Kubernetes YAML最佳实践和策略
2020-12-26 05:27
标签:git message match 打开 http except protoc from created YAML的问题之一就是很难描述清单文件之间的约束或关系。 Kubernetes YAML文件的静态检查生态系统可以分为以下几类: 在本文中,你将学习到六个不同的工具: Let‘s Go ~~~ 首先部署一个基准服务,以便后面测试对比 部署完成并验证如下: 以上YAML文件能部署成功,但是,它遵循最佳做法吗? Let‘s start. kubeval的前提是与Kubernetes的任何交互都通过其REST API进行。 安装kubeval 现在我们来改下base.yaml,删除 然后使用kubeval对base.yaml检查 输出看到一个WARN,提示selector是必须的字段 检查PASS kubeval之类的工具的优势在于,咱们可以在部署周期的早期发现此类错误。 kube-score会对你提供的YAML清单进行分析,并针对集群的内置检查对其进行评分。 从如上可以看到针对这个文件给出的建议,比如资源限制、镜像TAG、Pod网络策略等。不错吧,非常好用的工具。。。 当然,kube-score并不可扩展,并且您不能添加或调整策略。 Config-lint是用于验证以YAML,JSON,Terraform,CSV和Kubernetes清单编写的配置文件的工具。 安装Config-lint Config-lint并没有对Kubernetes清单进行内置检查。你必须编写自己的规则才能执行任何验证。 假设咱们希望检查部署中的镜像是否总是从可信任的仓库(例如kubeops.net/app:1.0 )中提取。 一个完整的规则集如下所示: 如果要测试检查,可以将规则集另存为check_image_repo.yaml。 可以看到Every expression fails,检测不通过。 输出不报错即为成功。 Config-lint是一个很有前途的框架,可以让你使用YAML DSL为Kubernetes YAML清单编写自定义检查。 Copper V2是一个使用自定义检查来验证清单的框架,就像config-lint一样。 安装Copper 与config-lint相似,Copper并没有提供内置检查。 执行检查 现在修改为 更多用法参见 Conftest是用于配置数据的测试框架,可用于检查和验证Kubernetes清单。 安装Conftest 与config-lint和copper类似,conftest没有任何内置检查。 首先创建一个新目录conftest-checks和一个名为check_image_registry.rego的文件,其内容如下: 先修改base.yaml, 再次修改为base.yaml, 更多用法参见 最后一个工具了,Polaris既可以安装在集群内部,也可以作为命令行工具来静态分析Kubernetes清单。 安装Polaris,这里只安装命令行模式 安装完成后,就可以使用Polaris对base.yaml进行检查 另外,可以只输出评分 下面使用YAML代码段定义了一个称为checkImageRepo的新检查: 现在base.yaml的image为: 结果显示"Message": "Image registry is not valid", "Success": false, 从输出看到 "Message": "Image registry is valid","Success": true,,检查通过。。。 尽管有很多工具可以对Kubernetes YAML文件进行验证,评分和整理,但重要的是要有一个健康的模型来设计和执行检查。 Kubernetes YAML最佳实践和策略 标签:git message match 打开 http except protoc from created 原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/1648324/2546488
如果你希望检查是否已从受信任的注册表中提取部署到群集中的所有映像,该怎么办?
如何防止没有Pod安全策略的工作负载提交到集群?
集成静态检查可以在更接近开发生命周期的时间内捕获错误和违反策略的行为。
并且由于改善了资源定义的有效性和安全性,因此你可以相信生产工作负载遵循最佳实践。
Kubeval
Kube-score
Config-lint
Copper
Conftest
Polaris基准服务
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: http-echo
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: http-echo
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: http-echo
spec:
containers:
- name: http-echo
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args: ["-text", "hello-world"]
ports:
- containerPort: 5678
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: http-echo
spec:
ports:
- port: 5678
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: http-echo[root@k8s-node001 Test]# kubectl get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
http-echo-57dd74545-rtxzm 1/1 Running 0 65s
http-echo-57dd74545-trst7 1/1 Running 0 65s
[root@k8s-node001 Test]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
http-echo ClusterIP 10.102.221.64 kubeval
因此,可以使用API模式来验证给定的YAML输入是否符合该模式。wget https://github.com/instrumenta/kubeval/releases/latest/download/kubeval-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xf kubeval-linux-amd64.tar.gz
cp kubeval /usr/local/bin selector:
matchLabels:
app: http-echo[root@k8s-node001 Test]# kubeval base.yaml
WARN - base.yaml contains an invalid Deployment (http-echo) - selector: selector is required
PASS - base.yaml contains a valid Service (http-echo)
然后恢复selector,再次检查[root@k8s-node001 Test]# kubeval base.yaml
PASS - base.yaml contains a valid Deployment (http-echo)
PASS - base.yaml contains a valid Service (http-echo)
另外,您不需要访问集群即可运行检查-它们可以脱机运行。
默认情况下,kubeval会根据最新的未发布的Kubernetes API模式验证资源。
更多用法详情请参见官网kube-score
kube-score提供在线版和离线版
本文偷懒就用在线版了
首先打开https://kube-score.com/ ,然后在输入框贴入写好的YAML清单,这里以上文base.yaml来分析
解析结果如下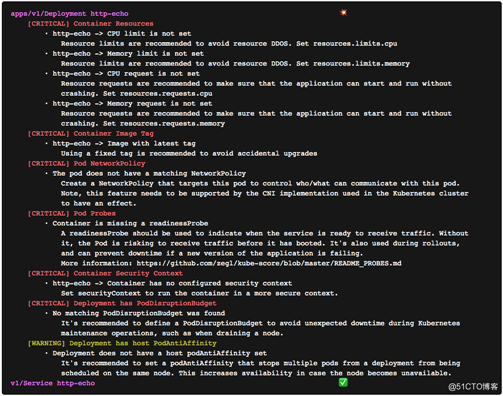
如果要编写自定义检查以符合组织策略,则可以使用以下四个工具之一:config-lint,copper,conftest或Polaris。Config-lint
