数据结构 - 数组模拟非循环和循环队列(Java实现)
2021-05-13 15:28
标签:span str 解决 推出 oop catch 溢出 boolean vpd ??上图可以看出队列空间大小为 \(6\),但是这样模拟队列会有一些问题,当取出数据的时候,下面的数组的位置已经不能被使用了,当 \(rear = 5\) 时队列已经满了,那么下面空的位置不能够被使用,此时叫做 "假溢出" 或者 "假满",也就是数组的位置不能够被复用,我们使用循环队列就可以解决这个问题。 ??按照上述策略我们就可以区别开来队列满和队列空的判断条件,只是此时数组大小为 \(5\),队列的实际大小为 \(4\),因为我们预留出来的一个空间。 数据结构 - 数组模拟非循环和循环队列(Java实现) 标签:span str 解决 推出 oop catch 溢出 boolean vpd 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zut-syp/p/13130210.html数组模拟非循环队列
思路分析
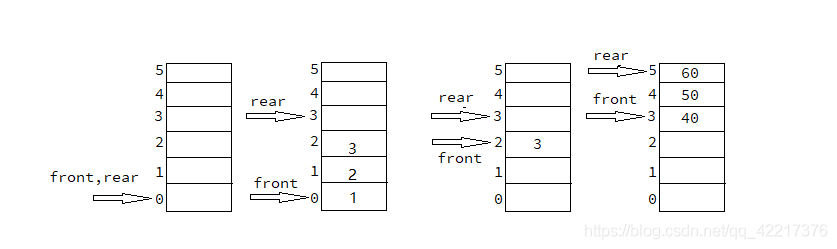
代码实现
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
//数组使用一次就不能使用,没有达到复用的效果
public class ArrayQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先进先出 FIFO
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(3);
char key = ‘ ‘;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据");
System.out.println("d(del):取出数据");
System.out.println("t(top):查看队头");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case ‘s‘:
queue.showQueue();
break;
case ‘e‘:
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
case ‘a‘:
System.out.print("请输入要添加的数字:");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.EnQueue(value);
break;
case ‘d‘:
try {
int result = queue.DeQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据为:%d\n", result);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case ‘t‘:
try {
int top = queue.Top();
System.out.printf("队头数据为:%d\n", top);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("退出成功");
}
}
//数组模拟队列
class ArrayQueue {
private int maxSize; //数组最大容量
private int front; //队尾
private int rear; //队头
private int[] array; //模拟队列
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
array = new int[maxSize];
front = 0;//front指向队头
rear = 0;//指向队尾的后一个
}
//判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == maxSize;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
//添加数据到队列
public void EnQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列已满,无法增加数据!");
return;
}
array[rear ++] = value;
}
//出队列
public int DeQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无法取数据");
}
int value = array[front ++];
return value;
}
//显示所有数据
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空,无法显示任何数据");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i 数组模拟循环队列
思路分析
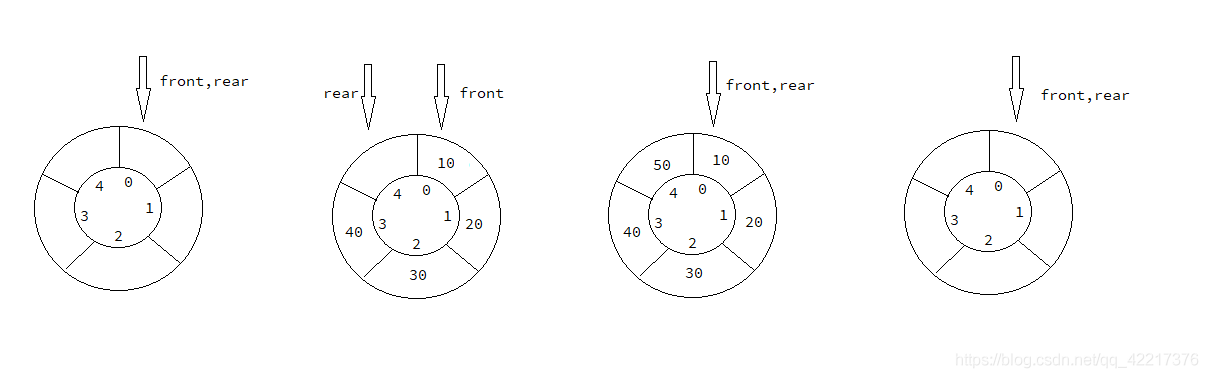 ??上面的图中我们可以发现,此时的队列的大小为 \(5\),无论是队列满还是队列为空的时候,判断的条件都是 \(front = rear\),此时我们使用的方法就是将这个循环队列预留出来一个空间,当这个环形队列中还剩一个空间时就表示这个队列已满,见下图。
??上面的图中我们可以发现,此时的队列的大小为 \(5\),无论是队列满还是队列为空的时候,判断的条件都是 \(front = rear\),此时我们使用的方法就是将这个循环队列预留出来一个空间,当这个环形队列中还剩一个空间时就表示这个队列已满,见下图。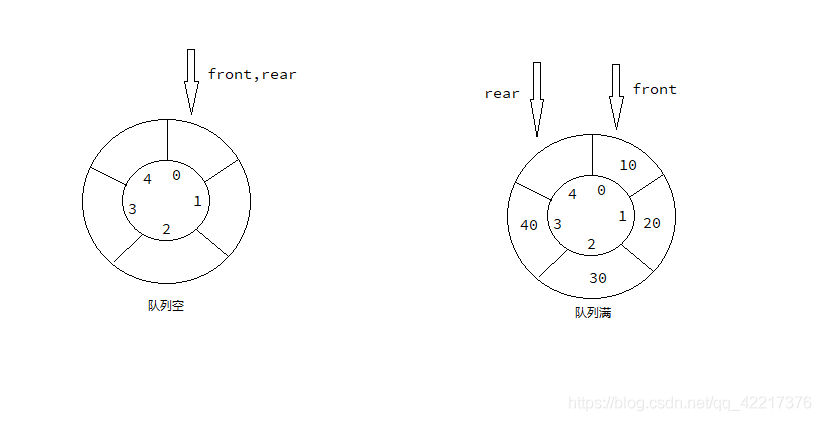
代码实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CircleQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先进先出 FIFO
CircleQueue queue = new CircleQueue(4);
char key = ‘ ‘;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据");
System.out.println("d(del):取出数据");
System.out.println("t(top):查看队头");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case ‘s‘:
queue.showQueue();
break;
case ‘e‘:
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
case ‘a‘:
System.out.print("请输入要添加的数字:");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.EnQueue(value);
break;
case ‘d‘:
try {
int result = queue.DeQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据为:%d\n", result);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case ‘t‘:
try {
int top = queue.Top();
System.out.printf("队头数据为:%d\n", top);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("退出成功");
}
}
//数组模拟队列
class CircleQueue {
private int maxSize; //数组最大容量
private int front; //队尾
private int rear; //队头
private int[] array; //模拟队列
public CircleQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
array = new int[maxSize];
front = 0;//front指向队头
rear = 0;//指向队尾的后一个
}
//判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
//添加数据到队列
public void EnQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列已满,无法增加数据!");
return;
}
array[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
//出队列
public int DeQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无法取数据");
}
int value = array[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
//显示所有数据
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空,无法显示任何数据");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i