标签:style blog class code java ext
拷贝构造函数何时会被调用?
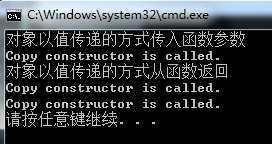
1. 对象以值传递的方式传入函数参数
2.对象以值传递的方式从函数返回
3.对象需要通过另外一个对象进行初始化
下面我们来看代码:

//#include //using namespace std;
//template //T:队列的类型,char,int,double,包括自己的struct 。MAX:循环队列的最大长度
//class Queue
//{
//private:
// T p[MAX];//队列用的数组
// int head, tail;//头尾下标
//public:
// //在定义时预处理
// inline Queue() { clear(); }
// //预处理过程,使头尾下标都是0
// inline void clear() { head = tail = 0; }
// //循环队列压入:把元素压入队列,如果队尾超出了循环队列的最大长度,把队尾下标变成0
// inline void push(const T& n) { p[tail++] = n; if (tail == MAX) tail = 0; }
// //循环队列弹出:弹出队头元素,即在现有队列中最先加入的元素。同样使用了循环优化.
// inline void pop() { if (++head == MAX) head = 0; }
// //函数返回循环队列中的队头元素
// inline T& top() { return p[head]; }
// //判断队列是否为空
// inline bool empty() {return head == tail;}
//};
//
////定义队列:
//Queue q;
////在使用时可以直接用q.clear() 清空,q.push(x)压入要加入的元素,x = q.top() 找到队头元素, q.pop()弹出队头元素,q.empty()判队列是否为空
//Queue cq;
//int main()
//{
// int i,n=10;
// int x;
// int array[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
// char array_[10]={‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘,‘f‘,‘g‘,‘h‘,‘i‘,‘j‘};
// for(i=0;i// {
// cq.push(array_[i]);
// }
// for(i=0;i// {
// cout // cq.pop();
// }
//
// return 0;
//}
//函数模板
//template
#include
#include //反正切,知道两对边,求弧度(要自己转化成角度)
/*int main(void)
{
double result;
double x = 10.0, y = 10.0;
result = atan2(y, x);
printf("The arc tangent ratio of %lf is %.1lf\n", (y / x), result*180/3.1415926);
return 0;
}*/
//#include //#include
////传入的参数为弧度
//int main(void)
//{
// double result, x = 0.5;
//
// result = sin(x);
// printf("The sin() of %lf is %lf\n", x, result);
// return 0;
//}
//弧度转化角度:弧度*180/PI
//角度转化弧度:角度*PI/180
//#include //#include //const double PI=acos(-1.0);
////sin传入的参数的是弧度
//void main()
//{
// int z=30;
// double x = 10.0, y = 10.0;
// double result;
// //sin30结果
// printf("sin(%d)=%.2lf\n",z,sin(2*PI*z/360.0));
// result=atan2(y, x); //结果返回是弧度
// printf("The arc tangent ratio of %lf is %.1lf\n", (y / x), result*180/PI);
// //sin45的结果
// printf("sin(%.0f)=%.2lf\n",result*180/PI,sin(result)); //注意不要用%d
//}
//桶排序思想
//假如要排序的是数字是 2 4 5 5 5 8 8 9 1 1
//#include//#define length 10
//int main()
//{
// //数组元素值全部初始化为0
// int array[length]={0};
// int i,j;
// int n;
// for(i=0;i// {
// scanf("%d",&n);
// array[n]++;
// }
// for (i = 0; i // {
// for(j=0;j// printf("%d ",i);
// }
//
// return 0;
//}
// Ba 2 Da 4 Ea 5 Eb 5 Ec 5 Ha 8 Hb 8 Ia 9 Aa 1 Ab 1
//#include//#define length 10
//
//struct node
//{
// char country[6]; //国家
// int count; //金牌数
//};
//int main()
//{
// int i,j,n;
// int array[10][10]={0}; //数组内的元素是结构体索引
// int index[10]={0}; //存储每行队列(数组)内元素个数
// struct node ary[length]={
// {"Ba",2},{"Da",4},{"Ea",5},{"Eb",5},
// {"Ec",5},{"Ha",8},{"Hb",8},{"Ia",9},
// {"Aa",1},{"Ab",1}};
// for(i=0;i// {
// n=ary[i].count; //桶子编号
// array[n][index[n]]=i; //存储结构体数组索引
// index[n]++;
// }
// for(i=0;i// {
// for(j=0;j// {