wget https://github.com/stelligent/config-lint/releases/download/v1.6.0/config-lint_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
tar -zxf config-lint_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
mv config-lint /usr/local/bin/
规则被写为YAML文件,称为规则集,并具有以下结构:version: 1
description: Rules for Kubernetes spec files
type: Kubernetes
files:
- "*.yaml"
rules:
# list of rules
实施此类检查的config-lint规则如下所示:- id: MY_DEPLOYMENT_IMAGE_TAG
severity: FAILURE
message: Deployment must use a valid image tag
resource: Deployment
assertions:
- every:
key: spec.template.spec.containers
expressions:
- key: image
op: starts-with
value: "kubeops.net/"version: 1
description: Rules for Kubernetes spec files
type: Kubernetes
files:
- "*.yaml"
rules:
- id: DEPLOYMENT_IMAGE_REPOSITORY
severity: FAILURE
message: Deployment must use a valid image repository
resource: Deployment
assertions:
- every:
key: spec.template.spec.containers
expressions:
- key: image
op: starts-with
value: "kubeops.net/"
然后使用config-lint执行检查[root@k8s-node001 Test]# config-lint -rules check_image_repo.yaml base.yaml
[
{
"AssertionMessage": "Every expression fails: And expression fails: image does not start with kubeops.net/",
"Category": "",
"CreatedAt": "2020-11-02T08:28:43Z",
"Filename": "base.yaml",
"LineNumber": 0,
"ResourceID": "http-echo",
"ResourceType": "Deployment",
"RuleID": "DEPLOYMENT_IMAGE_REPOSITORY",
"RuleMessage": "Deployment must use a valid image repository",
"Status": "FAILURE"
}
]
现在我们来改下images地址为image: kubeops.net/http-echo,再来检查一次[root@k8s-node001 Test]# config-lint -rules check_image_repo.yaml base.yaml
[]
但是,如果您想表达更复杂的逻辑和检查该怎么办?
YAML对此是否也有限制?
如果您可以使用真正的编程语言来表达这些检查,该怎么办?接下来看CopperCopper
但是,Copper不使用YAML定义检查。
相反,测试是用JavaScript编写的,而Copper提供了一个包含一些基本帮助程序的库,以帮助读取Kubernetes对象和报告错误。https://github.com/cloud66-oss/copper/releases/download/2.0.1/linux_amd64_2.0.1
mv linux_amd64_2.0.1 copper
chmod + x copper
mv copper /usr/local/bin/
让我们自定义一个检查,以确保部署镜像tag必须非latest。
check_image_repo.js$$.forEach(function($){
if ($.kind === ‘Deployment‘) {
$.spec.template.spec.containers.forEach(function(container) {
var image = new DockerImage(container.image);
if (image.tag === ‘latest‘) {
errors.add_error(‘no_latest‘,"latest is used in " + $.metadata.name, 1)
}
});
}
});[root@k8s-node001 Test]# copper validate --in=base.yaml --validator=check_image_tag.js
Check no_latest failed with severity 1 due to latest is used in http-echo
Validation failedimage: kubeops.net/http-echo:v1.0.0[root@k8s-node001 Test]# copper validate --in=base.yaml --validator=check_image_tag.js
Validation successfulConftest
测试使用专用查询语言Rego编写的。wget https://github.com/open-policy-agent/conftest/releases/download/v0.21.0/conftest_0.21.0_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
tar -xzf conftest_0.21.0_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
mv conftest /usr/local/binpackage main
deny[msg] {
input.kind == "Deployment"
image := input.spec.template.spec.containers[_].image
not startswith(image, "kubeops.net/")
msg := sprintf("image ‘%v‘ doesn‘t come from kubeops.net repository", [image])
}image: docker.io/http-echo
使用conftest执行检测[root@k8s-node001 Test]# conftest test --policy ./conftest-checks base.yaml
FAIL - base.yaml - image ‘docker.io/http-echo:v1.0.0‘ doesn‘t come from kubeops.net repository
2 tests, 1 passed, 0 warnings, 1 failure, 0 exceptionsimage: kubeops.net/http-echo[root@k8s-node001 Test]# conftest test --policy ./conftest-checks base.yaml
2 tests, 2 passed, 0 warnings, 0 failures, 0 exceptionsPolaris
作为命令行工具运行时,它包含多个内置检查,涉及诸如安全性和最佳实践等方面,类似于kube-score。
另外,你可以使用它来编写类似于config-lint,copper和conftest的自定义检查。
