《Web Development with Go》JWT认证
2021-05-13 00:30
标签:count method eth 代码 dde rsa password json secret 时间晚了,先来一版调通的JWT普通认证, 明天再弄一个通过中间件,及gorilla,negroni库的认证, 这样正规些, 但认证通过之后,如何对应权限? 由于jwt-go从2升到3,还有rsa 1024加密有对应关系, 真的弄好好久。 一,生成rsa密钥对,必须1024 二,jwt的初始化方法改变 三,claims的写法也与书中不同 四,私钥和公钥在使用之前,还要作一次解析手脚 五,在认证jwt时,要使用jwt-go的request库,并按规则写好函数 六,完整代码: 《Web Development with Go》JWT认证 标签:count method eth 代码 dde rsa password json secret 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/aguncn/p/12003920.htmlopenssl genrsa -out app.rsa 1024
openssl rsa -in app.rsa -pubout > app.rsa.pub
t := jwt.New(jwt.SigningMethodRS512)
claims := make(jwt.MapClaims)
claims["iss"] = "admin"
claims["CustomUserInfo"] = struct {
Name string
Role string
}{user.UserName, "Member"}
claims["exp"] = time.Now().Add(time.Minute * 20).Unix()
t.Claims = claims
priKey, err := jwt.ParseRSAPrivateKeyFromPEM(signKey)
pubKey, err := jwt.ParseRSAPublicKeyFromPEM(verifyKey)
"github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go/request"
。。。
token, err := request.ParseFromRequest(r,
request.AuthorizationHeaderExtractor,
func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
// since we only use one private key to sign the tokens,
// we also only use its public counter part to verify
return pubKey, nil
})
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
jwt "github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go"
"github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go/request"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
// using asymmetric crypto/RSA keys
// location of the files used for signing and verification
const (
privKeyPath = "keys/app.rsa" // openssl genrsa -out app.rsa 1024
pubKeyPath = "keys/app.rsa.pub" // openssl rsa -in app.rsa -pubout > app.rsa.pub
)
const (
SecretKey = "welcome to wangshubo‘s blog"
)
// verify key and sign key
var (
verifyKey, signKey []byte
)
//struct User for parsing login credentials
type User struct {
UserName string `json:"username"`
Password string `json:"password"`
}
// read the key files before starting http handlers
func init() {
var err error
signKey, err = ioutil.ReadFile(privKeyPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Error reading private key")
return
}
verifyKey, err = ioutil.ReadFile(pubKeyPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Error reading private key")
return
}
}
// reads the login credentials, checks them and creates JWT the token
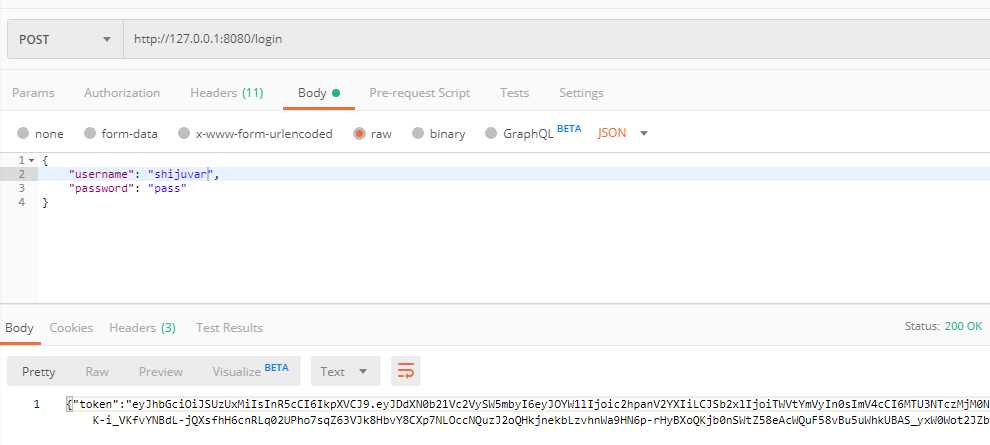
func loginHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var user User
//decode into User struct
err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&user)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error in request body")
return
}
log.Println(user.UserName, user.Password)
// validate user credentials
if user.UserName != "shijuvar" || user.Password != "pass" {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Wrong info")
return
}
// create a signer for rsa 256
t := jwt.New(jwt.SigningMethodRS512)
// set our claims
claims := make(jwt.MapClaims)
claims["iss"] = "admin"
claims["CustomUserInfo"] = struct {
Name string
Role string
}{user.UserName, "Member"}
claims["exp"] = time.Now().Add(time.Minute * 20).Unix()
t.Claims = claims
priKey, err := jwt.ParseRSAPrivateKeyFromPEM(signKey)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("ParseRSAPrivateKeyFromPEM:", err.Error())
return
}
tokenString, err := t.SignedString(priKey)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Sorry, error while Signing Token!")
