JAVA学习之-I/O流
2021-05-05 07:28
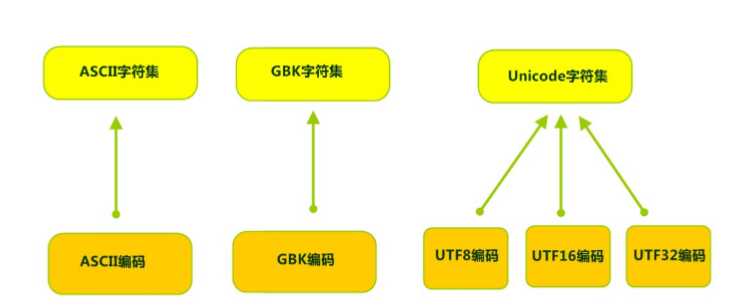
标签:辅助 常用方法 sep end mic 多个 遍历文件 fileinput 文件 一,流的概念 内存与存储设备之间传输数据的通道。 二,流的分类 2.1,按方向,以内存为基准。 输入流:将存储设备中的数据读取到内存中。 输出流:将内存中的数据写入到存储设备中。 2.2,按单位, 字节流:以字节为单位,可以读写任何数据。 字符流:以字符为单位,只能读写文本数据。 2.3,按功能, 节点流:具有实际传输数据的读写功能。 过滤流:节点流的基础上增强功能。 三,字节流 3.1,字节流抽象类 3.1.1 InputStream:字节输入流 public int read(){} public int read(byte[]b){} public int read(byte[]b,int off,int len){} OutputStream:字节输出流 public void write(int n){} public void write(byte[]b){} public void write(byte[]b,int off,int len){} 3.2,字节节点流 3.2.1 FileInputStream: public int read(){}:单个字节读取,返回读取的字节。 public int read(byte[]b):从流中读取多个字节存入数组,返回读取的实际字节数,如果到文件末尾处,返回-1. 创建FileInputStream对象 传入,路径名或File对象。调用方法。 3.2.2 FileOutputStream: public void write(byte[]b){} :将字节数组中的字节写入流 public void write(byte[]b,int off,int len){}。写出有效长度的字节 3.3,字节过滤流(缓冲流):提高I/O效率,减少访问磁盘次数,写入时写入到缓冲区,刷新后进入文件 3.3.1BufferedInputStream : 字节缓冲输出流,缓冲流不具有实际传输功能,需要传入节点流 3.3.2 BufferedOutputStream:字节缓冲输出流 3.3.3 缓冲流边读边写复制文件 3.4,对象流(序列化反序列化) :增强了缓冲区的功能,增强了读写八种基本数据类型和字符串的功能,增强了读写对象的功能。,使用流传输对象的过程,成为序列反序列 序列化的前提: * 1 序列化要求:序列化类以及对象属性必须要实现Serializable (标记接口) 3.4.1 ObjectOutputStream : 序列化 writeObject(Object obj) 向流中写入一个对象,序列化 3.4.2ObjectInputStream :反序列化 readObject():从流中读取一个对象 四,字符编码 4.1 计算机中储存的信息都是用二进制数表示的,而我们在屏幕上看到的数字、英文、标点符号、汉字等字符是二进制 数转换之后的结果。 按照某种规则,将字符存储到计算机中,称为编码 。反之,将存储在计算机中的二进制数按照 某种规则解析显示出来,称为解码 计算机要准确的存储和识别各种字符集符号,需要进行字符编码,一套字符集必然至少有一套字符编码。常见字符 集有ASCII字符集、GBK字符集、Unicode字符集等。 4.2 字符编码 Character Encoding : 就是一套自然语言的字符与二进制数之间的对应规则。 字符集:Charset :也叫编码表。是一个系统支持的所有字符的集合,包括各国家文字、标点符号、图形符 号、数字等。 4.2.1 ASCII字符集 : (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)基本的ASCII字符集,使用7位(bits)表示一个字符,共128字符。ASCII的扩展字符集使用8位(bits) 表示一个字符,共256字符。 ISO-8859-1字符集:拉丁码表, GB2312:简体中文码表。GBK:最常用的中文码表,完全兼容GB2312。GB18030:最新的中文码表。收录汉字70244个,采用多字节编码,每个字可以由1个、2个或4个字节 组成。支持中国国内少数民族的文字,同时支持繁体汉字以及日韩汉字等。 Unicode字符集 :Unicode编码系统为表达任意语言的任意字符而设计,是业界的一种标准,也称为统一码、标准万国 码。最多使用4个字节的数字来表达每个字母、符号,或者文字。有三种编码方案,UTF-8、UTF-16和UTF32。最为常用的UTF-8编码。 UTF-8编码规则: 1. 128个US-ASCII字符,只需一个字节编码。 2. 拉丁文等字符,需要二个字节编码。 3. 大部分常用字(含中文),使用三个字节编码。 4. 其他极少使用的Unicode辅助字符,使用四字节编码。 五,字符流 5.1字符流抽象类 5.1.1 Reader :字符输入流 public int read(){} public int read(char[]c){} public int read(char[]c,int off,int len){} Writer:字符输出流 public void write(int n){} public void write(String str){} public void write(char[] c){} 5.2 字符节点流 5.2.1 FileReader: 文件字符输入流 public int read(){} ,每次可以读取一个字符的数据,提升为int类型,读取到文件末尾,返回 -1 public int read(char[]c) 从流中读取多个字符,存储到数组中,返回读到的有效字符数,如果达到文件尾部返回-1. 5.2.2 FileWriter :文件字符输出流 public void write(int c){} 写出一个字符 1. 虽然参数为int类型四个字节,但是只会保留一个字符的信息写出。 2. 未调用close方法,数据只是保存到了缓冲区,并未写出到文件中FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt"); 因为FileWriter内置缓冲区的原因,如果不关闭输出流,无法写出字符到文件中。但是关闭的流对象,是无法继续写出数据 的。如果我们既想写出数据,又想继续使用流,就需要 flush 方法了。 flush :刷新缓冲区,流对象可以继续使用。 close :先刷新缓冲区,然后通知系统释放资源。流对象不可以再被使用了。 public void write(char[] cbuf) 和 write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) ,write(String str) 将数组中的字符,字符串写入输出流。 数据追加续写:每次程序运行,创建输出流对象,都会清空目标文件的数据 public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) : 创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的 文件。 public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) : 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt",true); 构造方法,参数中都需要传入一个boolean类型的值, true 表示追加数据, false 表示清空原有数据。 