【图像识别】基于模板匹配算法实现身份证号码识别matlab源码
2021-05-31 16:01
标签:aop starting remove variable work break 搜索 ado open 本文主要介绍几种基于灰度的图像匹配算法:平均绝对差算法(MAD)、绝对误差和算法(SAD)、误差平方和算法(SSD)、平均误差平方和算法(MSD)、归一化积相关算法(NCC)、序贯相似性检测算法(SSDA)、hadamard变换算法(SATD)。下面依次对其进行讲解。 平均绝对差算法(Mean Absolute Differences,简称MAD算法),它是Leese在1971年提出的一种匹配算法。是模式识别中常用方法,该算法的思想简单,具有较高的匹配精度,广泛用于图像匹配。 设S(x,y)是大小为mxn的搜索图像,T(x,y)是MxN的模板图像,分别如下图(a)、(b)所示,我们的目的是:在(a)中找到与(b)匹配的区域(黄框所示)。 在搜索图S中,以(i,j)为左上角,取MxN大小的子图,计算其与模板的相似度;遍历整个搜索图,在所有能够取到的子图中,找到与模板图最相似的子图作为最终匹配结果。 MAD算法的相似性测度公式如下。显然,平均绝对差D(i,j)越小,表明越相似,故只需找到最小的D(i,j)即可确定能匹配的子图位置: 其中: ①思路简单,容易理解(子图与模板图对应位置上,灰度值之差的绝对值总和,再求平均,实质:是计算的是子图与模板图的L1距离的平均值)。 ②运算过程简单,匹配精度高。 ①运算量偏大。 ②对噪声非常敏感。 —————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— 绝对误差和算法(Sum of Absolute Differences,简称SAD算法)。实际上,SAD算法与MAD算法思想几乎是完全一致,只是其相似度测量公式有一点改动(计算的是子图与模板图的L1距离),这里不再赘述。 完整代码添加QQ1575304183 【图像识别】基于模板匹配算法实现身份证号码识别matlab源码 标签:aop starting remove variable work break 搜索 ado open 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ttmatlab/p/14743283.html简介:
MAD算法
介绍
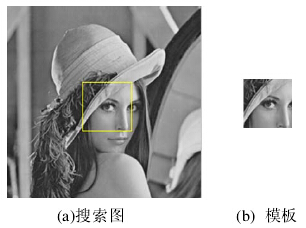
?
算法思路
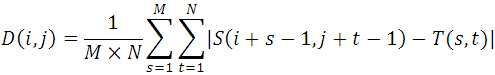
?
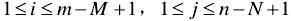
?
算法评价:
优点:
缺点:
SAD算法
介绍
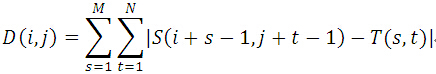
?
function varargout = homework2(varargin)
% HOMEWORK2 M-file for homework2.fig
% HOMEWORK2, by itself, creates a new HOMEWORK2 or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = HOMEWORK2 returns the handle to a new HOMEWORK2 or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% HOMEWORK2(‘CALLBACK‘,hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in HOMEWORK2.M with the given input arguments.
%
% HOMEWORK2(‘Property‘,‘Value‘,...) creates a new HOMEWORK2 or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before homework2_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to homework2_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE‘s Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help homework2
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 20-May-2013 21:21:00
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct(‘gui_Name‘, mfilename, ...
‘gui_Singleton‘, gui_Singleton, ...
‘gui_OpeningFcn‘, @homework2_OpeningFcn, ...
‘gui_OutputFcn‘, @homework2_OutputFcn, ...
‘gui_LayoutFcn‘, [] , ...
‘gui_Callback‘, []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before homework2 is made visible.
