2.SpringBoot学习(二)——ConfigurationProperties
2021-04-20 06:27
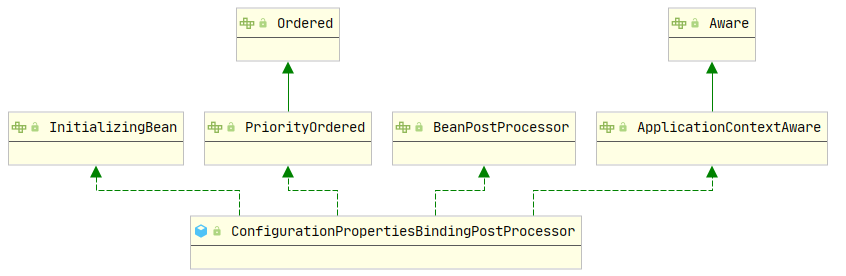
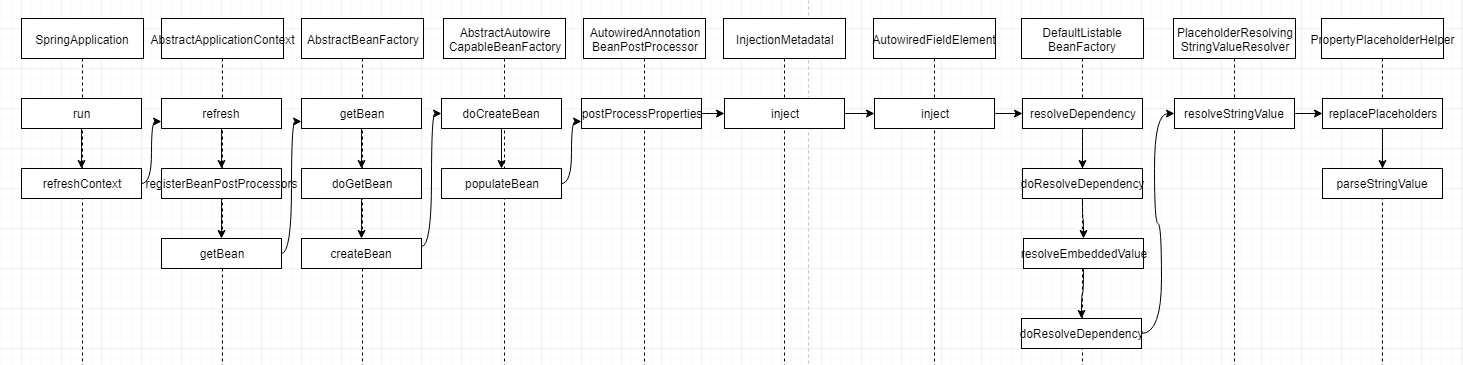
标签:available npoi main lua catch short test tab inter Annotation for externalized configuration. Add this to a class definition or a @Bean method in a @Configuration class if you want to bind and validate some external Properties (e.g. from a .properties file). Binding is either performed by calling setters on the annotated class or, if @ConstructorBinding is in use, by binding to the constructor parameters. Note that contrary to @Value, SpEL expressions are not evaluated since property values are externalized. 一个外部化配置的注解。如果您要绑定和验证某些外部属性(例如,来自.properties文件),则将其添加到类定义或 @Configuration 类中的 @Bean 方法中。 绑定可以通过在带注释的类上调用setter来执行,或者,如果正在使用 @ConstructorBinding,则可以通过绑定到构造函数参数来执行。 请注意,与@Value相反,由于属性值是外部化的,因此不评估SpEL表达式。 application.properties UserProperties.java UserProps.java UserController.java spring-boot/spring-boot-02-config 启动 SpringBoot02ConfigApplication.main 方法,在 spring-boot-02-config.http 访问如下两个地址,输出 “zhangsan‘s age is 20” 表示请求成功 @SpringBootApplication 注解是一个复合注解,它里面包含一个 @ConfigurationPropertiesScan,这个里面又有一个 @EnableConfigurationProperties,@ConfigurationProperties 的作用与它有关。 @ConfigurationProperties 中通过 @Import 引入一个 EnableConfigurationPropertiesRegistrar,它里面有一个 registerBeanDefinitions 方法 registerBeanDefinitions 调用一个 registerInfrastructureBeans ,这个方法将 属性绑定后置处理器、bean 校验器、元数据注入到 registry 中,这里的 registry 保存了所有 bean 信息。 通过查看类图可以知道,ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 是 BeanPostProcessor 的一个实现类 它在 bean 实例化的时候发生作用,BeanPostProcessor 提供了 postProcessBeforeInitialization 和 postProcessAfterInitialization 两个方法 在 ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法中提供了对于属性值的注入 在 bind 方法中,通过 ConfigurationPropertiesBinder 来绑定 ConfigurationProperties 中属性 到这里已经比较清晰了,后面的就是从 应用上下文中获取属性值,然后转换成对应的类型,再将属性值设置给目标对象。 这个流程中,doCreateBean 前面的流程实际上是 spirng bean 的初始化流程,在初始化过程中,会对 bean 的依赖和字段进行填充;BeanPostProcessor 也是在这个阶段发生作用 使用注解进行 bean 注入的时候,会有一个 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 的处理类,它里面有一个 postProcessProperties 方法 InjectionMetadata 是类的注入元数据,这里通过它来对 bean 中的属性进行注入,它里面提供了多种注入元件,而 ConfigurationProperties 主要通过字段属性进行注入 AutowiredFieldElement 的 inject 方法实现如下 接下来调用流程是 resolveDependency -> doResolveDependency -> resolveEmbeddedValue 最后调用到 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,通过解析配置文件获取到最终值 2.SpringBoot学习(二)——ConfigurationProperties 标签:available npoi main lua catch short test tab inter 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/col-smile/p/13285850.html1.简介
1.1 概述
1.2 特点
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ConfigurationProperties {
String value() default "";
String prefix() default "";
boolean ignoreInvalidFields() default false;
boolean ignoreUnknownFields() default true;
}
1.3 对比 @Value
@Configuration
@Value
功能
批量注入配置文件中的属性
一个个指定
松散绑定(松散语法)
支持
不支持
SPEL语法
不支持
支持
JSR303数据校验
支持
不支持
复杂类型封装
支持
不支持
2.环境
3.代码
3.1 代码结构
3.2 maven 依赖
3.3 配置文件
user.prop.name=zhangsan
