密码引擎-加密API实现与测试 20181308邵壮
2021-05-15 17:27
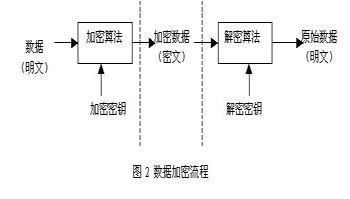
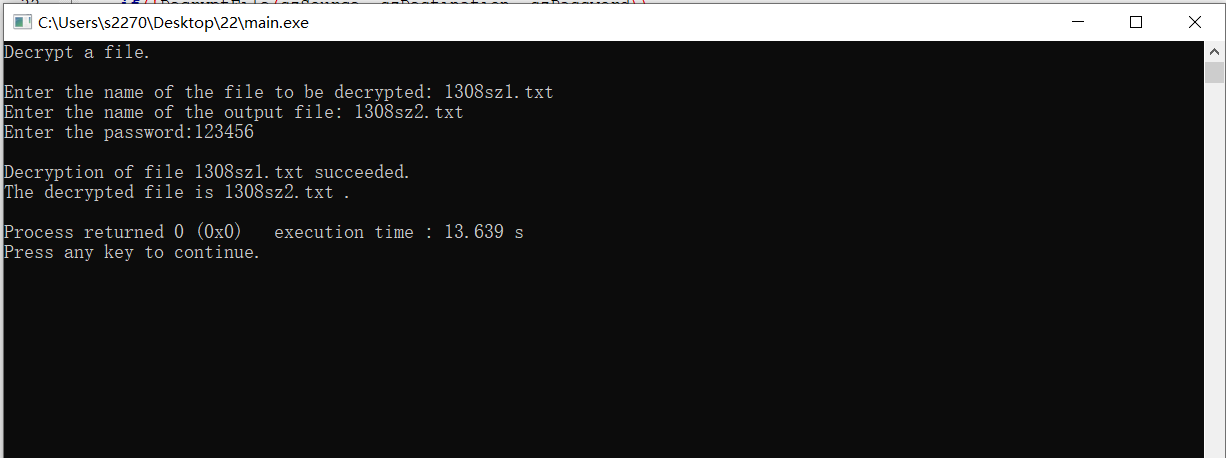
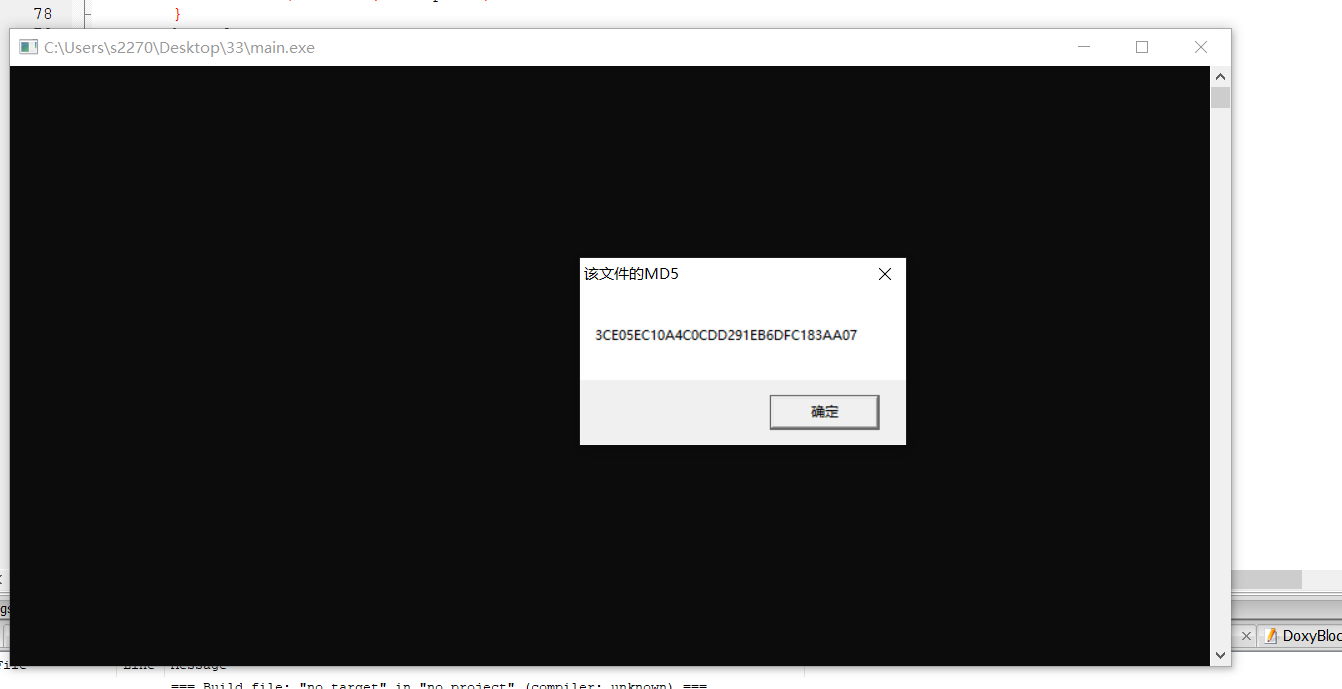
标签:算法 摘要 xpl code 数据文件 window 代码 etc explore 1、熟悉Windows CryptoAPI提供的常用函数接口。 2、掌握Windows CryptoAPI的使用。 3、利用Windows CryptoAPI设计和实现一个小型密码系统(如文件加密机),完成加解密、摘要运算、数字签名等功能。 1. 先编写一个加密的代码,使用Windows crypticAPI实现。 结果如图: 2.编写一个解密的代码,使用Windows crypticAPI实现。 3. 编写一个计算文件的代码,使用Windows crypticAPI实现文件的MD5计算。 用写好的代码测试123.dll,启动代码结果: 以下是代码共三个:分别是加密解密和计算MD5 加密 #include #define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0400 #define MY_ENCODING_TYPE (PKCS_7_ASN_ENCODING | X509_ASN_ENCODING) #define KEYLENGTH 0x00800000 void HandleError(char *s); #define ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM CALG_RC4 #define ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE 8 BOOL EncryptFile( PCHAR szSource, PCHAR szDestination, PCHAR szPassword); void main(void) {
CHAR szSource[100];
CHAR szDestination[100];
CHAR szPassword[100]; printf("Encrypt
a file. \n\n"); printf("Enter
the name of the file to be encrypted: "); scanf("%s",szSource); printf("Enter
the name of the output file: "); scanf("%s",szDestination); printf("Enter
the password:"); scanf("%s",szPassword); if(EncryptFile(szSource,
szDestination, szPassword)) { printf("Encryption
of the file %s was a success. \n", szSource); printf("The
encrypted data is in file %s.\n",szDestination); } else { HandleError("Error
encrypting file!"); }
} static BOOL EncryptFile( PCHAR
szSource, PCHAR
szDestination, PCHAR
szPassword) //-------------------------------------------------------------------- // Parameters passed are: // szSource, the name of the input, a
plaintext file. // szDestination, the name of the output, an
encrypted file to be // created. // szPassword, the password. { FILE
*hSource; FILE
*hDestination; HCRYPTPROV
hCryptProv; HCRYPTKEY
hKey; HCRYPTHASH
hHash; PBYTE
pbBuffer; DWORD
dwBlockLen; DWORD
dwBufferLen; DWORD
dwCount; if(hSource
= fopen(szSource,"rb")) { printf("The
source plaintext file, %s, is open. \n", szSource); } else {
HandleError("Error
opening source plaintext file!"); }
if(hDestination
= fopen(szDestination,"wb")) { printf("Destination
file %s is open. \n", szDestination); } else { HandleError("Error
opening destination ciphertext file!"); } if(CryptAcquireContext( &hCryptProv,
NULL, NULL,
PROV_RSA_FULL,
0)) { printf("A
cryptographic provider has been acquired. \n"); } else { if(CryptAcquireContext( &hCryptProv,
NULL,
NULL,
PROV_RSA_FULL,
