3.SpringBoot学习(一)——第一个Web应用
2021-04-21 12:27
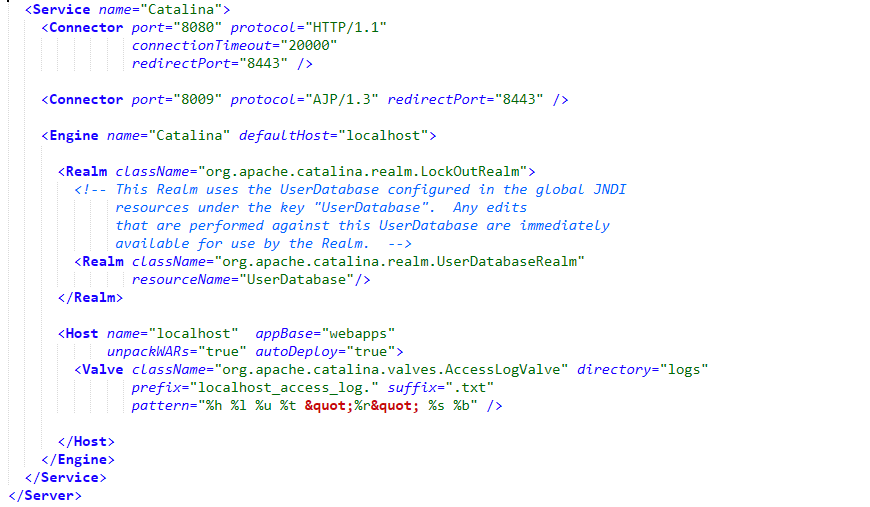
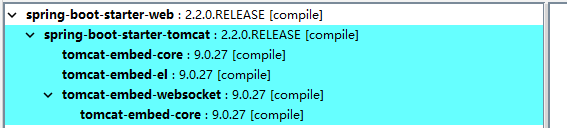
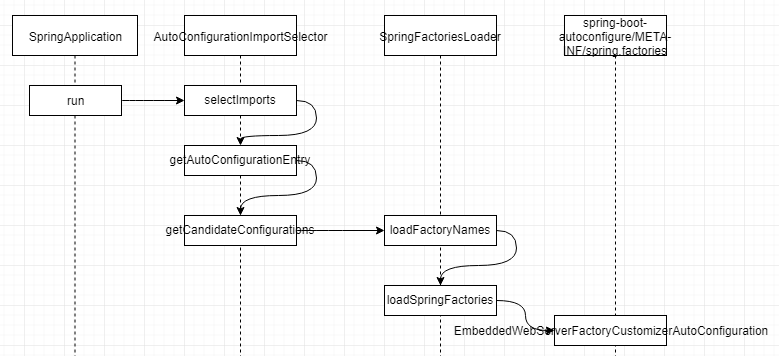
标签:XML efault anti condition server 生成 lstat var nmon Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can "just run". We take an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need minimal Spring configuration. Spring Boot 可以轻松创建单独的,基于生产级的 Spring 应用程序,您需要做的可能“仅仅是去运行”。 我们提供了 Spring Platform 对 Spring 框架和第三方库进行处理,尽可能的降低使用的复杂度。大多数情况下 Spring Boot 应用只需要非常少的配置。 Spring 是一种生态,它包含各种组件,针对开发中存在的问题提供了多种解决方案; Spring Boot 为快速启动且最小化配置的 Spring 应用而设计,并且具备用于构建生产级应用的各种特性,提供了一些内置 starter; Spring 应用需要复杂配置,一般在需要在 xml 中配置各种依赖;Spring Boot 简化了这些配置,默认使用注解进行扫描,最多只需要在 application.properties 中提供额外配置; 使用 maven 构建 Spring 应用需要提供各种 pom 依赖;而 Spring Boot 只需要提供了 starter 即可,starter 中已经对所需依赖进行了封装; Spring 应用最终需要打成 war 包放到 Severlet 容器中进行运行;而 Spring Boot 可以打成 jar 包,使用 java -jar 命令直接运行; ... DemoController.java spring-boot/spring-boot-01-demo 启动 SpringBootDemoApplication.main 方法,访问如下地址,页面显示 “demo” 表示服务运行正常 从 main 方法开始 SpringApplication.run -> ConfigurableApplicationContext SpringApplication.run -> ConfigurableApplicationContext ,跟踪 tomcat 的创建过程,主要看 createApplicationContext() 和 refreshContext() 方法 createApplicationContext() 创建 spring 应用 最终创建的应用类型和 webApplicationType 有关,webApplicationType 在 SpringApplication 的构造函数中进行实例化 默认类型为 WebApplicationType.SERVLET 在 refreshContext 中调用了 refresh(context) 方法,这里的 applicationContext 为 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 然后调用 AbstractApplicationContext.refresh() 方法 onRefresh() 是一个钩子方法,根据上面分析,这里使用的是 servlet,所以会调用到 ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh() 在 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 