数据结构与算法(八)-二叉树(斜二叉树、满二叉树、完全二叉树、线索二叉树)
2021-06-18 02:04
标签:length 大小 线性结构 http [] 创建 2.2.3 vat too 前言:前面了解了树的概念和基本的存储结构类型及树的分类,而在树中应用最广泛的种类是二叉树 创建测试方法: 本系列参考书籍: 《写给大家看的算法书》 《图灵程序设计丛书 算法 第4版》 数据结构与算法(八)-二叉树(斜二叉树、满二叉树、完全二叉树、线索二叉树) 标签:length 大小 线性结构 http [] 创建 2.2.3 vat too 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lfalex0831/p/9698249.html一、简介
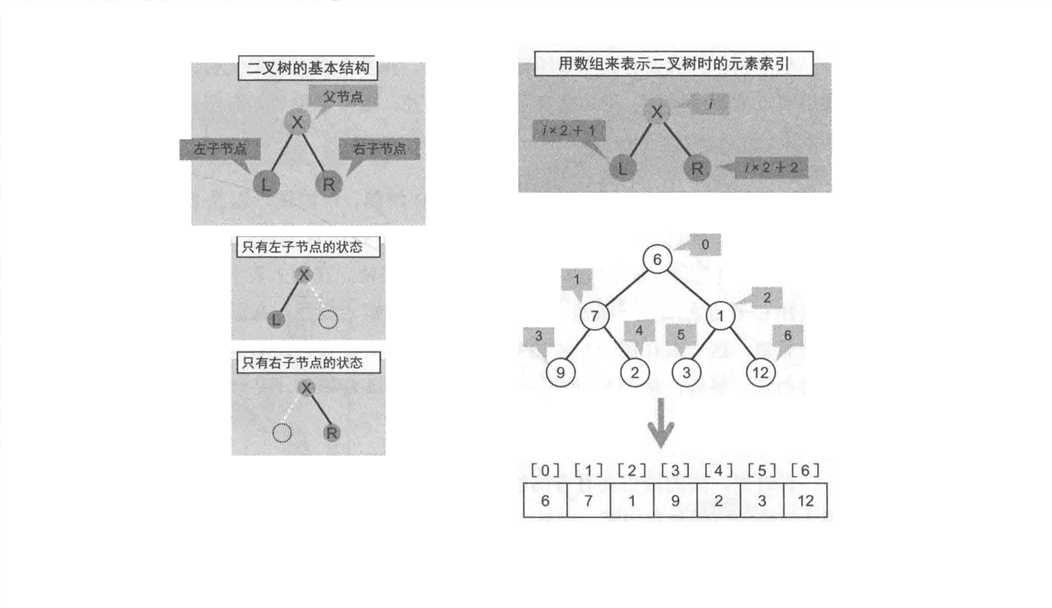