CRYPT_NEWKEYSET))//创建密钥容器 { //创建密钥容器成功,并得到CSP句柄 printf("A
new key container has been created.\n"); } else { HandleError("Could
not create a new key container.\n"); } } if(CryptCreateHash( hCryptProv,
CALG_MD5,
0,
0,
&hHash)) {
printf("A hash object has been created. \n"); }
else {
HandleError("Error
during CryptCreateHash!\n");
} if(CryptHashData( hHash,
(BYTE
*)szPassword, strlen(szPassword),
0)) { printf("The
password has been added to the hash. \n"); } else { HandleError("Error
during CryptHashData. \n"); } if(CryptDeriveKey( hCryptProv,
ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM,
hHash,
KEYLENGTH,
&hKey)) { printf("An
encryption key is derived from the password hash. \n"); } else { HandleError("Error
during CryptDeriveKey!\n"); } CryptDestroyHash(hHash);
hHash
= NULL; dwBlockLen
= 1000 - 1000 % ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE; if(ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE
> 1) dwBufferLen
= dwBlockLen + ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE; else
dwBufferLen
= dwBlockLen; if(pbBuffer
= (BYTE *)malloc(dwBufferLen)) { printf("Memory
has been allocated for the buffer. \n"); } else {
HandleError("Out
of memory. \n"); } do
{
dwCount
= fread(pbBuffer, 1, dwBlockLen, hSource); if(ferror(hSource)) {
HandleError("Error
reading plaintext!\n"); } if(!CryptEncrypt( hKey, 0, feof(hSource), 0, //保留 pbBuffer, //输入被加密数据,输出加密后的数据 &dwCount, //输入被加密数据实际长度,输出加密后数据长度 dwBufferLen)) //pbBuffer的大小。 {
HandleError("Error
during CryptEncrypt. \n"); }
fwrite(pbBuffer,
1, dwCount, hDestination); if(ferror(hDestination)) {
HandleError("Error
writing ciphertext."); } }
while(!feof(hSource));
if(hSource)
fclose(hSource);
if(hDestination)
fclose(hDestination);
if(pbBuffer)
free(pbBuffer);
if(hKey)
CryptDestroyKey(hKey);
if(hHash)
CryptDestroyHash(hHash);
if(hCryptProv)
CryptReleaseContext(hCryptProv,
0); return(TRUE);
} void HandleError(char *s) {
fprintf(stderr,"An error occurred in running the program.
\n");
fprintf(stderr,"%s\n",s);
fprintf(stderr, "Error number %x.\n", GetLastError());
fprintf(stderr, "Program terminating. \n");
exit(1); } 解密 #include #define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0400 #define MY_ENCODING_TYPE (PKCS_7_ASN_ENCODING | X509_ASN_ENCODING) #define KEYLENGTH 0x00800000 void HandleError(char *s); //-------------------------------------------------------------------- #define ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM CALG_RC4 #define ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE 8 BOOL DecryptFile( PCHAR szSource, PCHAR szDestination, PCHAR szPassword); void main(void) { CHAR