这样创建的输出流对象,就可以指定是否追加续写了。 写出换行:\r\n 小贴士:字符流,只能操作文本文件,不能操作图片,视频等非文本文件 5.3字符过滤流(缓冲流) 5.3.1 BufferedReader 字符缓冲输入流 读取文本 特有方法,读一行 readLine() 5.3.2 BufferedWriter 字符缓冲输出流 写入文件 特有方法,写换行 newLine() 跨平台 5.4 打印流 printWriter() 封装了print()/println()方法,支持写入后换行,支持数据原样打印。 5.5 转换流 InputStreamReader: 字节 转字符 转换流 java.io.InputStreamReader ,是Reader的子类,是从字节流到字符流的桥梁。它读取字节,并使用指定 的字符集将其解码为字符。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集。 OutputStreamWriter: 字符 转字节 转换流 java.io.OutputStreamWriter ,是Writer的子类,是从字符流到字节流的桥梁。使用指定的字符集将字符 编码为字节。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集。 InputStreamReader(InputStream in) : 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。 InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) : 创建一个指定字符集的字符流 OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in) : 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。 OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in, String charsetName) : 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。 六,File类,FileFilter 6.1 File类:代表物理盘符中的一个文件或文件夹,无论该路径下是否存在文件或者目录,都不影响File对象的创建。 java.io.File 类是文件和目录路径名的抽象表示,主要用于文件和目录的创建、查找和删除等操作。 6.2 构造方法 public File(String pathname) :通过将给定的路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建新的 File实例。 public File(String parent, String child) :从父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。 public File(File parent, String child) :从父抽象路径名和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。 6.3 常用方法 public String getAbsolutePath() :返回此File的绝对路径名字符串。 public String getPath() :将此File转换为路径名字符串。 public String getName() :返回由此File表示的文件或目录的名称。 public boolean renameTo(File file):修改文件名(包含剪切功能) lastModified() 最后一次修改的时间 canWrite():是否可写 isHidden():是否隐藏 isAbsolute():是否是绝对路径 public long length() :返回由此File表示的文件的长度。 API中说明:length(),表示文件的长度。但是File对象表示目录,则返回值未指定。 public boolean exists() :此File表示的文件或目录是否实际存在。 public boolean isDirectory() :此File表示的是否为目录。 public boolean isFile() :此File表示的是否为文件。 public boolean createNewFile() :当且仅当具有该名称的文件尚不存在时,创建一个新的空文件。 public boolean delete() :删除由此File表示的文件或目录。delete方法,如果此File表示目录,则目录必须为空才能删除,直接删除最深层目录。 deleteOnExit():退出JVM时,虚拟机删除 public boolean mkdir() :创建由此File表示的目录。 public boolean mkdirs() :创建由此File表示的目录,包括任何必需但不存在的父目录。 public String[] list() :返回一个String数组,表示该File目录中的所有子文件或目录。 6.4FileFilter接口,文件过滤器接口 是File的过滤器。 该接口的对象可以传递给File类的 listFiles(FileFilter) 作为参数, 接口中只有一个方法。boolean accept(File pathname) :测试pathname是否应该包含在当前File目录中,符合则返回true。 6.5练习 七,Properties实现流操作 java.util.Properties 继承于 Hashtable ,来表示一个持久的属性集。它使用键值结构存储数据,每个键及其 对应值都是一个字符串。该类也被许多Java类使用,比如获取系统属性时, System.getProperties 方法就是返回 一个 Properties 对象。 public Properties() :创建一个空的属性列表。 public Object setProperty(String key, String value) : 保存一对属性。 public String getProperty(String key) :使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性值。 public Set 与流相关: public void load(InputStream inStream) : 从字节输入流中读取键值对 public void store (OutputStream):将键值对写入流 小贴士:文本中的数据,必须是键值对形式,可以使用空格、等号、冒号等符号分隔 JAVA学习之-I/O流 标签:辅助 常用方法 sep end mic 多个 遍历文件 fileinput 文件 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ff52531314/p/13191442.htmlpublic class TestFileInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1创建FileInputStream对象
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:\\bbb.txt");