二、分类及实现
2.1 分类
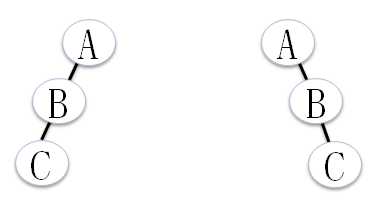



2.2 普通二叉树
2.2.1 二叉树的遍历分类
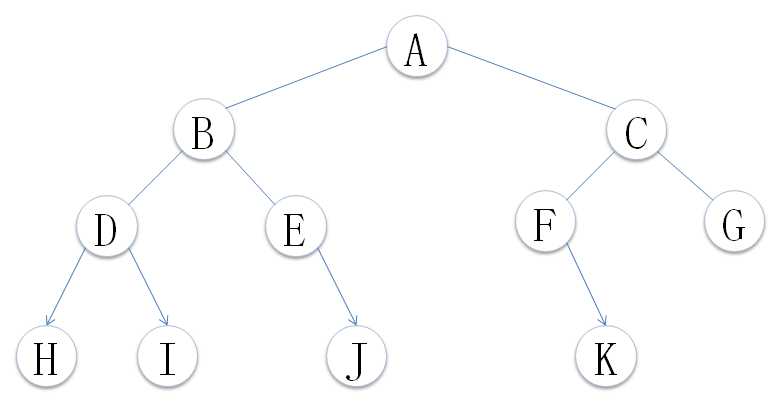

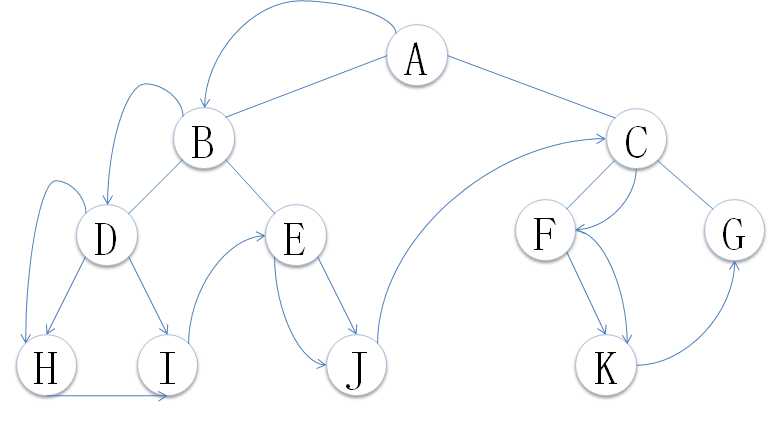

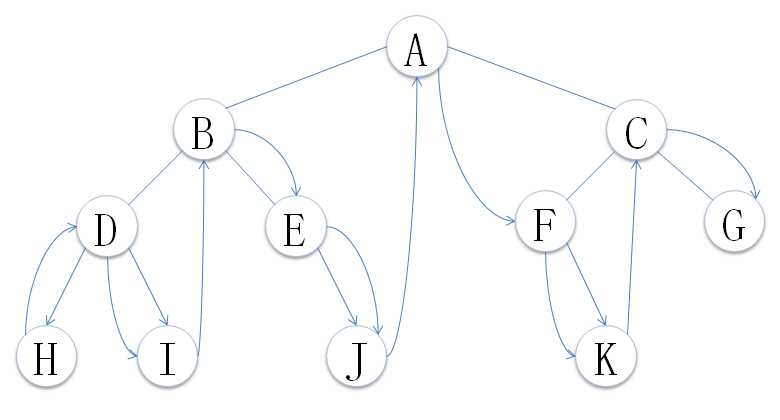

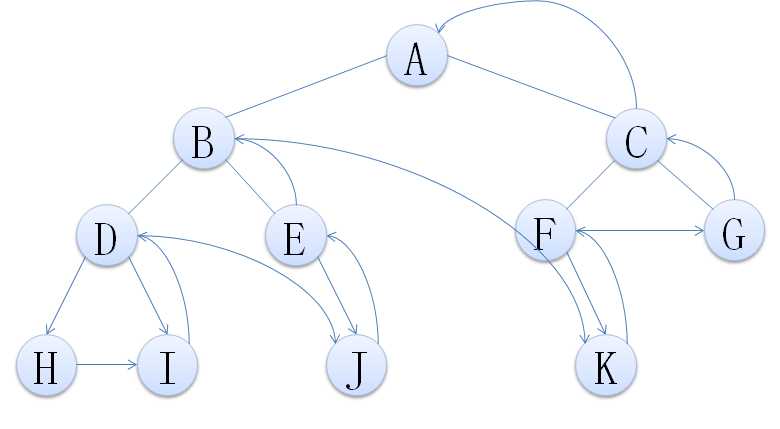


2.2.2 递归
public static Integer getNums(Integer index) {
//边界条件
if (index==1) {
return 1;
} else if (index==2) {
return 1;
} else {
//递归前进
return getNums(index - 1) + getNums(index - 2);
}
}
2.2.3 二叉树实现
public class BinaryTree
BinaryTree() 创建一个空背包
print() 遍历树
size() 获取二叉树元素大小
isEmpty() 是否为空树 class Node {
String str;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}


public class BinaryTree {
private char[] strs;
private int index;
private Node root;
BinaryTree(String str) {
strs = str.toCharArray();
root = new Node();
createBinaryTree(root);
System.out.println("11");
}
private void createBinaryTree(Node node) {
int currentIndex = index;
if (currentIndexstrs.length) {
char str = strs[currentIndex];
index++;
if (String.valueOf(str).isEmpty()||str==‘ ‘) {
node.str = null;
} else {
node.leftNode = new Node();
node.rightNode = new Node();
node.str = String.valueOf(strs[currentIndex]);
createBinaryTree(node.leftNode);
createBinaryTree(node.rightNode);
}
}
}
}


public void print() {
int level = 1;
iterator(root,level,"根节点");
}
private void iterator(Node node, int level, String str) {
if (node.str==null||node.str.isEmpty()) {
} else {
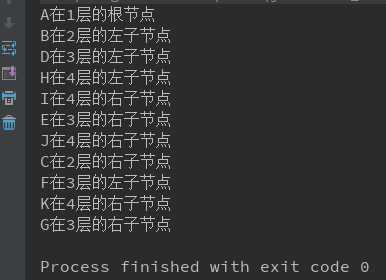
System.out.println(node.str + "在" + level + "层的"+str);
iterator(node.leftNode,level+1,"左子节点");
iterator(node.rightNode,level+1,"右子节点");
}
}
public Boolean isEmpty() {
return strs.length ;
}
public int size() {
return strs.length;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree("ABDH I E J CF K G ");
tree.print();
}