szSource[100]; CHAR
szDestination[100]; CHAR
szPassword[100]; printf("Decrypt
a file. \n\n"); printf("Enter
the name of the file to be decrypted: "); scanf("%s",szSource); printf("Enter
the name of the output file: "); scanf("%s",szDestination); printf("Enter
the password:"); scanf("%s",szPassword); if(!DecryptFile(szSource,
szDestination, szPassword)) { printf("\nError
decrypting file. \n"); } else {
printf("\nDecryption
of file %s succeeded. \n", szSource); printf("The
decrypted file is %s .\n",szDestination); } } static BOOL DecryptFile( PCHAR
szSource, PCHAR
szDestination, PCHAR
szPassword) { FILE
*hSource; FILE
*hDestination; HCRYPTPROV
hCryptProv; HCRYPTKEY
hKey; HCRYPTHASH
hHash; PBYTE
pbBuffer; DWORD
dwBlockLen; DWORD
dwBufferLen; DWORD
dwCount; BOOL
status = FALSE; if(!(hSource
= fopen(szSource,"rb"))) { HandleError("Error
opening ciphertext file!"); } if(!(hDestination
= fopen(szDestination,"wb"))) { HandleError("Error
opening plaintext file!"); }
if(!CryptAcquireContext( &hCryptProv,
NULL,
NULL,
PROV_RSA_FULL,
0)) { HandleError("Error
during CryptAcquireContext!"); } if(!CryptCreateHash( hCryptProv,
CALG_MD5,
0,
0,
&hHash)) { HandleError("Error
during CryptCreateHash!"); } if(!CryptHashData( hHash,
(BYTE
*)szPassword, strlen(szPassword),
0))
{ HandleError("Error
during CryptHashData!"); } if(!CryptDeriveKey( hCryptProv,
ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM,
hHash,
KEYLENGTH,
&hKey)) {
HandleError("Error
during CryptDeriveKey!"); } CryptDestroyHash(hHash);
hHash
= 0; dwBlockLen
= 1000 - 1000 % ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE; dwBufferLen
= dwBlockLen; if(!(pbBuffer
= (BYTE *)malloc(dwBufferLen))) { HandleError("Out
of memory!\n"); } do
{ dwCount
= fread( pbBuffer,
1,
dwBlockLen,
hSource);
if(ferror(hSource)) { HandleError("Error
reading ciphertext!"); } if(!CryptDecrypt( hKey,
0,
feof(hSource),
0,
pbBuffer,
&dwCount)) { HandleError("Error
during CryptDecrypt!"); } fwrite( pbBuffer,
1,
dwCount,
hDestination);
if(ferror(hDestination)) { HandleError("Error
writing plaintext!"); } }
while(!feof(hSource)); status
= TRUE; if(hSource)
fclose(hSource);
if(hDestination)
fclose(hDestination);
if(pbBuffer)
free(pbBuffer);
if(hKey)
CryptDestroyKey(hKey);
if(hHash)
CryptDestroyHash(hHash);
if(hCryptProv)
CryptReleaseContext(hCryptProv,
0); return
status; } void HandleError(char *s) {
fprintf(stderr,"An error occurred in running the program.
