python 中级tkinter示例 文件管理器
标签:设置 scrollbar 一级目录 清空 空间 odi 情况 情况下 llb
不多逼逼,上代码
# -*-coding: utf-8-*-
import os
from time import sleep
from tkinter import *
class DirList(object):
def __init__(self, initdir=None):
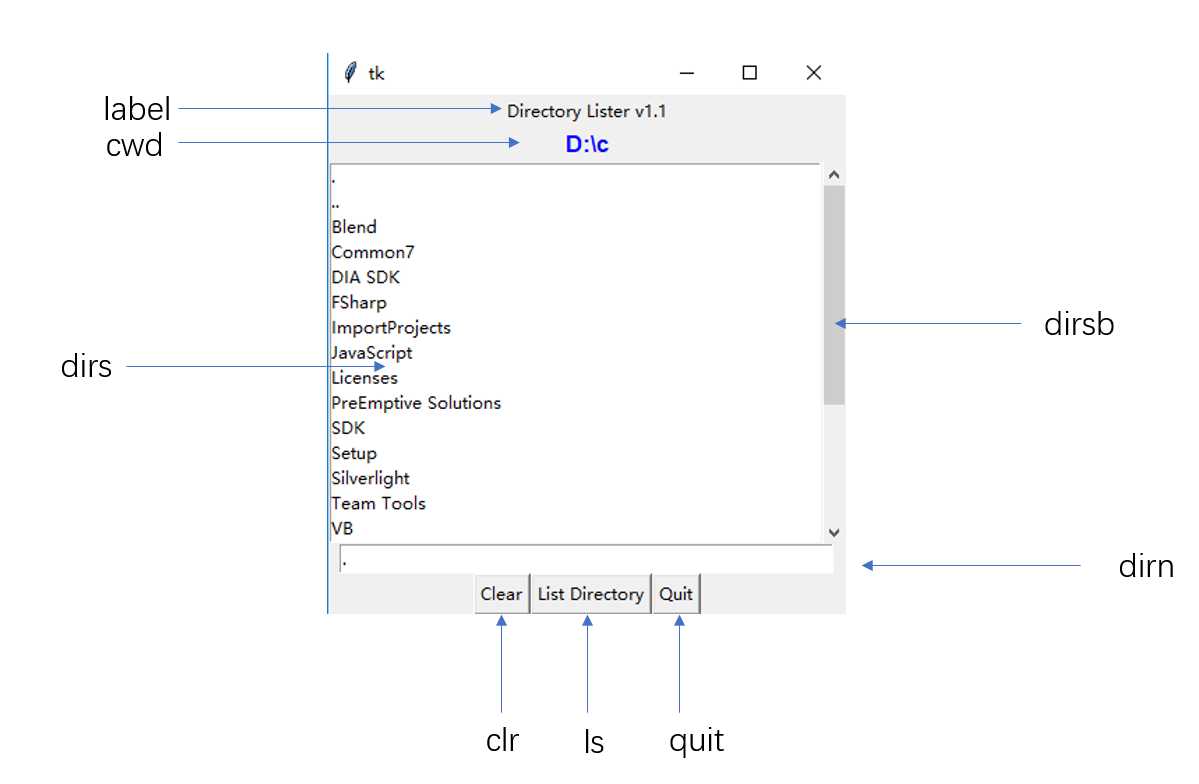
# 第一个标签:self.label,就是Directory Lister v1.1
self.top = Tk()
self.label = Label(self.top, text=‘Directory Lister v1.1‘)
self.label.pack()
# 第二个标签:self.dirl,就是当前文件目录路径
self.cwd = StringVar(self.top) # cwd是Tk()变量,用来跟踪当前所在目录的名字,以字符串形式?现在并没有将值传入
self.dirl = Label(self.top, fg=‘blue‘, font=(‘Helvetica‘, 12, ‘bold‘))
self.dirl.pack()
# 定义整个GUI程序核心,即主体部分,用框架(包含列表框和滚动条)这一组件形式表现
self.dirfm = Frame(self.top) # 框架组件,纯容器,包含其他组件
self.dirsb = Scrollbar(self.dirfm) # 滚动条,在这里是对列表框提供滚动功能
self.dirsb.pack(side=RIGHT, fill=Y) # 将列表框放置在右侧,并且填满竖直方向
self.dirs = Listbox(self.dirfm, height=15, width=50,
yscrollcommand=self.dirsb.set)
# 列表框,参数依次是父组件、高度、宽度以及竖直方向滚动命令,其中竖直方向滚动命令就设置为滚动条
self.dirs.bind(‘‘,
self.setDirAndGo) # 绑定回调函数setDirAndGo,但是‘‘是指鼠标双击列表框中的任意一项内容时,调用回调函数setDirAndGo()
self.dirsb.config(command=self.dirs.yview) # 表示滚动条对列表框进行竖直方向的滚动
self.dirs.pack(side=LEFT, fill=BOTH) # 列表框放置在左侧,并填满框架的剩余空间(BOTH)
self.dirfm.pack()
# 定义输入框,收集键盘输入
self.dirn = Entry(self.top, width=50, textvariable=self.cwd) # textvariable参数是指输入的内容,在本例中是输入文件目录,默认值是当前文件目录
self.dirn.bind(‘‘, self.doLS) # 绑定回调函数doLS,但是‘‘是指用户在输入框输完文本后,按下回车键,就会调用函数doLS()
self.dirn.pack()
# 定义按钮框架,包含三个按钮
self.bfm = Frame(self.top)
self.clr = Button(self.bfm, text=‘Clear‘, command=self.clrDir, activeforeground=‘white‘,
activebackground=‘blue‘) # "clear"按钮,回调函数是清楚所有文件clrDir()
self.ls = Button(self.bfm, text=‘List Directory‘, command=self.doLS, activeforeground=‘white‘,
activebackground=‘green‘) # "go"按钮,回调函数是doLS()
self.quit = Button(self.bfm, text=‘Quit‘, command=self.top.quit, activeforeground=‘white‘,
activebackground=‘red‘) # 退出按钮
self.clr.pack(side=LEFT)
