python智能图片识别系统(图片切割、图片识别、区别标识)
2021-04-02 06:28
标签:border 服务 write redirect similar append _for 图像 log @ 你好! python flask图片识别系统使用到的技术有:图片背景切割、图片格式转换(pdf转png)、图片模板匹配、图片区别标识。 第一组: 图片1: 第二组: 这会搞个复杂些的,也是实用的图片 图片1:(图片仅供交流,侵权删) 图片背景切割 pdf转png代码: 图片比较不同: flask路由部分: 写这个功能的代码是费了很大劲的,路过的朋友点个赞哈。 python智能图片识别系统(图片切割、图片识别、区别标识) 标签:border 服务 write redirect similar append _for 图像 log 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hongming-blogs/p/13499012.html
技术介绍
运行效果

图片2:
开始上传:
上传成功、图片预览:
(emmm..抱歉图片大小未处理,有点大哈)
识别效果: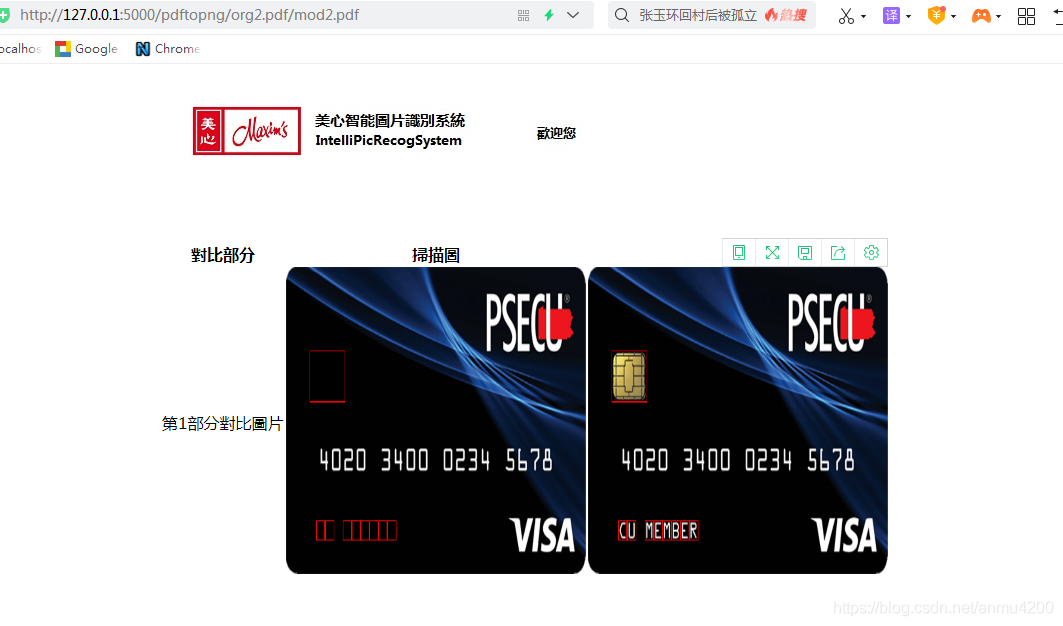
成功了。。。
图片2:
你会发现,其实图片2是图片1的子图,这下我们看看程序处理的效果: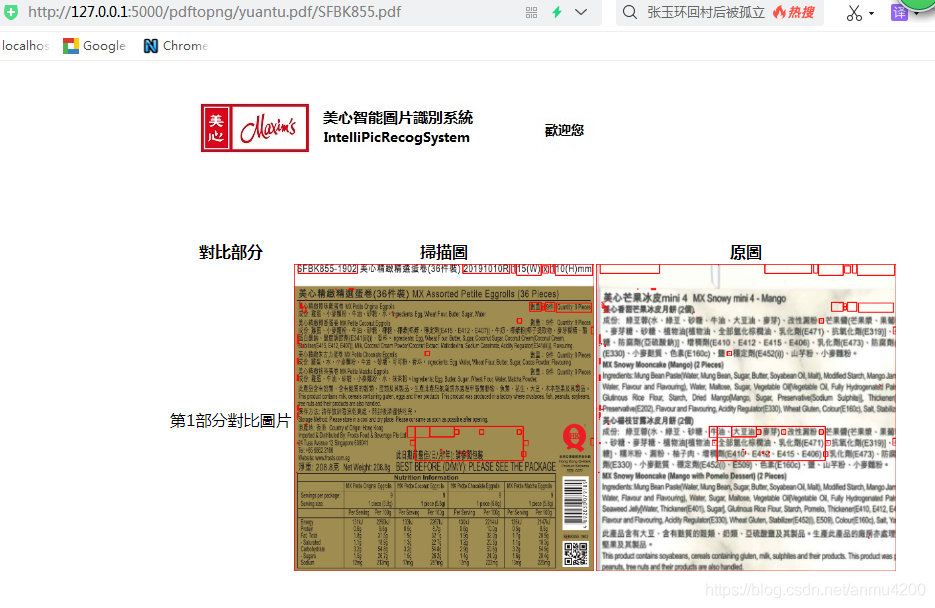
还可以哈,截取了图片1中的匹配部分,然后标识出来了区别关键代码
from PIL import Image
import cv2
import os
from common.util import Util
# 图片去除周围白色
def img_cut_white(img_path, cut_img_path, tagrt_rgb_x, tagrt_rgb_y):
# img_path = "./images/notebook.png"
img = Image.open(img_path)
rgb_im = img.convert(‘RGB‘)
width, height = img.size
# 打印图片的宽高
print(width, height)
# 把高度分为8份,后续用这8个点高度作为高度循环
list_target_height = [height / 8, height / 4, 3 * height / 8, height / 2, 5 * height / 8, 3 * height / 4]
x0,x1 = get_pointx(bypara="1",width=width,height=height,list_target_height=list_target_height,rgb_im=rgb_im,tagrt_rgb=tagrt_rgb_x)
y0, y1 = get_pointx(bypara="2", width=width, height=height, list_target_height=list_target_height, rgb_im=rgb_im,
tagrt_rgb=tagrt_rgb_y)
print(x0, x1)
print(y0, y1)
# 按照两个对角像素点切割图片
Util().cut_img_by_point(img_path=img_path,x0=x0,x1=x1,y0=y0,y1=y1,cut_img_path=cut_img_path)
# 获取x0,x1,y0,y1
def get_pointx(bypara=None,width=None,height=None,list_target_height=None,rgb_im=None,tagrt_rgb=None):
‘‘‘
:param bypara: 1代表进行获取x0,x1的逻辑,2代表进行获取y0,y1的逻辑
:param width: 图片宽度
:param height: 图片高度
:param list_target_height:
:param rgb_im: 转换为“RGB”通道的图片
:param tagrt_rgb: rgb突变范围值
:return:
‘‘‘
x0 = 0
x1 = 0
y0 = 0
y1 = 0
# 多个目标高度,每个像素点的rgb之和
multi_point_rgb_sum = 0
# 多个目标高度像素点的所有像素点rgb总和的平均值
list_rgb_sum_avg = []
if bypara == ‘1‘:
for i in range(width):
for j in range(len(list_target_height)):
# print("i:",i)
# print("list_target_height[j]:",list_target_height[j])
r, g, b = rgb_im.getpixel((i, list_target_height[j]))
# 一个点的rgb和
point_sum = r + g + b
multi_point_rgb_sum += point_sum
# print(point_sum, multi_point_rgb_sum)
list_rgb_sum_avg.append(multi_point_rgb_sum / 6)
