WPF 折线/坐标点绘制 曲线抽稀 (Douglas-Peucker)道格拉斯-普克算法
标签:活着 5* index rstp 差距 等于 数据保存 jpg color
这个算法经常用,例如GIS,数据保存,数据绘制都会用到。
算法是1973提出的,久经考验的算法,具体详情可以参考百度。
算法比较简单,大意是:
① 给出一个限定值表示距离
② 点集合活着坐标集合的首尾自定相连接成为直线,并会记录首尾两点到输出集合
③ 记录后寻找集合中距离这个直线最远的点,当这个点的距离超过限定值时,记录这个点,并由此将集合分为两段,首到点,点到尾
④ 对每个线段重复步骤②,步骤③,直至结束
也可以参考其他网友给出的算法推导.
其中 找出最远点的点的算法,可以利用 三个点形成的面积,也就是三角形的面积。
其中求出点到线的距离,也就是三角形的高。
我们可以认为首尾连接的线是底部边,我们有底部边的起点和终点坐标,可以利用向量公式,尾坐标减去首坐标,求出向量坐标后,再利用向量的求模公式求出长度。
最后三角形面积除以底的长度乘与2就等于高度了。
截图
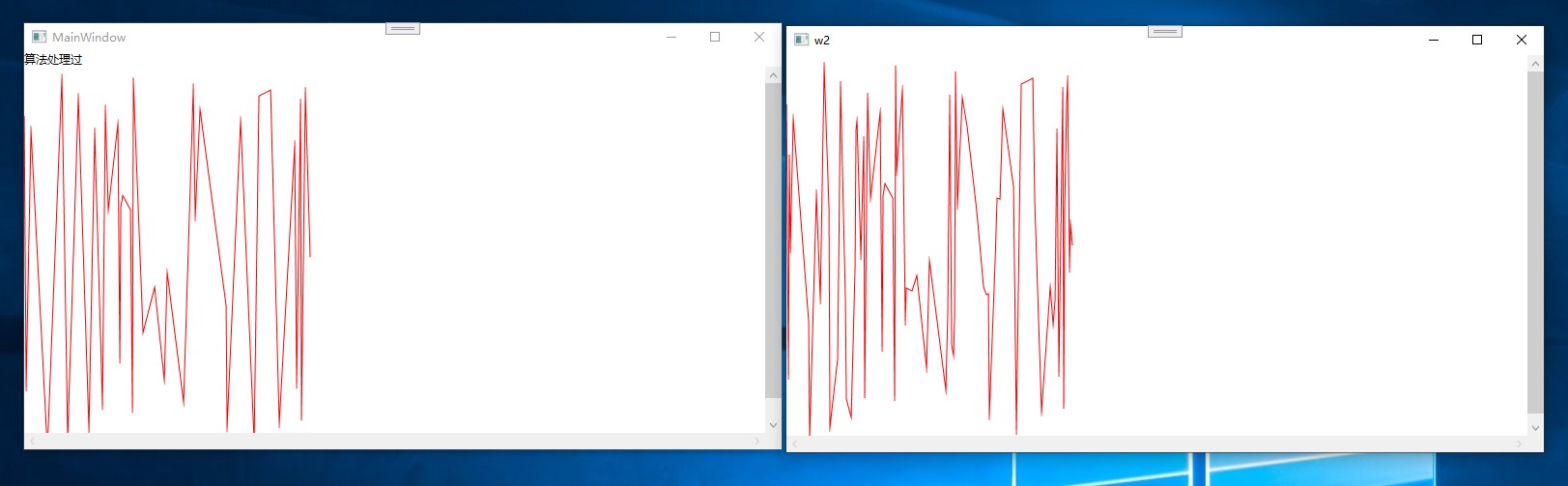
代码是现成的,虽然实现也不困难, 偷懒....