function homework2_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to homework2 (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for homework2
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes homework2 wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = homework2_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
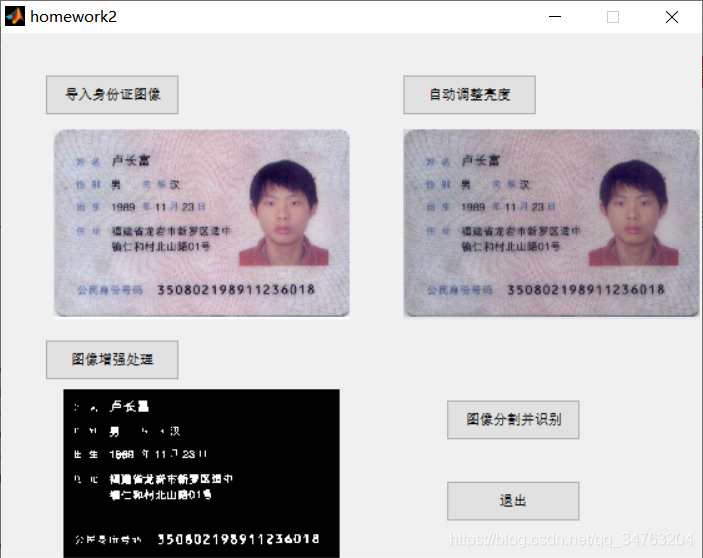
%载入原始身份证图像的回调函数
% --- Executes on button press in OriginalImg.
function OriginalImg_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to OriginalImg (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[FileName,PathName] = uigetfile(‘*.jpg‘,‘Select an image‘);
if PathName~=0
str = [PathName,FileName];
T=imread(str);
axes(handles.Img);
imshow(T);
end
%图像自动亮度调整的回调函数
% --- Executes on button press in autoLight.
function autoLight_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to autoLight (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
axes(handles.Img);
T=getimage;
low_out=0.2; high_out=0.9;
gamma=1.518;
hsv=rgb2hsv(T);
I=hsv(:,:,3);
minL=min(min(I));
maxL=max(max(I));
J=imadjust(I,[minL;maxL],[low_out;high_out],gamma);
hsv(:,:,3)=J;
rgb_atuoI=hsv2rgb(hsv);
axes(handles.Light);
imshow(rgb_atuoI);
%图像二值化的回调函数
% --- Executes on button press in DIP.
function DIP_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to DIP (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
axes(handles.Img);
I=getimage;
[m,n,r]=size(I);%图像的像素为width*height
%%%%%蓝色字体变黑
myI=double(I);
for i=1:m
for j=1:n
if((myI(i,j,1)>=15)&&(myI(i,j,1)=90))&&((myI(i,j,3)=135))) % 蓝色RGB的灰度范围
I(i,j,1)=40; %红色分量
I(i,j,2)=40; %绿色分量
I(i,j,3)=40; %蓝色分量
end
end
end
%figure, imshow(I);title(‘变色后的图像‘);
width=round(0.9*n);height=round(0.87*m);
rx=round(0.05*n);cy=round(0.075*m);
I=subim(I,height,width,rx,cy);
%figure,imshow(I);
if sum(size(I)>0)==3 %倘若是彩色图--2维*3,先转换成灰度图
I=rgb2gray(I);
end
%figure,imhist(I);
x=3;%行数分为x部分
y=1;%列数分为y部分
BW=erzhihua(I,x,y);
[n m l]=size(BW);%图像的像素为m*n
c = [0.65*m 0.65*m m m];
r = [0 0.85*n 0.85*n 0];
BW = roifill(BW,c,r);
BW=imadjust(BW);%使用imadjust函数对图像进行增强对比度
% Convert to BW
threshold = graythresh(BW);
BW =~im2bw(BW,0.6*threshold);
[image_h image_w]=size(BW);
% Remove all object containing fewer than (imagen/80) pixels
BW = bwareaopen(BW,floor(image_w/80));
% 滤波
%h=fspecial(‘average‘,1);
%BW=im2bw(round(filter2(h,BW)));
%imwrite(d,‘4.均值滤波后.jpg‘);
axes(handles.Binary);
imshow(BW);
%图像分割与识别按钮的回调函数
% --- Executes on button press in OCR.
