Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:3. 线性关系| 时间线| 热图
2021-06-17 04:03
标签:rap 差值 参数 bar subject 可视化 ati 图片 stat lmplot() tsplot() / heatmap() Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:3. 线性关系| 时间线| 热图 标签:rap 差值 参数 bar subject 可视化 ati 图片 stat 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/shengyang17/p/9710430.html1. 线性关系数据可视化
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
% matplotlib inline
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
sns.set_context("paper")
# 设置风格、尺度
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(‘ignore‘)
# 不发出警告
# 基本用法
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
print(tips.head())
# 加载数据
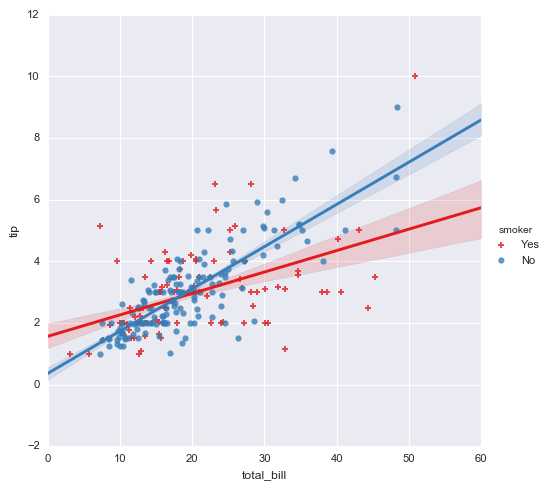
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", hue = ‘smoker‘,data=tips,palette="Set1",
ci = 70, # 误差值
size = 5, # 图表大小
markers = [‘+‘,‘o‘], # 点样式
)
# 拆分多个表格
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", col="smoker", data=tips)
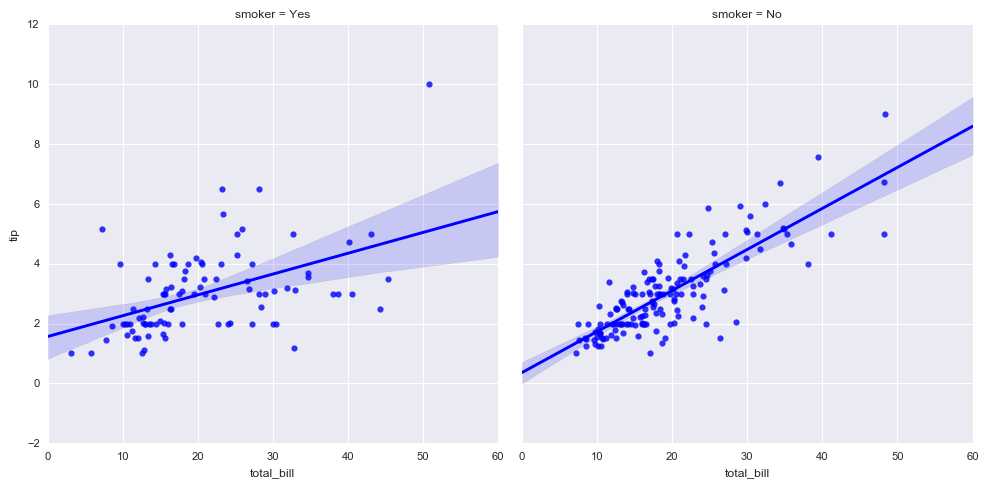
