PHP实现二叉树深度优先遍历(前序、中序、后序)和广度优先遍历(层次)实例详解
2018-09-07 14:05
本文实例讲述了PHP实现二叉树深度优先遍历(前序、中序、后序)和广度优先遍历(层次)。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
前言:
深度优先遍历:对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个结点只能访问一次。要特别注意的是,二叉树的深度优先遍历比较特殊,可以细分为先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。具体说明如下:
前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树
中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树
后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点
广度优先遍历:又叫层次遍历,从上往下对每一层依次访问,在每一层中,从左往右(也可以从右往左)访问结点,访问完一层就进入下一层,直到没有结点可以访问为止。
例如对于一下这棵树:
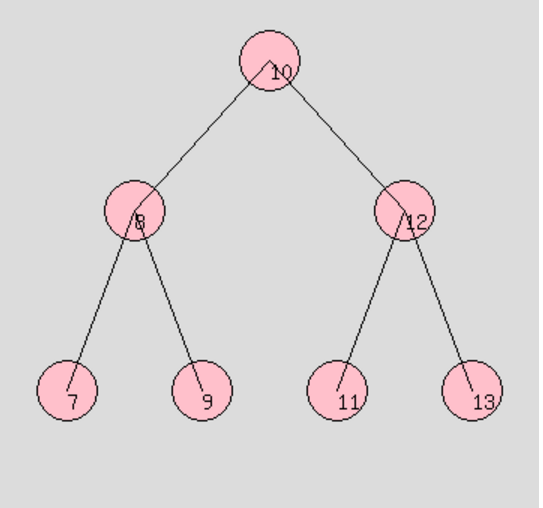
深度优先遍历:
前序遍历:10 8 7 9 12 11 13
中序遍历:7 8 9 10 11 12 13
后序遍历:7 9 8 11 13 12 10
广度优先遍历:
层次遍历:10 8 12 7 9 11 13
二叉树的深度优先遍历的非递归的通用做法是采用栈,广度优先遍历的非递归的通用做法是采用队列。
深度优先遍历:
1、前序遍历:
/** * 前序遍历(递归方法) */ private function pre_order1($root) { if (!is_null($root)) { //这里用到常量__FUNCTION__,获取当前函数名,好处是假如修改函数名的时候,里面的实现不用修改 $function = __FUNCTION__; echo $root->key . ; $this->$function($root->left); $this->$function($root->right); } } /** * 前序遍历(非递归方法) * 因为当遍历过根节点之后还要回来,所以必须将其存起来。考虑到后进先出的特点,选用栈存储。 */ private function pre_order2($root) { // $stack = new splstack(); // $stack->push($root); // while(!$stack->isEmpty()){ // $node = $stack->pop(); // echo $node->key. ; // if(!is_null($node->right)){ // $stack->push($node->right); // } // if(!is_null($node->left)){ // $stack->push($node->left); // } // } if (is_null($root)) { return; } $stack = new splstack(); $node = $root; while (!is_null($node) !$stack->isEmpty()) { while (!is_null($node)) { //只要结点不为空就应该入栈保存,与其左右结点无关 $stack->push($node); echo $node->key . ; $node = $node->left; } $node = $stack->pop(); $node = $node->right; } } //前序遍历 public function PreOrder() { // 所在对象中的tree属性保存了一个树的引用 // $this->pre_order1($this->tree->root); $this->pre_order2($this->tree->root); }
说明:1、我将所有的遍历方法都封装在一个类 traverse 里面了。2、pre_order2方法中,在使用栈的过程中,我使用的是PHP标准库SPL提供的splstack,如果你们习惯使用数组的话,可以使用 array_push() 和array_pop() 模拟实现。
2、中序遍历:
/** * 中序遍历(递归方法) */ private function mid_order1($root) { if (!is_null($root)) { $function = __FUNCTION__; $this->$function($root->left); echo $root->key . ; $this->$function($root->right); } } /** * 中序遍历(非递归方法) * 因为当遍历过根节点之后还要回来,所以必须将其存起来。考虑到后进先出的特点,选用栈存储。 */ private function mid_order2($root) { if (is_null($root)) { return; } $stack = new splstack(); $node = $root; while (!is_null($node) !$stack->isEmpty()) { while (!is_null($node)) { $stack->push($node); $node = $node->left; } $node = $stack->pop(); echo $node->key . ; $node = $node->right; } } //中序遍历 public function MidOrder() { // $this->mid_order1($this->tree->root); $this->mid_order2($this->tree->root); }
3、后序遍历:
/** * 后序遍历(递归方法) */ private function post_order1($root) { if (!is_null($root)) { $function = __FUNCTION__; $this->$function($root->left); $this->$function($root->right); echo $root->key . ; } } /** * 后序遍历(非递归方法) * 因为当遍历过根节点之后还要回来,所以必须将其存起来。考虑到后进先出的特点,选用栈存储。 * 由于在访问了左子节点后怎么跳到右子节点是难点,这里使用一个标识lastVisited来标识上一次访问的结点 */ private function post_order2($root) { if (is_null($root)) { return; } $node = $root; $stack = new splstack(); //保存上一次访问的结点引用 $lastVisited = NULL; $stack->push($node); while(!$stack->isEmpty()){ $node = $stack->top();//获取栈顶元素但不弹出 if(($node->left == NULL && $node->right == NULL) ($node->right == NULL && $lastVisited == $node->left) ($lastVisited == $node->right)){ echo $node->key. ; $lastVisited = $node; $stack->pop(); }else{ if($node->right){ $stack->push($node->right); } if($node->left){ $stack->push($node->left); } } } } //后序遍历 public function PostOrder() { // $this->post_order1($this->tree->root); $this->post_order2($this->tree->root); }
