python之Beautiful Soup的基本用法
2021-04-23 06:29
YPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40/loose.dtd">
标签:class 支持 tor tag 利用 简单 panel list attrs
Beautiful Soup就是Python的一个HTML或XML的解析库,可以用它来方便地从网页中提取数据。它有如下三个特点:
- Beautiful Soup提供一些简单的、Python式的函数来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。
- Beautiful Soup自动将输入文档转换为Unicode编码,输出文档转换为UTF-8编码。你不需要考虑编码方式,除非文档没有指定一个编码方式,这时你仅仅需要说明一下原始编码方式就可以了。
- Beautiful Soup已成为和lxml、html6lib一样出色的Python解释器,为用户灵活地提供不同的解析策略或强劲的速度。
首先,我们要安装它:pip install bs4,然后安装 pip install beautifulsoup4.
Beautiful Soup支持的解析器
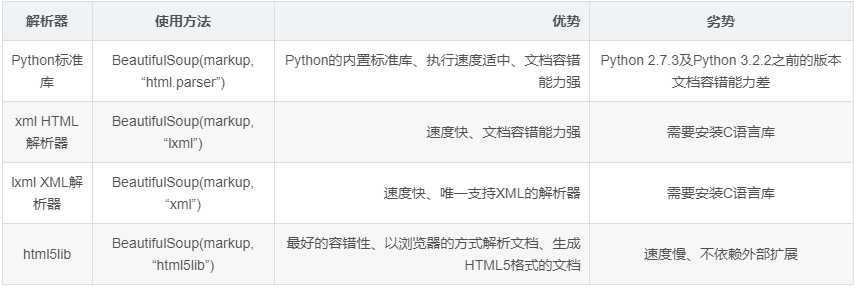
下面我们以lxml解析器为例:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(‘Hello
‘, ‘lxml‘) print(soup.p.string)
结果:
Hello
beautiful soup美化的效果实例:
html = """The Dormouse‘s story The Dormouse‘s story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were , Lacie and Tillie; and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, ‘lxml‘)
#调用prettify()方法。这个方法可以把要解析的字符串以标准的缩进格式输出 print(soup.prettify()) print(soup.title.string)
结果:
<span> The Dormouse</span><span>‘</span><span>s story</span> class="title" name="dromouse"> The Dormouse‘s story
class="story"> Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> , class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2"> Lacie and class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3"> Tillie ; and they lived at the bottom of a well.
class="story"> ...
The Dormouse‘s story
下面举例说明选择元素、属性、名称的方法
html = """The Dormouse‘s story The Dormouse‘s story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well....
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, ‘lxml‘)
print(‘输出结果为title节点加里面的文字内容:\n‘,soup.title)
print(‘输出它的类型:\n‘,type(soup.title))
print(‘输出节点的文本内容:\n‘,soup.title.string)
print(‘结果是节点加其内部的所有内容:\n‘,soup.head)
print(‘结果是第一个p节点的内容:\n‘,soup.p)
print(‘利用name属性获取节点的名称:\n‘,soup.title.name)
#这里需要注意的是,有的返回结果是字符串,有的返回结果是字符串组成的列表。
# 比如,name属性的值是唯一的,返回的结果就是单个字符串。
# 而对于class,一个节点元素可能有多个class,所以返回的是列表。
print(‘每个节点可能有多个属性,比如id和class等:\n‘,soup.p.attrs)
print(‘选择这个节点元素后,可以调用attrs获取所有属性:\n‘,soup.p.attrs[‘name‘])
print(‘获取p标签的name属性值:\n‘,soup.p[‘name‘])
print(‘获取p标签的class属性值:\n‘,soup.p[‘class‘])
print(‘获取第一个p节点的文本:\n‘,soup.p.string)
结果:
输出结果为title节点加里面的文字内容:
输出它的类型:
输出节点的文本内容:
The Dormouse‘s story
结果是节点加其内部的所有内容:
结果是第一个p节点的内容:
The Dormouse‘s story
利用name属性获取节点的名称:
title
每个节点可能有多个属性,比如id和class等:
{‘class‘: [‘title‘], ‘name‘: ‘dromouse‘}
选择这个节点元素后,可以调用attrs获取所有属性:
dromouse
获取p标签的name属性值:
dromouse
获取p标签的class属性值:
[‘title‘]
获取第一个p节点的文本:
The Dormouse‘s story
在上面的例子中,我们知道每一个返回结果都是bs4.element.Tag类型,它同样可以继续调用节点进行下一步的选择。
html = """The Dormouse‘s story """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, ‘lxml‘) print(‘获取了head节点元素,继续调用head来选取其内部的head节点元素:\n‘,soup.head.title) print(‘继续调用输出类型:\n‘,type(soup.head.title)) print(‘继续调用输出内容:\n‘,soup.head.title.string)
结果:
获取了head节点元素,继续调用head来选取其内部的head节点元素:The Dormouse<span>‘</span><span>s story</span> 继续调用输出类型: class ‘bs4.element.Tag‘> 继续调用输出内容: The Dormouse‘s story
(1)find_all()
find_all,顾名思义,就是查询所有符合条件的元素。给它传入一些属性或文本,就可以得到符合条件的元素,它的功能十分强大。
find_all(name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs)
他的用法:
html=‘‘‘‘‘‘ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, ‘lxml‘) print(‘查询所有ul节点,返回结果是列表类型,长度为2:\n‘,soup.find_all(name=‘ul‘)) print(‘每个元素依然都是bs4.element.Tag类型:\n‘,type(soup.find_all(name=‘ul‘)[0])) #将以上步骤换一种方式,遍历出来 for ul in soup.find_all(name=‘ul‘): print(‘输出每个u1:‘,ul.find_all(name=‘li‘)) #遍历两层 for ul in soup.find_all(name=‘ul‘): print(‘输出每个u1:‘,ul.find_all(name=‘li‘)) for li in ul.find_all(name=‘li‘): print(‘输出每个元素:‘,li.string)Hello
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo
- Bar
结果:
查询所有ul节点,返回结果是列表类型,长度为2:
[
- class="list" id="list-1">
- class="element">Foo
- class="element">Bar
- class="element">Jay
- class="list list-small" id="list-2">
- class="element">Foo
- class="element">Bar

python之Beautiful Soup的基本用法
标签:class 支持 tor tag 利用 简单 panel list attrs
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiao02fang/p/13269984.html
下一篇:Java学习(二十一)