user.prop.age=20
3.4 java代码
@Component
@Validated // JSR303数据校验
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user.prop")
public class UserProperties {
@NotBlank
private String name;
@Range(min = 1, max = 200)
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@Component
public class UserProps {
@Value("${user.prop.name}")
private String name;
// SPEL 表达式
@Value("#{10 * 2}")
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserProperties userProperties;
@Autowired
private UserProps userProps;
@GetMapping("/user/get/1")
public String getUser1() {
return userProperties.getName() + "‘s age is " + userProperties.getAge();
}
@GetMapping("/user/get/2")
public String getUser2() {
return userProps.getName() + "‘s age is " + userProps.getAge();
}
}
3.5 git 地址
4.结果
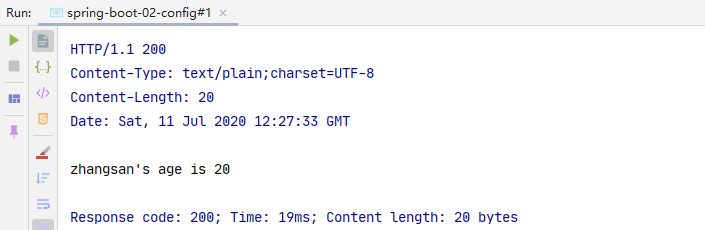
5.源码分析
5.1 @ConfigurationProperties 原理分析
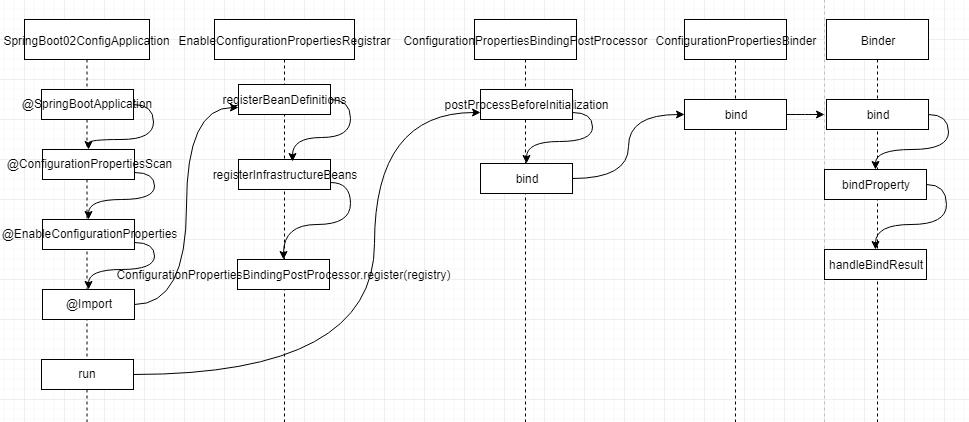
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerInfrastructureBeans(registry);
ConfigurationPropertiesBeanRegistrar beanRegistrar = new ConfigurationPropertiesBeanRegistrar(registry);
getTypes(metadata).forEach(beanRegistrar::register);
}
static void registerInfrastructureBeans(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor.register(registry);
ConfigurationPropertiesBeanDefinitionValidator.register(registry);
ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetadata.register(registry);
}
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 属性绑定
bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean.get(this.applicationContext, bean, beanName));
return bean;
}
BindResult> bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean propertiesBean) {
Bindable> target = propertiesBean.asBindTarget();
// 获取目标 bean 上的 @ConfigurationProperties 注解
ConfigurationProperties annotation = propertiesBean.getAnnotation();
// 获取 BindHandler
BindHandler bindHandler = getBindHandler(target, annotation);
// 通过配置的 prefix 和 BindHandler 进行属性绑定
return getBinder().bind(annotation.prefix(), target, bindHandler);
}
5.2 @Value 原理分析
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
// 判断是否已缓存,如果缓存了,直接获取
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
// 如果没有缓存,需要从 beanFactory 中获取具体值,然后缓存起来
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set@Override
@Nullable
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(@Nullable String value) {
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
String result = value;
for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) {
result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result);
if (result == null) {
return null;
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) throws BeansException {
String resolved = this.helper.replacePlaceholders(strVal, this.resolver);
if (trimValues) {
resolved = resolved.trim();
}
return (resolved.equals(nullValue) ? null : resolved);
}
6.参考
上一篇:Python中鸭子类型
文章标题:2.SpringBoot学习(二)——ConfigurationProperties
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/77005.html