public class Douglas_Peucker
{
///
/// Douglas-Peucker算法
///
/// 坐标点集合
/// 限定值
///
public static List DouglasPeuckerReduction
(List Points, Double Tolerance)
{
if (Points == null || Points.Count 3)
return Points;
Int32 firstPoint = 0;
Int32 lastPoint = Points.Count - 1;
List pointIndexsToKeep = new List();
//默认添加首尾两点
pointIndexsToKeep.Add(firstPoint);
pointIndexsToKeep.Add(lastPoint);
//首尾两点不能相同
while (Points[firstPoint].Equals(Points[lastPoint]))
{
lastPoint--;
}
//递归计算
DouglasPeuckerReduction(Points, firstPoint, lastPoint,
Tolerance, ref pointIndexsToKeep);
//返回集合
List returnPoints = new List();
pointIndexsToKeep.Sort();
foreach (Int32 index in pointIndexsToKeep)
{
returnPoints.Add(Points[index]);
}
return returnPoints;
}
///
/// 递归计算每个点到线段的长度,并分段递归重复计算
///
/// 点集合
/// 首点
/// 尾点
/// 限定值
/// 点集合下标
private static void DouglasPeuckerReduction(List
points, Int32 firstPoint, Int32 lastPoint, Double tolerance,
ref List pointIndexsToKeep)
{
Double maxDistance = 0;
Int32 indexFarthest = 0;
//遍历每个点
for (Int32 index = firstPoint; index )
{
Double distance = PerpendicularDistance
(points[firstPoint], points[lastPoint], points[index]);
//只寻找线段上最长的点
if (distance > maxDistance)
{
//替换值
maxDistance = distance;
//记录下标
indexFarthest = index;
}
}
//确定最大值超过限定值且不为首点
if (maxDistance > tolerance && indexFarthest != 0)
{
//记录最大距离的点的下标
pointIndexsToKeep.Add(indexFarthest);
//分段计算 Startpoint-MaxDistance
DouglasPeuckerReduction(points, firstPoint,
indexFarthest, tolerance, ref pointIndexsToKeep);
//分段计算 MaxDistance-Lastpoint
DouglasPeuckerReduction(points, indexFarthest,
lastPoint, tolerance, ref pointIndexsToKeep);
}
}
///
/// 求出点到两点的距离
///
/// 线段的起点
/// 线段的终点
/// 计算的点
///
public static Double PerpendicularDistance
(Point Point1, Point Point2, Point Point)
{
//Area = |(1/2)(x1y2 + x2y3 + x3y1 - x2y1 - x3y2 - x1y3)| *Area of triangle
//Base = v((x1-x2)2+(x1-x2)2) *Base of Triangle*
//Area = .5*Base*H *Solve for height
//Height = Area/.5/Base
//求面积
Double area = Math.Abs(.5 * (Point1.X * Point2.Y + Point2.X *
Point.Y + Point.X * Point1.Y - Point2.X * Point1.Y - Point.X *
Point2.Y - Point1.X * Point.Y));
//求首尾两点的长度
Double bottom = Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(Point1.X - Point2.X, 2) +
Math.Pow(Point1.Y - Point2.Y, 2));
//三角形面积除以底*2=高
//三角形面积除以高*2=底
Double height = area / bottom * 2;
return height;
//Another option
//Double A = Point.X - Point1.X;
//Double B = Point.Y - Point1.Y;
//Double C = Point2.X - Point1.X;
//Double D = Point2.Y - Point1.Y;
//Double dot = A * C + B * D;
//Double len_sq = C * C + D * D;
//Double param = dot / len_sq;
//Double xx, yy;
//if (param //{
// xx = Point1.X;
// yy = Point1.Y;
//}
//else if (param > 1)
//{
// xx = Point2.X;
// yy = Point2.Y;
//}
//else
//{
// xx = Point1.X + param * C;
// yy = Point1.Y + param * D;
//}
//Double d = DistanceBetweenOn2DPlane(Point, new Point(xx, yy));
}
}
使用这个算法后,能够将点减少很多,在视觉上差距不大,适用于很多点的时候,绘制困难,通过这个算法减少点的数量.
WPF 折线/坐标点绘制 曲线抽稀 (Douglas-Peucker)道格拉斯-普克算法
标签:活着 5* index rstp 差距 等于 数据保存 jpg color
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/T-ARF/p/14616343.html
评论