//2读取(输入)
//2.1单个字节读取
// int data=0;
// while((data=fis.read())!=-1) {
// System.out.print((char)data);
// }
//2.2一次读取多个字节(效率高)
byte[] buf=new byte[1024];
//fis.read(buf);//读取5个字节
int len=0;//保存读取的字节个数
while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1) {
System.out.println("读取字节个数:"+len);
System.out.println(new String(buf));
}
//3关闭
fis.close();
}
}
1 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("d:\\aaa.txt");
2 //2输出(写入)数据
3 fos.write(97);//97是a的ASCII吗
4 fos.write(98);
5 fos.write(99);
6 fos.write(57);
7 fos.write(55);
8 String say="ma hua teng li hai";
9 String say="马化腾制裁苹果";
10 fos.write(say.getBytes());
11 //3刷新(如果没有缓冲区不需要刷新)
12 fos.flush();
13 //4关毕
14 fos.close();
15 System.out.println("执行完毕");
public class TestBufferedInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建流
//1.1创建FileInputStream
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:\\bbb.txt");
//1.2创建缓冲流(有缓冲区 8K)
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
//2读取(输入)
//2.1 单个字节读取
// int data=0;
// while((data=bis.read())!=-1) {
// System.out.print((char)data);
// }
//2.2 一个读取多个字节
byte[] buf=new byte[5];
int len=0;
while((len=bis.read(buf))!=-1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,len));
}
//3关闭
bis.close();
}
}
public class TestBufferedOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建流
//1.1创建字节输出流(节点流,具有实际读写数据的功能)
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("d:\\buffer.txt");
//1.2创建缓冲流,传递节点流,默认缓冲区大小8K
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//2写入文件
for(int i=0;i10;i++) {
bos.write("好好学习,天天向上\r\n".getBytes());//写入缓冲区
//bos.flush();//刷新缓冲
}
//3关闭(自带flush功能)
bos.close();
System.out.println("写入完毕");
}
}
public class CopyFile2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1创建流
//1.1创建缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:\\timg.jpg"));
//1.2创建缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:\\timg3.jpg"));
//2边读边写
int data=0;
while((data=bis.read())!=-1) {
bos.write(data);
}
//3关闭(带有刷新功能)
bis.close();
bos.close();
System.out.println("复制完毕");
}
}
* 2 使用transient(瞬间的)修饰属性,则此属性不参与序列化
* 3 读取到文件尾部的标志:java.io.EOFException End Of Filepublic class TestObjectOuputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建流
//1.1创建节点流
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("d:\\object.txt");
//1.2创建对象输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//2.1写入基本数据类型
// oos.writeInt(97);
// oos.writeDouble(3.14);
// oos.writeBoolean(true);
//2.2写入引用类型数据
Student mahuateng=new Student("马化腾", 20);
Student mayun=new Student("马云", 22);
ArrayList
public class TestObjectInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建流
//1.1创建节点流
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:\\object.txt");
//1.2创建对象输入流
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//2.1读取基本数据
// int age=ois.readInt();
// double pi=ois.readDouble();
// boolean b=ois.readBoolean();
// System.out.println(age+" "+pi+" "+b);
//2.2读取引用类型数据
// Student stu=(Student)ois.readObject();
// Student stu2=(Student)ois.readObject();
// System.out.println(stu.toString());
// System.out.println(stu2.toString());
ArrayList
public class TestFileReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1创建FileReader对象(默认编码utf-8)