// printf("%s %d\n",ary[array[i][j]].country,ary[array[i][j]].count);
// }
// }
//}
//#include//
//int main()
// {
// int nVar = 0x12345678;
// int *pnVar = &nVar;
// char *pcVar = (char*)&nVar;
// short *psnVar = (short*)&nVar;
// printf("%08x \r\n", *pnVar);
// printf("%08x \r\n", *pcVar);
// printf("%08x \r\n", *psnVar);
// return 0;
// }
//拷贝构造函数
// 04.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
//#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class CDog
{
public:
unsigned int m_Weight;
unsigned int m_Age;
CDog(int weight,int age);
CDog(int weight = 20);
CDog(const CDog & theDog);
void SetAge(unsigned int age);
int GetAge ();
~CDog();
};
CDog::CDog(int weight,int age)
{
m_Weight = weight;
m_Age = age;
}
CDog::CDog(int weight)
{
m_Weight = weight;
}
CDog::CDog(const CDog & theDog)
{
m_Weight = theDog.m_Weight;
m_Age = theDog.m_Age;
printf("Copy constructor is called.\n");
}
void CDog::SetAge(unsigned int age)
{
m_Age = age;
}
int CDog::GetAge ()
{
return m_Age;
}
CDog::~CDog()
{
}
CDog CopyData(CDog m_dog)
{
return m_dog;
}
void test(CDog tmp)
{
}
CDog test2()
{
CDog temp;
cout"对象以值传递的方式从函数返回"endl;
return temp;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CDog Example;
cout"对象以值传递的方式传入函数参数"endl;
test(Example);
test2();
//对象需要通过另外一个对象进行初始化
//这里调用的是拷贝构造函数。而不是我们看到的赋值
CDog test3 = Example;
return 0;
}

浅拷贝与深拷贝
1.浅拷贝指的是只对对象中的数据成员进行简单的赋值。
2.默认拷贝构造函数执行的就是浅拷贝。
3.默认拷贝构造函数不会处理静态数据成员。
4.浅拷贝无法处理对象内的动态成员。
原因:浅拷贝仅仅是赋值,所以拷贝的对象的动态成员与原对象动态成员指向同一块内存,但是析构函数却会调用二次,
释放两次同一块内存,自然会出错。
5.深拷贝会在拷贝函数中为动态成员分配内存。
//代码来自:
//http://blog.csdn.net/lwbeyond/article/details/6202256 作者:lwbeyond
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class Rect
{
public:
Rect() // 构造函数,p指向堆中分配的一空间
{
p = new int(100);
}
~Rect() // 析构函数,释放动态分配的空间
{
if(p != NULL)
{
delete p;
}
}
private:
int width;
int height;
int *p; // 一指针成员
};
int main()
{
Rect rect1;
Rect rect2(rect1); // 复制对象
return 0;
}
如果运行此程序,会出错。原因上面已经阐述。
修改成深拷贝:
//代码来自:
//http://blog.csdn.net/lwbeyond/article/details/6202256 作者:lwbeyond
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class Rect
{
public:
Rect() // 构造函数,p指向堆中分配的一空间
{
p = new int(100);
}
Rect(const Rect& r)
{
width = r.width;
height = r.height;
//p = new int(100); // 为新对象重新动态分配空间
p = new int; // 为新对象重新动态分配空间
*p = *(r.p);
}
~Rect() // 析构函数,释放动态分配的空间
{
if(p != NULL)
{
delete p;
}
}
private:
int width;
int height;
int *p; // 一指针成员
};
int main()
{
Rect rect1;
Rect rect2(rect1); // 复制对象
return 0;
}
成功运行。
避免调用默认拷贝构造函数的方法:
声明一个私有拷贝构造函数。
拷贝构造函数可有一个或者多个。
下面来自博客:http://blog.csdn.net/lwbeyond/article/details/6202256
对于一个类X, 如果一个构造函数的第一个参数是下列之一:
a)
X&
b) const X&
c) volatile
X&
d) const volatile
X&
且没有其他参数或其他参数都有默认值,那么这个函数是拷贝构造函数.
http://blog.csdn.net/lwbeyond/article/details/6202256
对于拷贝构造函数解释的很详细。
拷贝构造函数[c++],搜素材,soscw.com
拷贝构造函数[c++]
标签:style blog class code java ext
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/qiangua/p/3703752.html