2.3 线索二叉树
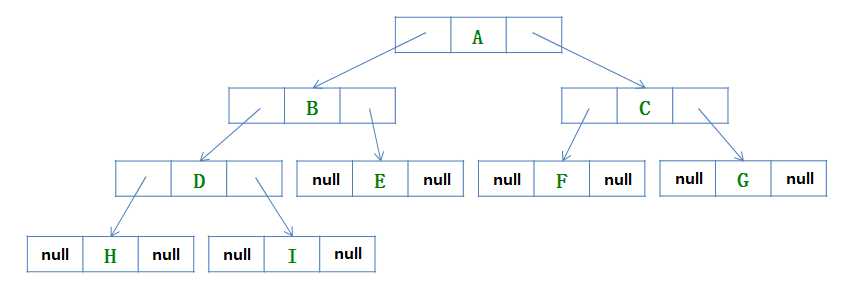
2.3.1 介绍

2.3.2 线索二叉树的实现
public class BinaryTree
BinaryTree() 创建一个空背包
InOrderTraverse() 中序遍历二叉树
boolean isEmpty() 是否为空树


public class ThreadBinaryTread {
private char[] strs;
private int index;
private Node root;
private Node pre;
ThreadBinaryTread(String str) {
strs = str.toCharArray();
root = new Node();
createBinaryTree(root);
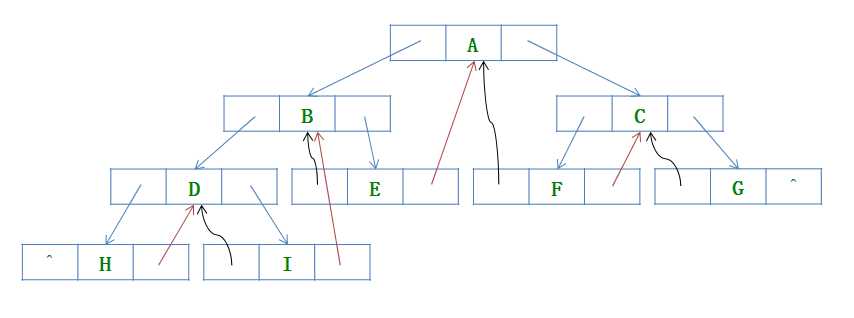
//创建完二叉树后,进行二叉树线索化
Node p = new Node();
p.ltag = 0;
p.rtag = 1;
pre = p;
inThreading(root);
pre.rightNode = p;
pre = p;
}
//中序遍历线索化
private void inThreading(Node node) {
if (node.str!=null&&!node.str.isEmpty()) {
inThreading(node.leftNode);
//如果该节点没有左子节点,则将前一个遍历的结点放入该左子节点的位置并将标志改为线索
if (node.leftNode.str == null || node.leftNode.str.isEmpty()) {
node.ltag = 1;
node.leftNode = pre;
}
//如果前一个遍历结点没有右子节点,则将本节点放到前一个节点的右子节点的位置上并将标志改为线索
if (pre.rightNode==null||pre.rightNode.str==null) {
pre.rtag = 1;
pre.rightNode = node;
}
pre = node;
inThreading(node.rightNode);
}
}
private void createBinaryTree(Node node) {
int currentIndex = index;
if (currentIndexstrs.length) {
char str = strs[currentIndex];
index++;
if (String.valueOf(str).isEmpty()||str==‘ ‘) {
node.str = null;
} else {
node.rightNode = new Node();
node.leftNode = new Node();
node.str = String.valueOf(strs[currentIndex]);
createBinaryTree(node.leftNode);
createBinaryTree(node.rightNode);
}
}
}
public void InOrderTraverse() {
Node node = pre.rightNode;
while (node!=pre) {
while (node.ltag==0) {
node = node.leftNode;
}
System.out.println(node.str);
while (node.rtag==1&&node.rightNode!=pre) {
node = node.rightNode;
System.out.println(node.str);
}
node = node.rightNode;
}
}
public Boolean isEmpty() {
return strs.length ;
}
class Node {
String str;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
//是否为线索,1:前驱线索;0:左子节点;
int ltag = 0;
//是否为线索,1:后继线索;0:右子节点;
int rtag = 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadBinaryTread tree = new ThreadBinaryTread("ABDH I E J CF K G ");
tree.InOrderTraverse();
}

三、总结
文章标题:数据结构与算法(八)-二叉树(斜二叉树、满二叉树、完全二叉树、线索二叉树)
文章链接:http://soscw.com/essay/95287.html