换句话说,Polaris结合了两类的优点:内置和自定义检查器。wget https://github.com/FairwindsOps/polaris/releases/download/1.2.1/polaris_1.2.1_linux_amd64.tar.gz
tar -zxf polaris_1.2.1_linux_amd64.tar.gz
mv polaris /usr/local/bin/
[root@k8s-node001 Test]# polaris audit --audit-path base.yaml
结果如下,信息比较多,这里只截取部分信息,自己可以仔细看看分析出来的结果。 "PolarisOutputVersion": "1.0",
"AuditTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"SourceType": "Path",
"SourceName": "base.yaml",
"DisplayName": "base.yaml",
"ClusterInfo": {
"Version": "unknown",
"Nodes": 0,
"Pods": 1,
"Namespaces": 0,
"Controllers": 1
},
"Results": [
{
"Name": "http-echo",
"Namespace": "",
"Kind": "Deployment",
"Results": {},
"PodResult": {
"Name": "",
"Results": {
"hostIPCSet": {
"ID": "hostIPCSet",
"Message": "Host IPC is not configured",
"Success": true,
"Severity": "danger",
"Category": "Security"
..............
"tagNotSpecified": {
"ID": "tagNotSpecified",
"Message": "Image tag is specified",
"Success": true,
"Severity": "danger",
"Category": "Images"
}
}
}
]
},
"CreatedTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
}
]
}[root@k8s-node001 Test]# polaris audit --audit-path base.yaml --format score
66
config_with_custom_check.yamlchecks:
checkImageRepo: danger
customChecks:
checkImageRepo:
successMessage: Image registry is valid
failureMessage: Image registry is not valid
category: Images
target: Container
schema:
‘$schema‘: http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema
type: object
properties:
image:
type: string
pattern: ^kubeops.net/.+$image: docker.io/http-echo:v1.0.0
我们来使用自定义的规则执行检查[root@k8s-node001 Test]# polaris audit --config config_with_custom_check.yaml --audit-path base.yaml
{
"PolarisOutputVersion": "1.0",
"AuditTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"SourceType": "Path",
"SourceName": "base.yaml",
"DisplayName": "base.yaml",
"ClusterInfo": {
"Version": "unknown",
"Nodes": 0,
"Pods": 1,
"Namespaces": 0,
"Controllers": 1
},
"Results": [
{
"Name": "http-echo",
"Namespace": "",
"Kind": "Deployment",
"Results": {},
"PodResult": {
"Name": "",
"Results": {},
"ContainerResults": [
{
"Name": "http-echo",
"Results": {
"checkImageRepo": {
"ID": "checkImageRepo",
"Message": "Image registry is not valid",
"Success": false,
"Severity": "danger",
"Category": "Images"
}
}
}
]
},
"CreatedTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
}
]
}
然后修改base.yaml的image为:image: kubeops.net/http-echo:v1.0.0
再次执行检查[root@k8s-node001 Test]# polaris audit --config config_with_custom_check.yaml --audit-path base.yaml
{
"PolarisOutputVersion": "1.0",
"AuditTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"SourceType": "Path",
"SourceName": "base.yaml",
"DisplayName": "base.yaml",
"ClusterInfo": {
"Version": "unknown",
"Nodes": 0,
"Pods": 1,
"Namespaces": 0,
"Controllers": 1
},
"Results": [
{
"Name": "http-echo",
"Namespace": "",
"Kind": "Deployment",
"Results": {},
"PodResult": {
"Name": "",
"Results": {},
"ContainerResults": [
{
"Name": "http-echo",
"Results": {
"checkImageRepo": {
"ID": "checkImageRepo",
"Message": "Image registry is valid",
"Success": true,
"Severity": "danger",
"Category": "Images"
}
}
}
]
},
"CreatedTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
}
]
}
更多用法参见总结
例如,如果你要考虑通过管道的Kubernetes清单,则kubeval可能是该管道中的第一步,因为它可以验证对象定义是否符合Kubernetes API模式。一旦此检查成功,你可以继续进行更详尽的测试,例如标准最佳实践和自定义策略。
Kube-score和Polaris是比较好的选择。
如果你有复杂的要求,并且想要自定义检查的细节,则应考虑使用copper ,config-lint和conftest。
尽管conftest和config-lint都使用更多的YAML来定义自定义验证规则,但是Copper允许访问一种真正的编程语言,这使其颇具吸引力。
但是,你应该使用其中之一并从头开始编写所有检查吗?还是应该使用Polaris并仅编写其他自定义检查?
这都取决于你自己,合适自己的才是最好的。。。
文章标题:Kubernetes YAML最佳实践和策略
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/38275.html