函数式编程与JS异步编程、手写Promise
2021-01-05 20:27
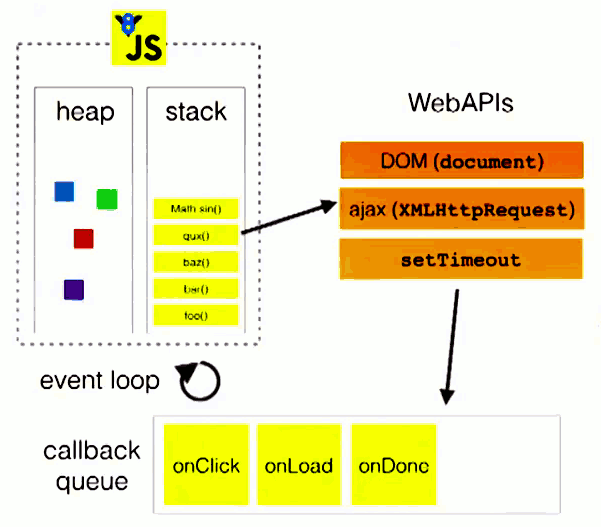
标签:time 调用 settime fir reduce 练习 完成 消息队列 fun 1. 异步编程:回调函数、事件监听、发布/订阅、Promises对象 2. EventLoop是主线程从"任务队列"中读取事件,这个过程是循环不断的,所以整个的这种运行机制又称为Event Loop(事件循环)。消息队列是一个事件的队列(也可以理解成消息的队列),IO设备完成一项任务,就在"任务队列"中添加一个事件,表示相关的异步任务可以进入"执行栈"了。 3. 宏任务 Macrotasks 就是参与了事件循环的异步任务;微任务 Microtasks 就是没有参与事件循环的“异步”任务。 修改后 要求:尽可能还原Promise中的每个API,并通过注释的方式描述思路和原理。 函数式编程与JS异步编程、手写Promise 标签:time 调用 settime fir reduce 练习 完成 消息队列 fun 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cssfirefly/p/14221439.html一、谈谈你是如何理解JS异步编程的,EventLoop、消息队列都是做什么的,什么是宏任务,什么是微任务?
代码题
一、将下面异步代码使用Promise的方式改进
let test = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
}, 100)
} catch (error) {
reject()
}
})
test.then((result) => {
return [‘11‘]
}).then((result) => {
result.push(‘22‘)
return result
}).then((result) => {
result.push(‘33‘)
return result
}).then((result) => {
console.log(result.join(‘ ‘))
})
二、基于以下代码完成下面4个函数
const _ = require("loadsh")
const fp = require("loadsh/fp")
const cars = [
{ name: "FF", horsepower: 660, dollar_value: 700000, in_stock: true },
{ name: "C12", horsepower: 650, dollar_value: 648000, in_stock: false },
{ name: "XKR-S", horsepower: 550, dollar_value: 132000, in_stock: false },
{ name: "R8", horsepower: 525, dollar_value: 114200, in_stock: false },
{ name: "One-77", horsepower: 750, dollar_value: 185000, in_stock: false },
{ name: "Huayra", horsepower: 700, dollar_value: 130000, in_stock: false },
]
// 练习1:使用函数组合fp.flowRight()重新实现下面函数
// let isLastInStock = function (cars) {
// let last_car = fp.last(cars)
// return fp.prop(‘in_stock‘, last_car)
// }
// console.log(isLastInStock(cars));
// let lastCar = function (cars) {
// return fp.last(cars)
// }
// let carProp = function (car) {
// return fp.prop(‘in_stock‘, car)
// }
// const f = _.flowRight(carProp, lastCar)
// console.log(f(cars))
// 联系2:使用fp。flowRight()、fp.prop()和fp.first()获取第一个car的name
// let firstCar = function (cars) {
// return fp.last(cars)
// }
// let carPropName = function (car) {
// return fp.prop(‘name‘, car)
// }
// const f = _.flowRight(carPropName, lastCar)
// console.log(f(cars))
// 联系3:使用帮助函数_average重构 averageDollarValue ,使用函数组合的方式实现
let _average = function (xs) {
return fp.reduce(fp.add, 0, xs) / xs.length
}//
// let averageDollarValue = function (cars) {
// let dollar_values = fp.map(function (car) {
// return car.dollar_value
// }, cars)
// return _average(dollar_values)
// }
// console.log(averageDollarValue(cars));
// 修改后:
// let dollar_values = function (cars) {
// let dollar_values = fp.map(function (car) {
// return car.dollar_value
// }, cars)
// return dollar_values
// }
// let p = fp.flowRight(_average, dollar_values)
// console.log(p(cars));
// 联系4:使用flowRight写一个sanitizeNames()函数,返回一个下滑线连接的小写字符串,把数组中的name转换为这种形式:
// 例如:sanitizeNames(["Hello World"]) => ["hello_world"]
let _underscore = fp.replace(/\W+/g, ‘_‘) //
let toLower = s => fp.lowerCase(s)
let sanitizeNames = fp.flowRight(_underscore, toLower)
console.log(sanitizeNames(["Hello World"]));
三、基于下面提供的代码,完成后续四个练习
// support.js
class Container {
static of(value) {
return new Container(value)
}
constructor(value) {
this._value = value
}
map(fn) {
return Container.of(fn(this._value))
}
}
class Maybe {
static of(x) {
return new Maybe(x)
}
isNothing() {