log.Printf("Token Signing error: %v\n", err)
return
}
response := Token{tokenString}
jsonResponse(response, w)
}
// only accessible with a valid token
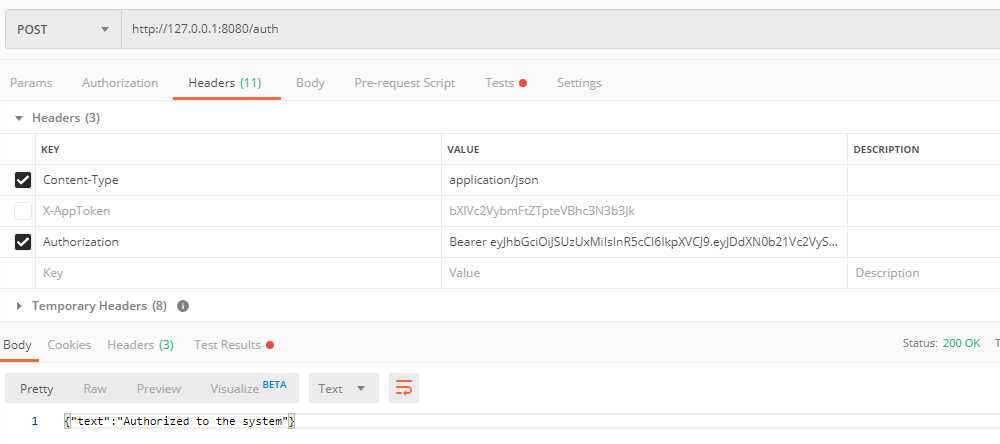
func authHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// validate the token
pubKey, err := jwt.ParseRSAPublicKeyFromPEM(verifyKey)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("ParseRSAPublicKeyFromPEM:", err.Error())
return
}
token, err := request.ParseFromRequest(r,
request.AuthorizationHeaderExtractor,
func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
// since we only use one private key to sign the tokens,
// we also only use its public counter part to verify
return pubKey, nil
})
if err != nil {
switch err.(type) {
case *jwt.ValidationError: // something was wrong during the validation
vErr := err.(*jwt.ValidationError)
switch vErr.Errors {
case jwt.ValidationErrorExpired:
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Token Expired, get a new one.")
return
default:
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error while Parsing Token!")
log.Printf("ValidationError error: %+v\n", vErr.Errors)
return
}
default: // something else went wrong
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error while Parsing Token!")
log.Printf("Token parse error: %v\n", err)
return
}
}
if token.Valid {
response := Response{"Authorized to the system"}
jsonResponse(response, w)
} else {
response := Response{"Invalid token"}
jsonResponse(response, w)
}
}
type Response struct {
Text string `json:"text"`
}
type Token struct {
Token string `json:"token"`
}
func jsonResponse(response interface{}, w http.ResponseWriter) {
json, err := json.Marshal(response)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.Write(json)
}
//Entry point of the program
func main() {
r := mux.NewRouter()
r.HandleFunc("/login", loginHandler).Methods("POST")
r.HandleFunc("/auth", authHandler).Methods("POST")
server := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8080",
Handler: r,
}
log.Println("Listening...")
server.ListenAndServe()
}
文章标题:《Web Development with Go》JWT认证
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/84926.html