:‘man‘
},
})解读:
v-model指令绑定data对象的picked属性,该属性默认指向type=‘radio‘的input的value;
复选框
Checked Name:{{checked}}
---
var app = new Vue({
el:‘#app‘,
data:{
message:‘Hello World!‘,
picked:‘man‘,
selected:"A",
checked:[],
},
})【demo】
2.9 组件
组件可以扩展 HTML 元素,封装可重用的代码。在较高层面上,组件是自定义元素;
通过Vue.component()接口将大型应用拆分为各个组件,从而使代码更好具有维护性、复用性以及可读性
注册组件
解读:
注册行为必须在创建实例之前;
component的template接口定义组件的html元素;
局部注册组件
Hello World
‘
}
var app = new Vue({
el:‘#app‘,
components:{
‘my-component‘:Child
}
})解读:
可以定义一个子组件,在实例的
components接口中将子组件挂载到父组件上,子组件只在父组件的作用域下有效;
特殊DOM模板将会限制组件的渲染
像这些包含固定样式的元素?,?
,?
,?