中调用 createWebServer() 创建 web 服务 这里的 factory 通过 ServletWebServerFactory 来实例化,所以创建 ServletWebServer 最终在 TomcatServletWebServerFactory 中创建了 Tomcat、Connector、Engine、Host 等,这里可以结合 apache-tomcat 的配置文件 server.xml 来分析几者之间的层级关系 先看下 spring-boot-starter-web 的依赖结构 spring-boot-starter-web 依赖了 spring-boot-starter-tomcat,又依赖了 tomcat-embed-core。但是只凭这个,并不能说明默认容器为 tomca 的原因。 要弄清这个问题,就要涉及到 Spring Boot 的自动装配,以及 WebServer 的装配。 @SpringBootApplication 是一个复合注解,它包含如下内容 其中 @EnableAutoConfiguration 和自动装配相关,@EnableAutoConfiguration 声明如下 @Import 导入一个 AutoConfigurationImportSelector,这个 Selector 中 selectImports() 实现如下 其中 getAutoConfigurationEntry 获取自动装配类型,它的实现如下 在 getCandidateConfigurations 获取所有自动装配类,这个方法通过 SpringFactoriesLoader 加载 META-INF/spring.factories 中的内容,在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 的 spring.factories 中有如下内容 其中有一条配置为 EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,这个即为内容 webServer 的自动装配类 它的实现如下 结合上面 spring-boot-starter-web 中引入了 tomcat-embed-core 依赖,可以发现,默认装配的类型即为 TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration 3.SpringBoot学习(一)——第一个Web应用 标签:XML efault anti condition server 生成 lstat var nmon 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/col-smile/p/13281796.html1.简介
1.1 概述
1.2 特点
1.3 对比 Spring
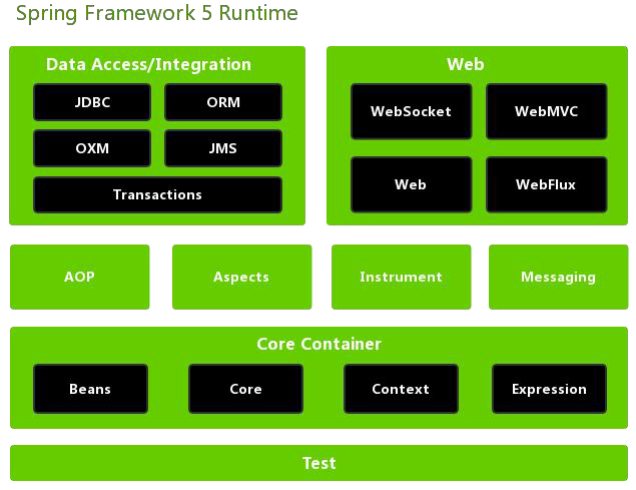
2.环境
3.代码
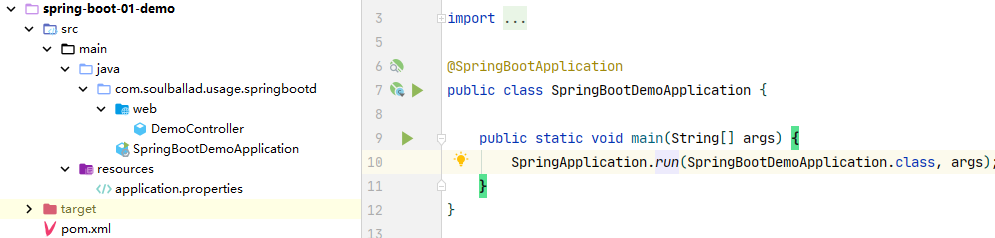
3.1 代码结构
3.2 maven 依赖
3.3 java代码
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("/demo")
public String demo() {
return "demo";
}
}
3.4 git 地址
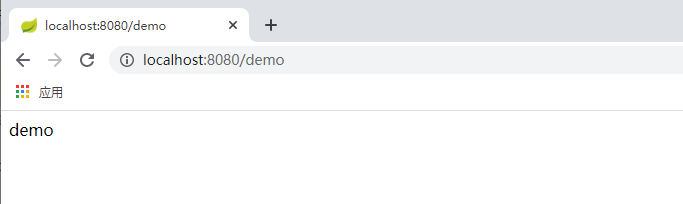
4.结果
### GET /demo
GET http://localhost:8080/demo
5.源码分析
5.1 Spring Boot 启动流程?
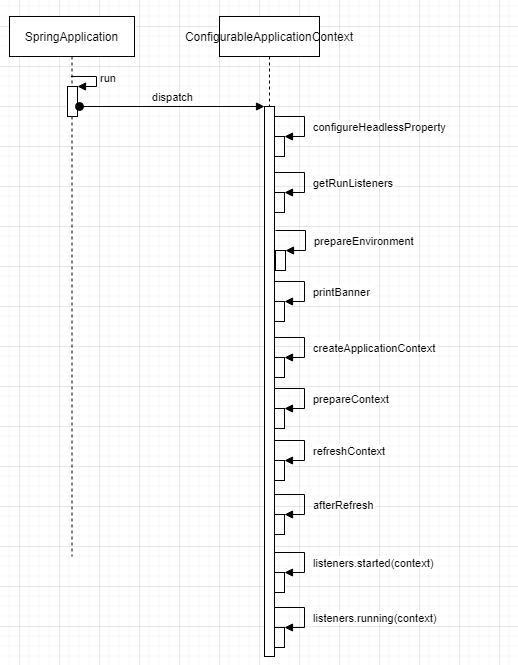
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection5.2 Spring Boot 如何加载 Tomcat?