function OCR_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to OCR (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
axes(handles.Binary);
imagen = getimage;
[image_h image_w]=size(imagen);
%figure;imshow(imagen);title(‘INPUT IMAGE‘)
% Convert to gray scale
if size(imagen,3)==3 %RGB image
imagen=rgb2gray(imagen);
end
%Storage matrix word from image
word=[ ];
re=imagen;
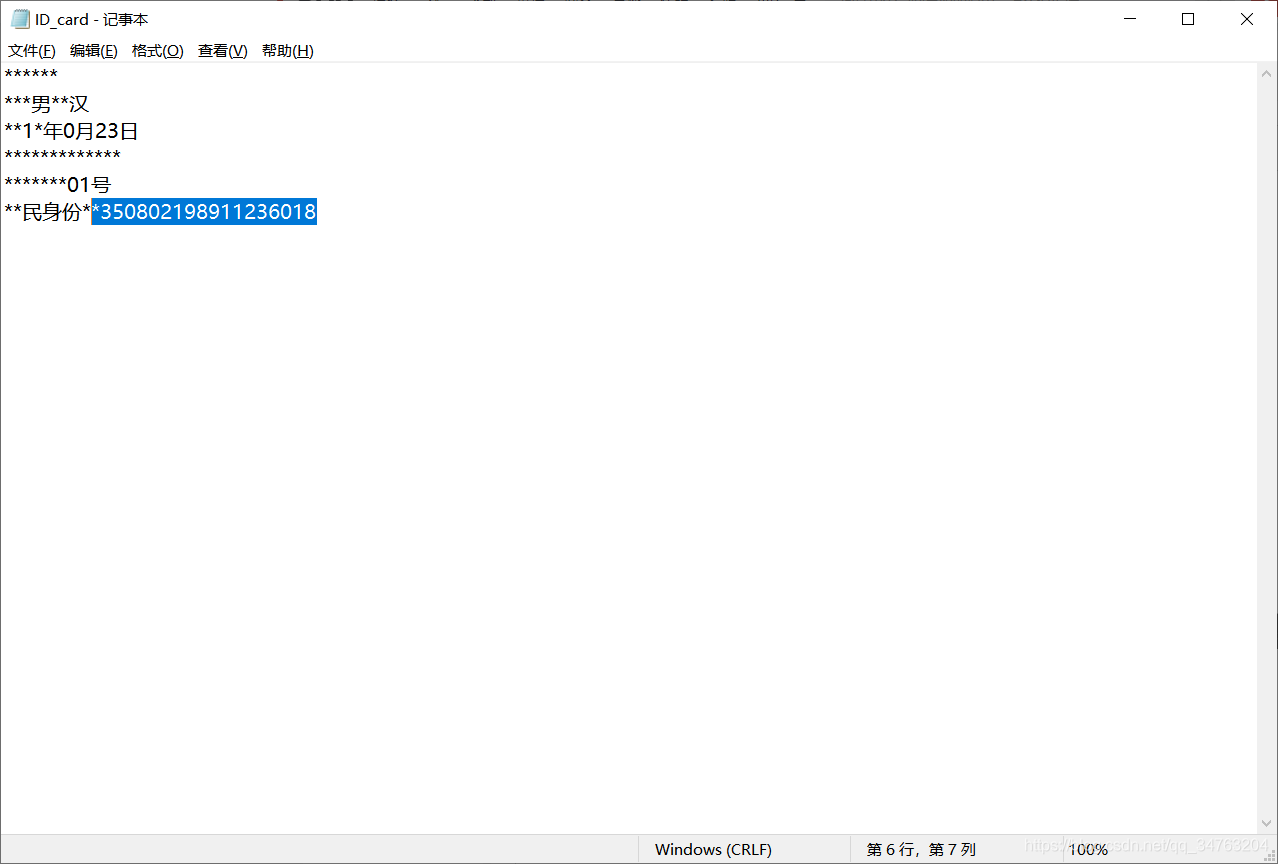
%Opens text.txt as file for write
fid = fopen(‘ID_card.txt‘, ‘wt‘);
% Load templates
load templates
global templates
% Compute the number of letters in template file
num_letras=size(templates,2);
figure;
plot_flag=1;
while 1
%Fcn ‘lines‘ separate lines in text
[fl re]=lines(re);
imgn=fl;
[line_h line_w]=size(fl);%记录下切割出来的一行字符的长宽
%Uncomment line below to see lines one by one
% imshow(fl);pause(1)
%-----------------------------------------------------------------
% Label and count connected components
[L Ne] = bwlabel(imgn);
n=1;%记录循环次数
while(n=-(image_w/pw)&&Owidth=-(line_h*0.3)&&Oheigth=0.8)&&(Uradio0)||(Oheigth>0))%两连通域重叠
elseif(flag==1)&&((Owidth>0))%两连通域重叠
if(((Uradio>=0.78)&&(Uradio=0.4*min(Square0,Square1)&&(Uwidth
?
?
文章标题:【图像识别】基于模板匹配算法实现身份证号码识别matlab源码
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/89780.html