\n");
fprintf(stderr,"%s\n",s);
fprintf(stderr, "Error number %x.\n", GetLastError());
fprintf(stderr, "Program terminating. \n");
exit(1); } // End of HandleError MD5 #include #define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0400 #define CHECK_NULL_RET(bCondition) if
(!bCondition) goto Exit0 #define BUFSIZE 1024 #define MD5LEN 16 BOOL GetContentMD5(
BYTE *pszFilePath,
BOOL bFile,
BOOL bUpperCase,
TCHAR *pszResult,
DWORD &dwStatus) {
BOOL bResult = FALSE;
HCRYPTPROV hProv = 0;
HCRYPTHASH hHash = 0;
HANDLE hFile = NULL;
BYTE rgbFile[BUFSIZE];
DWORD cbRead = 0;
BYTE rgbHash[MD5LEN];
DWORD cbHash = 0;
CHAR rgbDigitsL[] = "0123456789abcdef";
CHAR rgbDigitsU[] = "0123456789ABCDEF";
CHAR *rgbDigits = bUpperCase ? rgbDigitsU : rgbDigitsL;
TCHAR szResult[MD5LEN*2+1] = {0};
dwStatus = 0;
bResult = CryptAcquireContext(&hProv,
NULL,
NULL,
PROV_RSA_FULL,
CRYPT_VERIFYCONTEXT);
CHECK_NULL_RET(bResult);
bResult = CryptCreateHash(hProv, CALG_MD5, 0, 0, &hHash);
CHECK_NULL_RET(bResult);
if (bFile) {
hFile = CreateFile((TCHAR *)pszFilePath,
GENERIC_READ,
FILE_SHARE_READ,
NULL,
OPEN_EXISTING,
FILE_FLAG_SEQUENTIAL_SCAN,
NULL);
CHECK_NULL_RET(!(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE == hFile));
while (bResult = ReadFile(hFile, rgbFile, BUFSIZE,
&cbRead, NULL))
{
if (0 == cbRead)
{ break;
}
bResult = CryptHashData(hHash, rgbFile, cbRead, 0);
CHECK_NULL_RET(bResult);
} }
else {
bResult = CryptHashData(hHash, pszFilePath, strlen((CHAR *)pszFilePath),
0);
CHECK_NULL_RET(bResult); }
cbHash = MD5LEN;
if (bResult = CryptGetHashParam(hHash, HP_HASHVAL, rgbHash, &cbHash,
0)) {
TCHAR szTmpBuff[3] ;
for (DWORD i = 0; i
{
sprintf (szTmpBuff,