广度优先遍历:
1、层次遍历:
/** * 层次遍历(递归方法) * 由于是按层逐层遍历,因此传递树的层数 */ private function level_order1($root,$level){ if($root == NULL $level < 1){ return; } if($level == 1){ echo $root->key. ; return; } if(!is_null($root->left)){ $this->level_order1($root->left,$level - 1); } if(!is_null($root->right)){ $this->level_order1($root->right,$level - 1); } } /** * 层次遍历(非递归方法) * 每一层从左向右输出 元素需要储存有先进先出的特性,所以选用队列存储。 */ private function level_order2($root){ if(is_null($root)){ return; } $node = $root; //利用队列实现 // $queue = array(); // array_push($queue,$node); // // while(!is_null($node = array_shift($queue))){ // echo $node->key. ; // if(!is_null($node->left)){ // array_push($queue,$node->left); // } // if(!is_null($node->right)){ // array_push($queue,$node->right); // } // } $queue = new splqueue(); $queue->enqueue($node); while(!$queue->isEmpty()){ $node = $queue->dequeue(); echo $node->key. ; if (!is_null($node->left)) { $queue->enqueue($node->left); } if (!is_null($node->right)) { $queue->enqueue($node->right); } } } //层次遍历 public function LevelOrder(){ // $level = $this->getdepth($this->tree->root); // for($i = 1;$i <= $level;$i ++){ // $this->level_order1($this->tree->root,$i); // } $this->level_order2($this->tree->root); } //获取树的层数 private function getdepth($root){ if(is_null($root)){ return 0; } $left = getdepth($root -> left); $right = getdepth($root -> right); $depth = ($left > $right ? $left : $right) + 1; return $depth; }
说明:level_order2方法中,在使用队列的过程中,我使用的是PHP标准库SPL提供的splqueue,如果你们习惯使用数组的话,可以使用 array_push() 和array_shift() 模拟实现。
使用:
现在我们来看看客户端代码:
class Client { public static function Main() { try { //实现文件的自动加载 function autoload($class) { include strtolower($class) . .php; } spl_autoload_register(autoload); $arr = array(10, 8, 12, 7, 9, 11, 13); $tree = new Bst(); // $tree = new Avl(); // $tree = new Rbt(); $tree->init($arr); $traverse = new traverse($tree); $traverse->PreOrder(); // $traverse->MidOrder(); // $traverse->PostOrder(); // $traverse->LevelOrder(); } catch (Exception $e) { echo $e->getMessage(); } } } CLient::Main();
补充:
1. 在客户端中所使用的三个类 Bst、Avl、Rbt 大家可以参考前面一篇:《PHP实现绘制二叉树图形显示功能详解》
2. 为什么我推荐大家使用SPL标准库中提供的splstack和splqueue呢?这是我在某一篇文章中看到的:虽然我们可以使用传统的变量类型来描述数据结构,例如用数组来描述堆栈(Strack)– 然后使用对应的方式 pop 和 push(array_pop()、array_push()),但你得时刻小心,因为毕竟它们不是专门用于描述数据结构的 – 一次误操作就有可能破坏该堆栈。而 SPL 的 SplStack 对象则严格以堆栈的形式描述数据,并提供对应的方法。同时,这样的代码应该也能理解它在操作堆栈而非某个数组,从而能让你的同伴更好的理解相应的代码,并且它更快。原文地址:PHP SPL,遗落的宝石
3. 本文相关参考文章: 《C语言二叉树常见操作详解【前序,中序,后序,层次遍历及非递归查找,统计个数,比较,求深度】》、《Java实现二叉树的深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历算法示例》
更多关于PHP相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《PHP数据结构与算法教程》、《php程序设计算法总结》、《php字符串(string)用法总结》、《PHP数组(Array)操作技巧大全》、《PHP常用遍历算法与技巧总结》及《PHP数学运算技巧总结》
希望本文所述对大家PHP程序设计有所帮助。
上一篇:php正则
文章标题:PHP实现二叉树深度优先遍历(前序、中序、后序)和广度优先遍历(层次)实例详解
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/13195.html