FileReader fr=new FileReader("d:\\writer.txt");
//2读取
//2.1单个字符读取
//自动提升为int类型
// int data=0;
// while((data=fr.read())!=-1) {
// System.out.print((char)data);
// }
//2.2多个字符读取
char[] buf=new char[5];
int len=0;
while((len=fr.read(buf))!=-1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,len));
}
//3关闭
fr.close();
}
}
// 写出数据
fw.write(97); // 写出第1个字符
fw.write(‘b‘); // 写出第2个字符
fw.write(‘C‘); // 写出第3个字符
fw.write(30000); // 写出第4个字符,中文编码表中30000对应一个汉字。
// fw.close();public class TestFileWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建文件字符输出流(编码默认utf-8)
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("d:\\writer.txt",true);//为true支持续写
//2写入
for(int i=0;i10;i++) {
fw.write("大连是个好地方...\r\n");//换行
fw.flush();
}
//3关闭
fw.close();
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
public class FWWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用文件名称创建流对象
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");
// 字符串转换为字节数组
char[] chars = "黑马程序员".toCharArray();
// 写出字符数组
fw.write(chars); // 黑马程序员
// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是‘程‘,两个字节,也就是‘程序‘。
fw.write(b,2,2); // 程序
// 关闭资源
fos.close();
}
}public class TestBufferedReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1创建流
//1.1创建节点流
FileReader fr=new FileReader("d:\\buffer.txt");
//1.2创建缓冲流
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
//2读取
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
//3关闭
br.close();
}
}
public class TestBufferedWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1创建流
//1.1创建FileWriter
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("d:\\buffer.txt");
//1.2创建缓冲流
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
//2写入
for(int i=0;i5;i++) {
bw.write("好好学习,天天向上");
bw.newLine();//行终止符
bw.flush();//刷新
}
//3关闭
bw.close();
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
public class TestPrintWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1创建打印流
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter("d:\\print.txt");
//2打印方法
pw.println(97);//"97"
pw.println(3.14);//"3.14"
pw.println(true);//"true"
pw.println(new char[] {‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘});
//3关闭
pw.close();
System.out.println("打印完毕");
}
}
public class TestInputStreamReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建流
//1.1创建节点流
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:\\info.txt");
//1.2创建转换流 参数1 节点流 参数2 字符编码
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis, "GBK");
//2读取
int data;
while((data=isr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)data);
}
//3关闭
isr.close();
//1创建流
//1.1创建节点流
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("d:\\haha.txt");
//1.2创建转换流
OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "gbk");
//BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw);
//2写入
osw.write("哈哈");
//3关闭
osw.close();
}
}
// 文件路径名
String pathname = "D:\\aaa.txt";
File file1 = new File(pathname);
// 文件路径名
String pathname2 = "D:\\aaa\\bbb.txt";
File file2 = new File(pathname2);
// 通过父路径和子路径字符串
String parent = "d:\\aaa";
String child = "bbb.txt";
File file3 = new File(parent, child);
// 通过父级File对象和子路径字符串
File parentDir = new File("d:\\aaa");
String child = "bbb.txt";
File file4 = new File(parentDir, child);
