The normal way
Any HTML, CSS, JS or BootStrap template can be converted into a Django compatible template. The trick usually is to add {% static %} tags for the js, css and image files that we want to include in the html files. That can become a very lengthy task to do for a complete page.
Let us say that we download a template :
Template: Appco
Let us create a new django project and try to load the template into it, following are the steps that we would need to take:
Step 1
Create a new django project by:django-admin startproject MyProject
Step 2
cd into the project cd MyProject/ and start an app main:python manage.py startapp main
Step 3
Create a new folder called template inside the MyProject and a new folder main inside this templates folder. Now we need to create a folder static/ inside the MyProject/main folder and copy all the static files associated with the project there which in this case reside under the assets folder. So let us directly move the assets folder to the MyProject/main/static/ directory.
The file structure will now look something like this: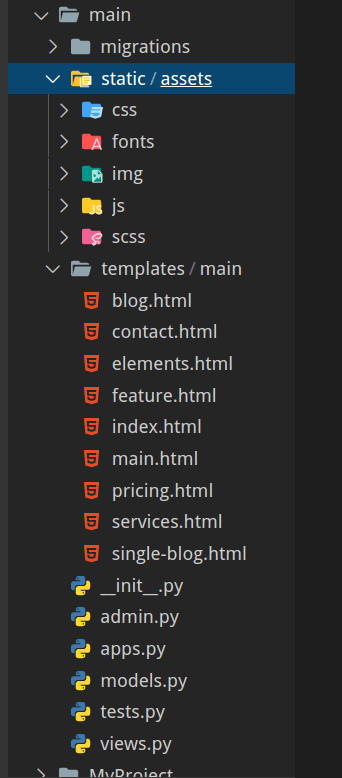
Step 4
Now for the most tiresome step we need to change every link to the css / js files in the html pages we need to render in the views.
Example:
needs to be changed to
Step 5
We need to include the line {% load static %} at the top of the html page in order to be able to use the static tag.
We need to include the app in the settings.py file by adding ‘main.apps.MainConfig‘ in the INSTALLED_APPS list and add a view for creating rendering the index page so modify the MyProject/main/views.py file and add the following:
from django.shortcuts import render
def index (request):
return render(request, ‘main/index.html‘)
and also add a url route for the same, create a file urls.py in MyProject/main/ and add the following code :
from . import views
from django.urls import path
app_name = ‘main‘
urlpatterns = [
path(‘‘, views.index, name=‘index‘),
]
now finally we need to add the following in the MyProject/MyProject/urls.py :
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path(‘admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
path(‘‘, include(‘main.urls‘, namespace=‘main‘)),
]
Step 6
Migrating the changes and running server :
python manage.py migrate python manage.py runserver
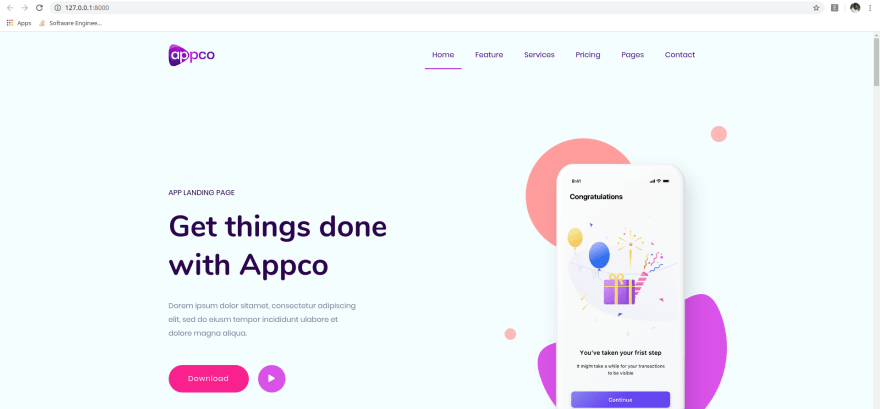
We can see that the page loads perfectly:
The djangify way
To ease up the above process, there exists a python package djangify which can be installed by:pip install djangify
The 1-3 and 5-6 steps remain the same but the package automatically does the step 4 for you, after installing the package just run the following command from your shell inside the MyProject directory:
djangify -d main/templates/main
and the tool will create a folder "Modified_files" in which there will be HTML with every CSS, JS reference converted to the django compatible reference, replacing the index.html in the main/templates/main/ with the same named file in main/templates/main/Modified_files/ we can easily see the same output as above.
The Modified_files will also contain the other html files converted into the desired format and thus can be directly used with views.py
Please feel free to drop a message at Ohuru in order to avail various development services offered by us.