multi_point_rgb_sum = 0
# 与白色背景图像的差值list
list_white_sub = get_listwhitesub(list_rgb_sum_avg)
list_white_sub_dup = list_white_sub.copy()
list_white_sub.reverse()
# 获得x0
for i in range(len(list_white_sub_dup)):
if list_white_sub_dup[i] > tagrt_rgb:
x0 = i
break
# 获得x1
for i in range(len(list_white_sub)):
# print(list_white_sub[i])
if list_white_sub[i] > tagrt_rgb:
x1 = (width - i)
break
return x0, x1
elif bypara == ‘2‘:
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
r, g, b = rgb_im.getpixel((j, i))
# r, g, b = rgb_im.getpixel(j, i)
# 一个点的rgb和
point_sum = r + g + b
multi_point_rgb_sum += point_sum
# print(point_sum, multi_point_rgb_sum)
list_rgb_sum_avg.append(multi_point_rgb_sum / width)
multi_point_rgb_sum = 0
# 与白色背景图像的差值list
list_white_sub = get_listwhitesub(list_rgb_sum_avg)
list_white_sub_dup = list_white_sub.copy()
list_white_sub.reverse()
# 获得y0
for i in range(len(list_white_sub_dup)):
if list_white_sub_dup[i] > tagrt_rgb:
y0 = i
break
# 获得y1
for i in range(len(list_white_sub)):
# print(list_white_sub[i])
if list_white_sub[i] > tagrt_rgb:
y1 = (height - i)
break
return y0, y1
# 获得list中相邻元素的差值list
def get_listsub(list2):
list3 = []
for i in range(len(list2)):
if i import fitz
import os
import datetime
from common.util import Util
from pdf2image import convert_from_path,convert_from_bytes
def pyMuPDF_fitz(pdfPath, imagePath):
startTime_pdf2img = datetime.datetime.now() # 开始时间
# print("imagePath=" + imagePath)
# pdfDoc = fitz.open(pdfPath)
# print(pdfPath)
images = convert_from_path(pdfPath)
for index, img in enumerate(images):
# for pg in range(pdfDoc.pageCount):
# page = pdfDoc[pg]
rotate = int(0)
# 每个尺寸的缩放系数为1.3,这将为我们生成分辨率提高2.6的图像。
# 此处若是不做设置,默认图片大小为:792X612, dpi=96
zoom_x = 1.33333333 # (1.33333333-->1056x816) (2-->1584x1224)
zoom_y = 1.33333333
# zoom_x = 1 # (1.33333333-->1056x816) (2-->1584x1224)
# zoom_y = 1
# mat = fitz.Matrix(zoom_x, zoom_y).preRotate(rotate)
# pix = img.getPixmap(matrix=mat, alpha=False)
# img.save(‘%s/page_%s.png‘ % (outputDir, index))
if not os.path.exists(imagePath): # 判断存放图片的文件夹是否存在
os.makedirs(imagePath) # 若图片文件夹不存在就创建
img.save(imagePath + ‘/‘ + ‘images_%s.png‘ % index)
# pix.writePNG(imagePath + ‘/‘ + ‘images_%s.png‘ % index) # 将图片写入指定的文件夹内
endTime_pdf2img = datetime.datetime.now() # 结束时间