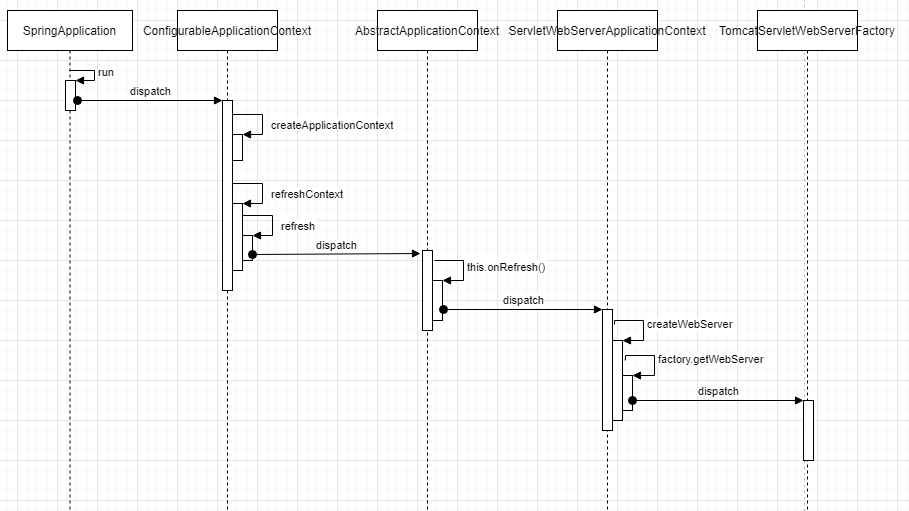
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// ...
try {
// ...
context = createApplicationContext();
// ...
refreshContext(context);
// ...
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// ...
return context;
}
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// ...
try {
// ...
this.onRefresh();
// ...
} catch (BeansException var9) {
// ...
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
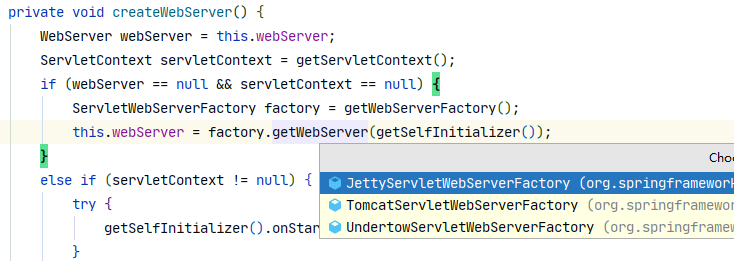
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
5.3 Spring Boot 默认容器为何是 tomcat?
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
@ConfigurationPropertiesScan
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
// ...
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
// ...
}
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata,
annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
// 是否开启自动装配,默认开启,可通过 spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration 进行配置
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
// 获取元注解中的属性,它是一个 LinkedHashMap
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 获取要自动装配类的类名
List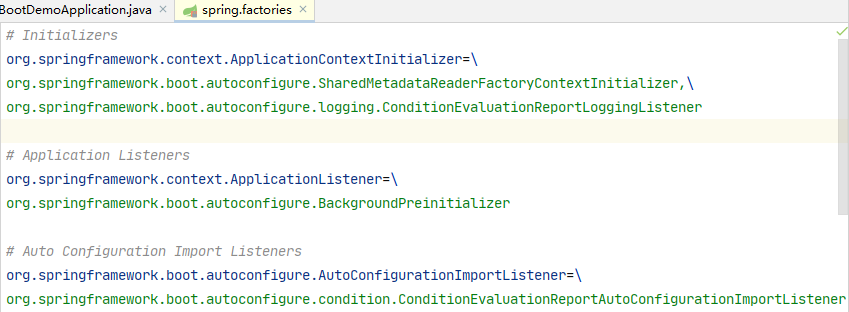

@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
public class EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Nested configuration if Tomcat is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
public static class TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration {
@Bean
public TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer(Environment environment,
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer(environment, serverProperties);
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Jetty is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Server.class, Loader.class, WebAppContext.class })
public static class JettyWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration {
@Bean
public JettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer jettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer(Environment environment,
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new JettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer(environment, serverProperties);
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Undertow is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class })
public static class UndertowWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration {
@Bean
public UndertowWebServerFactoryCustomizer undertowWebServerFactoryCustomizer(Environment environment,
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new UndertowWebServerFactoryCustomizer(environment, serverProperties);
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Netty is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(HttpServer.class)
public static class NettyWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration {
@Bean
public NettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer nettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer(Environment environment,
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new NettyWebServerFactoryCustomizer(environment, serverProperties);
}
}
}
下一篇:归并排序