# 多图表1
sns.lmplot(x="size", y="total_bill", hue="day", col="day",data=tips,
aspect=0.6, # 长宽比
x_jitter=.30, # 给x或者y轴随机增加噪音点
col_wrap=4, # 每行的列数
)
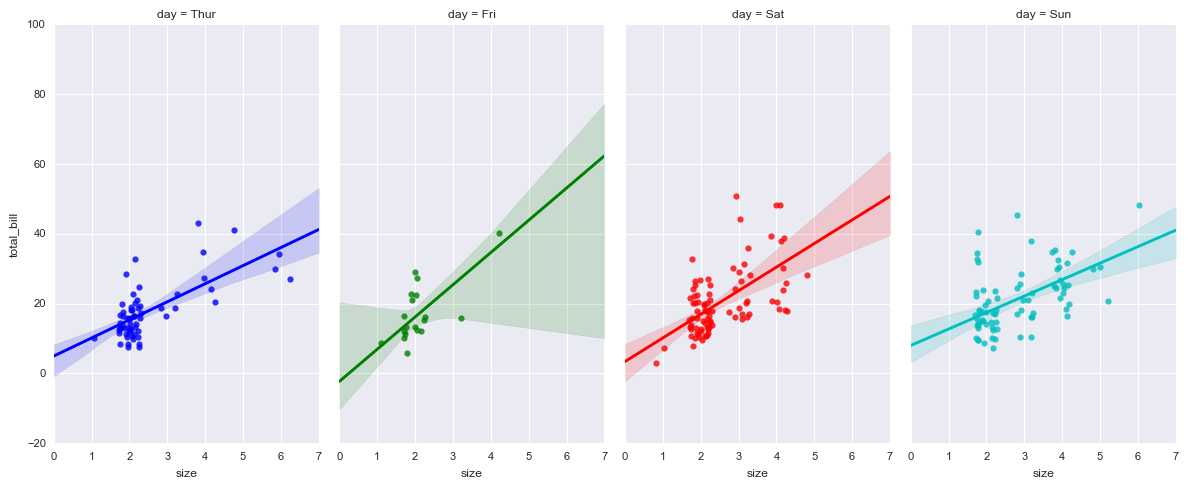
# 多图表2
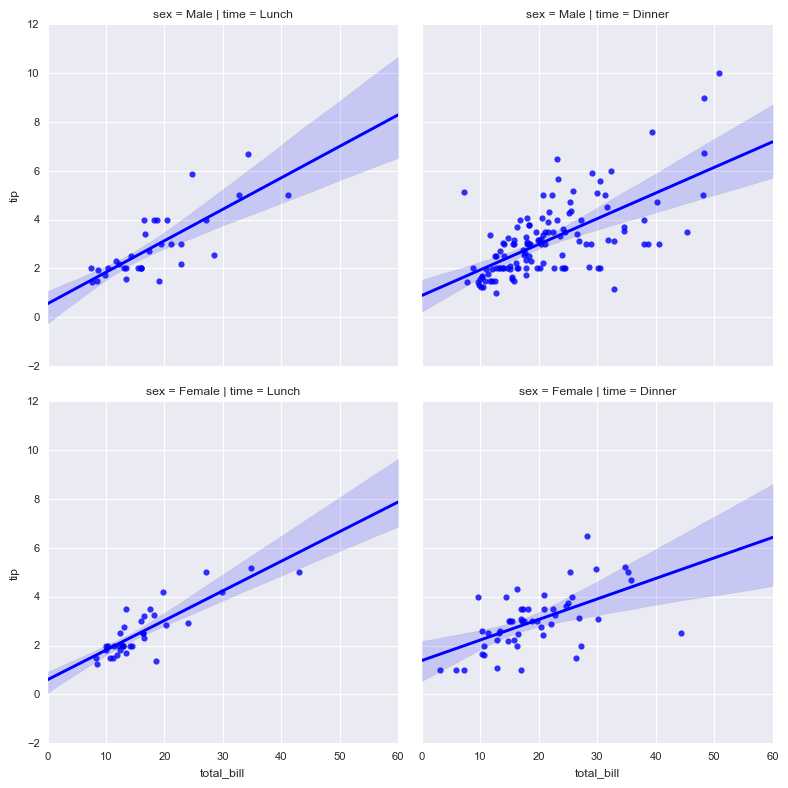
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", row="sex", col="time",data=tips, size=4)
# 行为sex字段,列为time字段
# x轴total_bill, y轴tip
# 非线性回归
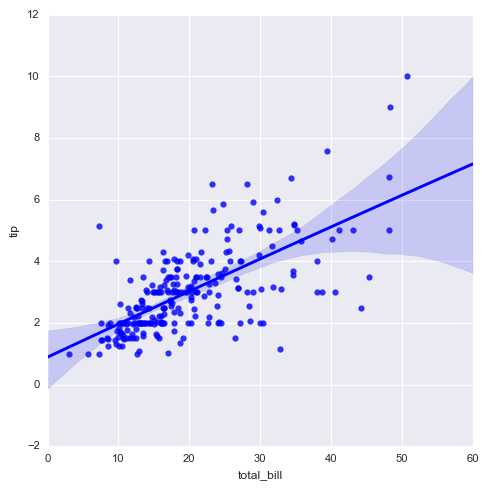
sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip",data=tips,
order = 2)
2. 时间线图表、热图
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
% matplotlib inline
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
sns.set_context("paper")
# 设置风格、尺度
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(‘ignore‘)
# 不发出警告
# 1、时间线图表 - tsplot()
# 简单示例
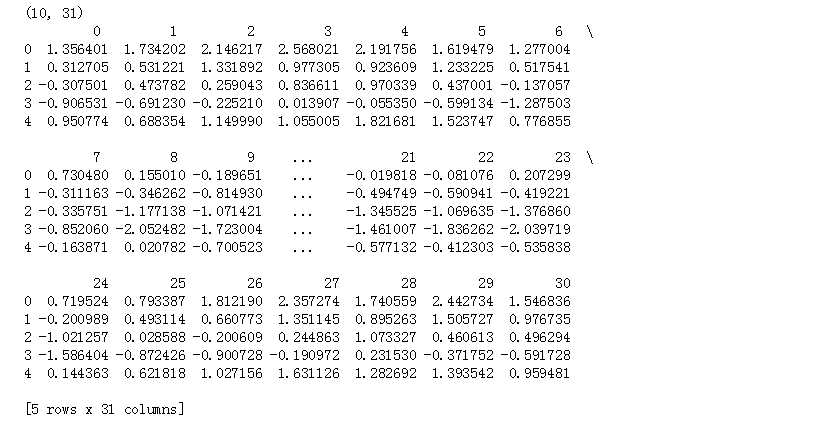
x = np.linspace(0, 15, 31)
data = np.sin(x) + np.random.rand(10, 31) + np.random.randn(10, 1)
print(data.shape)
print(pd.DataFrame(data).head())
# 创建数
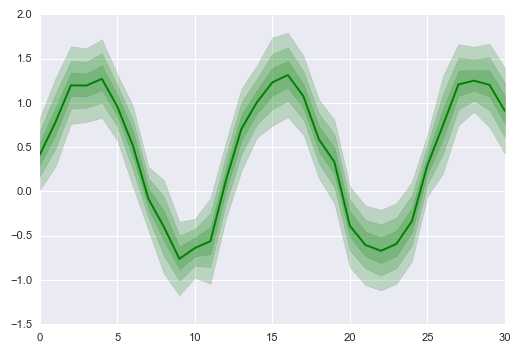
sns.tsplot(data=data,