# print(‘pdf2img时间=‘, (endTime_pdf2img - startTime_pdf2img).seconds)
def single_pyMuPDF_fitz(pdfPath, imagePath):
startTime_pdf2img = datetime.datetime.now() # 开始时间
# print("imagePath=" + imagePath)
# pdfDoc = fitz.open(pdfPath)
images = convert_from_path(pdfPath)
for index, img in enumerate(images):
# page = pdfDoc[pg]
rotate = int(0)
# 每个尺寸的缩放系数为1.3,这将为我们生成分辨率提高2.6的图像。
# 此处若是不做设置,默认图片大小为:792X612, dpi=96
zoom_x = 1.33333333 # (1.33333333-->1056x816) (2-->1584x1224)
zoom_y = 1.33333333
# zoom_x = 1 # (1.33333333-->1056x816) (2-->1584x1224)
# zoom_y = 1
# mat = fitz.Matrix(zoom_x, zoom_y).preRotate(rotate)
# pix = img.getPixmap(matrix=mat, alpha=False)
# pix.writePNG(imagePath) # 将图片写入指定的文件夹内
img.save(imagePath)
endTime_pdf2img = datetime.datetime.now() # 结束时间
# print(‘pdf2img时间=‘, (endTime_pdf2img - startTime_pdf2img).seconds)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# pdfPath = ‘../images/EWSC007.pdf‘
pdfPath = ‘SCAN855.PDF‘
##随机文件夹名字
imagePath = ‘SCAN855.png‘
# imagePath = ‘../images/image‘+str(Util().random_num())+‘.png‘
# imagePath = ‘../images/SCAN003.PDF‘
single_pyMuPDF_fitz(pdfPath, imagePath)
# # 遍历文件夹下所有文件
# work_dir = imagePath
# for parent, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(work_dir, followlinks=True):
# for filename in filenames:
# file_path = os.path.join(parent, filename)
# print(‘文件名:%s‘ % filename)
# print(‘文件完整路径:%s\n‘ % file_path)
# import the necessary packages
from skimage.measure import compare_ssim
import argparse
import imutils
import cv2
def get_img_result(path1, path2, path3, path4):
# construct the argument parse and parse the arguments
# ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# ap.add_argument("-f", "--first", required=True,
# help="first input image")
# ap.add_argument("-s", "--second", required=True,
# help="second")
# args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# load the two input images
imageA = cv2.imread(path1)
imageB = cv2.imread(path2)
# convert the images to grayscale
grayA = cv2.cvtColor(imageA, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
grayB = cv2.cvtColor(imageB, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# compute the Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) between the two
# images, ensuring that the difference image is returned
(score, diff) = compare_ssim(grayA, grayB, full=True)