public File[] listFiles() :返回一个File数组,表示该File目录中的所有的子文件或目录。调用listFiles方法的File对象,表示的必须是实际存在的目录,否则返回null,无法进行遍历 //遍历目录,搜索指定文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
File dir = new File("D:\\aaa");
printDir2(dir);
}
public static void printDir2(File dir) {
// 匿名内部类方式,创建过滤器子类对象
File[] files = dir.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return pathname.getName().endsWith(".java")||pathname.isDirectory();
}
});
// 循环打印
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()) {
System.out.println("文件名:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
} else {
printDir2(file);
}
}
} //lambda优化
public static void printDir3(File dir) {
// lambda的改写
File[] files = dir.listFiles(f ‐>{
return f.getName().endsWith(".java") || f.isDirectory();
});
// 循环打印
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()) {
System.out.println("文件名:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
} else {
printDir3(file);
}
}
}
} 

/**
* 案例2:
* 需求:使用递归删除文件夹
*
*/
public class TestFile3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
deleteDir(new File("D:\\aaa"));
}
//递归删除文件夹
public static void deleteDir(File dir) {
File[] listFiles = dir.listFiles();
if(listFiles!=null&&listFiles.length>0) {
for (File file : listFiles) {//file可能是文件夹,也可能文件
if(file.isDirectory()) {
//递归调用
deleteDir(file);
}else {
//直接删除
System.out.println(file.getName()+" 删除结果:"+file.delete());
}
}
}
//删除文件夹
System.out.println(dir.getName()+" 删除结果:"+dir.delete());
}
}
/**
* 案例1:需求:使用递归遍历文件夹中所有的文件,包括子文件夹中的文件。
分级打印 路径
*
*/
public class TestFile2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
listDir(new File("d:\\aaa"),0);
}
/**
* 递归遍历文件夹
*/
public static void listDir(File dir,int level) {
System.out.println(getSeprator(level)+dir.getAbsolutePath());
level++;//1
File[] files=dir.listFiles();
if(files!=null&&files.length>0) {
for (File file : files) {//file 可能是一个文件夹,也可能是文件
if(file.isDirectory()) {
//递归调用
listDir(file,level);
}else {
System.out.println(getSeprator(level)+file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
}
//根据级别获取空格
public static String getSeprator(int level) { // 0 1
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i
public class ProDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 创建属性集对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 添加键值对元素
properties.setProperty("filename", "a.txt");
properties.setProperty("length", "209385038");
properties.setProperty("location", "D:\\a.txt");
// 打印属性集对象
System.out.println(properties);
// 通过键,获取属性值
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("filename"));
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("length"));
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("location"));
// 遍历属性集,获取所有键的集合
Set
// 打印键值对
for (String key : strings ) {
System.out.println(key+" ‐‐ "+properties.getProperty(key));
}
}
}
输出结果: {filename=a.txt, length=209385038, location=D:\a.txt} a.txt 209385038 D:\a.txt filename ‐‐ a.txt length ‐‐ 209385038 location ‐‐ D:\a.txt public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 创建属性集对象
Properties pro = new Properties();
// 加载文本中信息到属性集
pro.load(new FileInputStream("read.txt"));
// 遍历集合并打印
Set
for (String key : strings ) {
System.out.println(key+" ‐‐ "+pro.getProperty(key));
}
}
}
输出结果: filename ‐‐ a.txt length ‐‐ 209385038 location ‐‐ D:\a.tx
下一篇:41.线程