err_style="ci_band", # 误差数据风格,可选:ci_band, ci_bars, boot_traces, boot_kde, unit_traces, unit_points
interpolate=True, # 是否连线
ci = [40,70,90], # 设置误差区间
color = ‘g‘ # 设置颜色
)
# 1、时间线图表 - tsplot()
# 简单示例
sns.tsplot(data=data, err_style="boot_traces",
n_boot=300 # 迭代次数
)
# 1、时间线图表 - tsplot()
# 参数设置
gammas = sns.load_dataset("gammas")
print(gammas.head())
print(‘数据量为:%i条‘ % len(gammas))
print(‘timepoint为0.0时的数据量为:%i条‘ % len(gammas[gammas[‘timepoint‘] == 0]))
print(‘timepoint共有%i个唯一值‘ % len(gammas[‘timepoint‘].value_counts()))
# print(gammas[‘timepoint‘].value_counts()) # 查看唯一值具体信息
# 导入数据
sns.tsplot(time="timepoint", # 时间数据,x轴
value="BOLD signal", # y轴value
unit="subject", #
condition="ROI", # 分类
data=gammas)
# gammas[[‘ROI‘, ‘subject‘]]

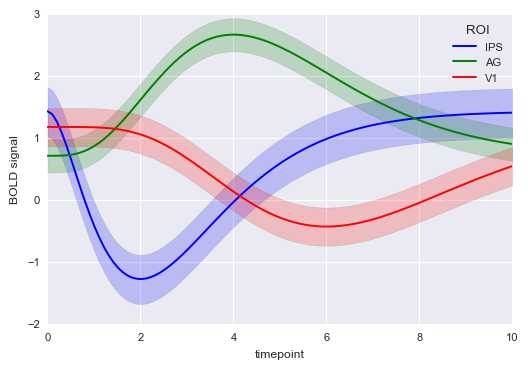
# 2、热图 - heatmap()
# 简单示例
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,12))
# 创建数据 - 10*12图表
sns.heatmap(df, # 加载数据
vmin=0, vmax=1 # 设置图例最大最小值
)
# 2、热图 - heatmap()
# 参数设置
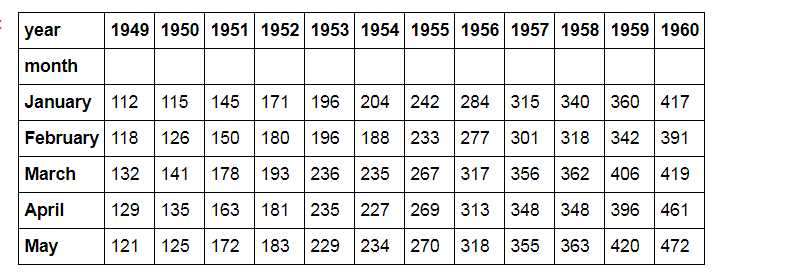
flights = sns.load_dataset("flights")
flights = flights.pivot("month", "year", "passengers")