diff = (diff * 255).astype("uint8")
print("SSIM: {}".format(score))
# threshold the difference image, followed by finding contours to
# obtain the regions of the two input images that differ
thresh = cv2.threshold(diff, 0, 255,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cnts = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = imutils.grab_contours(cnts)
# loop over the contours
for c in cnts:
# compute the bounding box of the contour and then draw the
# bounding box on both input images to represent where the two
# images differ
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
cv2.rectangle(imageA, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.rectangle(imageB, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# show the output images
# cv2.imshow("Original", imageA)
cv2.imwrite(path3, imageA)
# cv2.imshow("Modified", imageB)
cv2.imwrite(path4, imageB)
# cv2.imshow("Diff", diff)
# cv2.imshow("Thresh", thresh)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__==‘__main__‘:
get_img_result(‘static/images/modified_03.png‘, ‘static/images/original_03.png‘, ‘static/images/test1.png‘, ‘static/images/test2.png‘)
from flask import Flask, redirect, url_for, jsonify
import base64
from flask import request
import os
from flask import render_template
from basicclass import image_diff
import time
from datetime import timedelta
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
from common.image_util import random_num
from basicclass.pdfconvertpng import pyMuPDF_fitz, single_pyMuPDF_fitz
from common.util import Util
from basicclass.autocutpic import img_cut_white
from basicclass.teamplatemath import match_target
from common.globalparam import tagrt_rgb_x, tagrt_rgb_y, host_ip, port
from basicclass.imagediff import dif_two_pic,dif_mark
from basicclass.image_diff import get_img_result
import os
import shutil
from basicclass.getbackcolor import replace_border_color,get_dominant_color, replace_color
from basicclass.newimgcut import get_parts_similar,get_parts
from basicclass.hashdiff import compare_image_with_hash
app = Flask(__name__)
bl_files = [‘logo.jpg‘,‘meixin2.jpg‘]
bl_dirs = []
# 定义路由
@app.route(‘/hello/写在最后
交流:3459067873
上一篇:用C语言实现三子棋
文章标题:python智能图片识别系统(图片切割、图片识别、区别标识)
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/71282.html