TEXT("%c%c"), rgbDigits[rgbHash[i]>>4], rgbDigits[rgbHash[i] &
0xf]);
lstrcat(szResult, szTmpBuff);
}
bResult = TRUE; } Exit0:
dwStatus = GetLastError();
CryptDestroyHash(hHash);
CryptReleaseContext(hProv, 0);
CloseHandle(hFile);
lstrcpy(pszResult, szResult);
return bResult; } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
DWORD dwStatus = 0;
TCHAR szResult[MD5LEN*2+1] = {0};
TCHAR szFilePath[] = TEXT("C:\\123.dll");
CHAR szContent[] = "explorer.exe";
GetContentMD5((BYTE *)szFilePath,
TRUE, TRUE, szResult, dwStatus);
MessageBox(NULL, szResult, TEXT("该文件的MD5"), MB_OK);
return 0; } 这次实验难度很大,过程中遇到了很多的问题。感觉从一开始就无从下手,所以只能先去上网找资料和相关博客等学习。在看了很多的资料和相关解答之后虽然还是一头雾水,但是还算是有了不少的了解。在找到了相关代码之后,自己做了一些修改,也算是完成了这次的任务。也算是对Windows CryptoAPI有了一个初步的了解了。 利用Windows CryptoAPI进行加解密的一般步骤是怎样的? CryptoAPI使用两种密钥:会话密钥与公共/私人密钥对。会话密钥使用相同的加密和解密密钥,这种算法较快,但必须保证密钥的安全传递。公共/私人密钥对使用一个公共密钥和一个私人密钥,私人密钥只有专人才能使用,公共密钥可以广泛传播。如果密钥对中的一个用于加密,另一个一定用于解密。公共/私人密钥对算法很慢,一般只用于加密小批数据,例如用于加密会话密钥。 CryptoAPI支持两种基本的编码方法:流式编码和块编码。流式编码在明码文本的每一位上创建编码位,速度较快,但安全性较低。块编码在一个完整的块上(一般为64位)上工作,需要使用填充的方法对要编码的数据进行舍入,以组成多个完整的块。这种算法速度较慢,但更安全。 加密: 1、打开源文件 2、取得密钥容器(CSP)句柄 3、根据用户输入的密码创建一个会话密钥(即对称密钥,用于对原文件加密) 4、加密数据文件 5、清理工作,如释放Buffer空间、密钥句柄、CSP句柄等。 解密: 1、打开源文件 2、取得密钥容器(CSP)句柄 3、根据用户输入的密码创建一个会话密钥(即对称密钥,用于对原文件解密, 这里要求用户输入的密码与加密时输入的密码相同。在实际应用中,这个所谓用户输入的“密码”其实只是一个产生密钥的种子,一旦产生完会话密钥,则用户完全
可以忘记当初输入的“密码”,接收方可以使用传过来的密钥直接对加密文件进行解密,而不用再重复一次“生成密钥”的过程。) 4、解密数据文件 5、清理工作,如释放Buffer空间、密钥句柄、CSP句柄等。 密码引擎-加密API实现与测试 20181308邵壮 标签:算法 摘要 xpl code 数据文件 window 代码 etc explore 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/King-King/p/14701748.html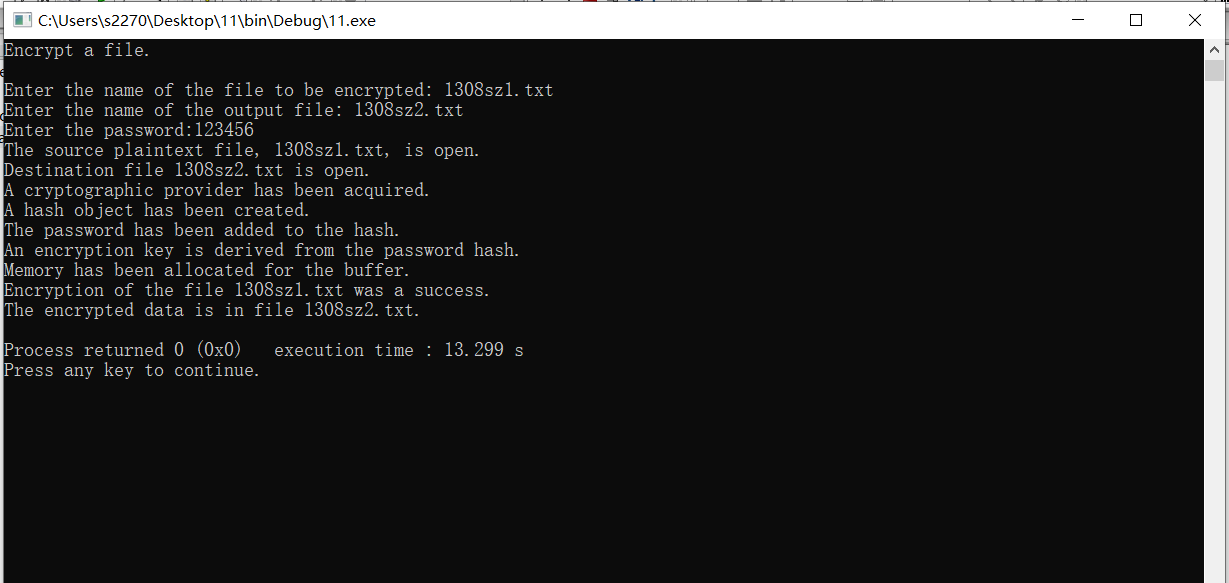
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include