print(flights.head())
# 加载数据
sns.heatmap(flights,
annot = True, # 是否显示数值
fmt = ‘d‘, # 格式化字符串
linewidths = 0.2, # 格子边线宽度
#center = 100, # 调色盘的色彩中心值,若没有指定,则以cmap为主
#cmap = ‘Reds‘, # 设置调色盘
cbar = True, # 是否显示图例色带
#cbar_kws={"orientation": "horizontal"}, # 是否横向显示图例色带
#square = True, # 是否正方形显示图表
)
flights.head()
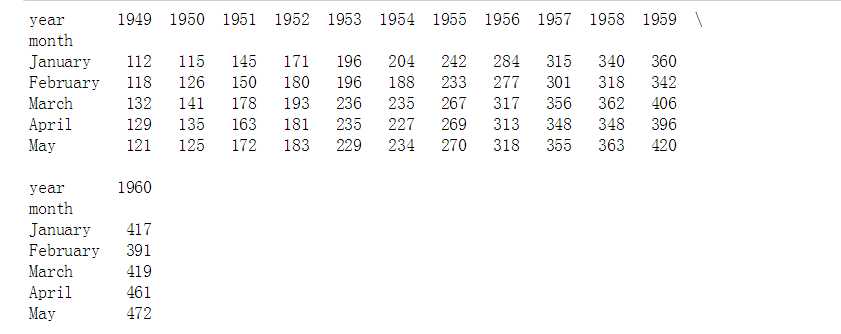
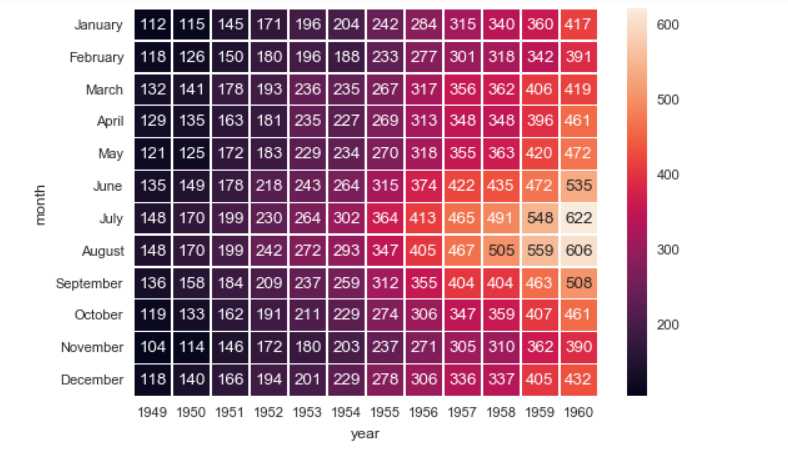
# 2、热图 - heatmap()
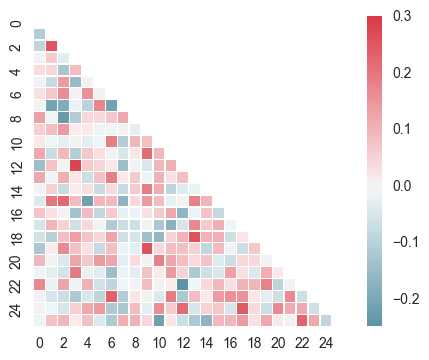
# 绘制半边热图
sns.set(style="white")
# 设置风格
rs = np.random.RandomState(33)
d = pd.DataFrame(rs.normal(size=(100, 26)))
corr = d.corr() # 求解相关性矩阵表格
# 创建数据
mask = np.zeros_like(corr, dtype=np.bool)
mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True
# 设置一个“上三角形”蒙版
cmap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
# 设置调色盘
sns.heatmap(corr, mask=mask, cmap=cmap, vmax=.3, center=0,
square=True, linewidths=0.2)
# 生成半边热图
文章标题:Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:3. 线性关系| 时间线| 热图
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/94868.html