self.ls.pack(side=LEFT)
self.quit.pack(side=LEFT)
self.bfm.pack()
# 初始化GUI程序,从当前目录开始,不理解。
if initdir:
self.cwd.set(os.curdir)
self.doLS()
# clr按钮的回调函数,清空Tk字符串变量cwd
def clrDir(self, ev=None):
self.cwd.set(‘‘)
# 列表框回调函数,设置了要达到的目录,以及调用doLS()函数
def setDirAndGo(self, ev=None):
check = self.dirs.get(
self.dirs.curselection()) # 列表框的get()方法是得到列表中的所有值(未传入参数),在传入参数(行号)的情况下是获得所选中的选项;curselection()是返回选中的元素的行号
if not check:
check = os.curdir
self.cwd.set(check) # 将cwd跟踪至列表框中某项目录
self.doLS()
# 整个GUI程序的关键,负责安全检查,若无问题,则调用os.listdir()取得新文件集合,并替换列表框列表
def doLS(self, ev=None):
# 安全检查
error = ‘‘ #error归零
tdir = self.cwd.get() # 以字符串形式返回cwd追踪目录
if not tdir: tdir = os.curdir # 若为空,则tdir设为当前目录
if not os.path.exists(tdir): # 文件不存在
error = tdir + ‘: no such file‘
elif not os.path.isdir(tdir): # 文件路径不存在
error = tdir + ‘: not a directory‘
# 若有错误,则最终目录设置为当前目录
if error:
self.cwd.set(error) # 将cwd设为error
self.top.update() # 刷新页面
sleep(2)
if not (hasattr(self, ‘last‘) and self.last):
self.last = os.curdir
self.cwd.set(self.last) # 重新设置cwd为当前目录
self.dirs.config(selectbackground=‘LightSkyBlue‘)
self.top.update() #刷新页面
return
self.cwd.set(‘FETCHING DIRECTORY CONTENTS...‘)
self.top.update()
dirlist = os.listdir(tdir) # 列出文件目录tdir下所有文件
dirlist.sort() # 排序
os.chdir(tdir) # 将当前工作目录设置为tdir
self.dirl.config(text=os.getcwd()) # 配置,将第二个标签内容定为当前工作目录
self.dirs.delete(0, END) # 删除旧目录下列表框的内容
self.dirs.insert(END, os.curdir) # 在新目录列表框的最后加入当前目录
self.dirs.insert(END, os.pardir) # 在新目录列表框的最后加入当前目录的上一级目录
for eachFile in dirlist: # 在新目录的列表框中,加入新目录下的所有文件
self.dirs.insert(END, eachFile)
self.cwd.set(os.curdir)
self.dirs.config(selectbackground=‘LightSkyBlue‘)
def main():
d = DirList(os.curdir)
mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
图形界面:
python 中级tkinter示例 文件管理器
标签:设置 scrollbar 一级目录 清空 空间 odi 情况 情况下 llb
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/francischeng/p/9562883.html
评论