return this._value === null || this._value === undefined
}
constructor(x) {
this._value = x
}
map(fn) {
return this.isNothing() ? this : Maybe.of(fn(this._value))
}
}
module.exports = { Maybe, Container }
const fp = require("loadsh/fp")
const { Maybe, Container } = require("./support")
// console.log(Maybe);
let maybe = Maybe.of([5, 6, 1])
let ex1 = (num) => {
// 函数实现
return maybe.map((x) => {
let a = fp.map(val => {
return fp.add(val, num)
}, x)
return a
})
}
console.log(ex1(1));
// 练习2:实现一个函数ex2,能够使用fp.first获取列表的第一个元素
let xs = Container.of([‘do‘, ‘ray‘, ‘me‘, ‘fa‘, ‘so‘, ‘la‘, ‘ti‘, ‘do2‘])
let ex2 = () => {
// 函数实现
return xs.map(x => {
return fp.first(x)
})
}
console.log(ex2());
// 练习3:实现一个函数ex3,使用safeProp和fp.first找到user的名字的首字母
let safeProp = fp.curry(function (x, o) {
return Maybe.of(o[x])
})
let user = { id: 2, name: ‘Albert‘ }
console.log(safeProp(‘name‘, user));
let ex3 = () => {
// 函数实现
return safeProp(‘name‘, user).map(x => fp.first(x))
}
console.log(ex3());
// 练习4:使用Maybe重写ex4,不要有if语句
let ex4 = function (n) {
// if (n) {
// return parseInt(n)
// }
// 实现
return n ? parseInt(n) : undefined
}
四、手写实现MyPromise源码
const PENDING = ‘pending‘; // 等待
const FULFILLED = ‘fulfilled‘; // 成功
const REJECTED = ‘rejected‘; // 失败
class MyPromise {
constructor (executor) {
try {
executor(this.resolve, this.reject)
} catch (e) {
this.reject(e);
}
}
// promsie 状态
status = PENDING;
// 成功之后的值
value = undefined;
// 失败后的原因
reason = undefined;
// 成功回调
successCallback = [];
// 失败回调
failCallback = [];
resolve = value => {
// 如果状态不是等待 阻止程序向下执行
if (this.status !== PENDING) return;
// 将状态更改为成功
this.status = FULFILLED;
// 保存成功之后的值
this.value = value;
// 判断成功回调是否存在 如果存在 调用
// this.successCallback && this.successCallback(this.value);
while(this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()()
}
reject = reason => {
// 如果状态不是等待 阻止程序向下执行
if (this.status !== PENDING) return;
// 将状态更改为失败
this.status = REJECTED;
// 保存失败后的原因
this.reason = reason;
// 判断失败回调是否存在 如果存在 调用
// this.failCallback && this.failCallback(this.reason);
while(this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()()
}
then (successCallback, failCallback) {
// 参数可选
successCallback = successCallback ? successCallback : value => value;
// 参数可选
failCallback = failCallback ? failCallback: reason => { throw reason };
let promsie2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
// 判断状态
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
// 判断 x 的值是普通值还是promise对象
// 如果是普通值 直接调用resolve
// 如果是promise对象 查看promsie对象返回的结果
// 再根据promise对象返回的结果 决定调用resolve 还是调用reject
resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject)
}catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0)
}else if (this.status === REJECTED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
// 判断 x 的值是普通值还是promise对象
// 如果是普通值 直接调用resolve
// 如果是promise对象 查看promsie对象返回的结果
// 再根据promise对象返回的结果 决定调用resolve 还是调用reject
resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject)
}catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0)
} else {
// 等待
// 将成功回调和失败回调存储起来
this.successCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
// 判断 x 的值是普通值还是promise对象
// 如果是普通值 直接调用resolve
// 如果是promise对象 查看promsie对象返回的结果
// 再根据promise对象返回的结果 决定调用resolve 还是调用reject
resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject)
}catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0)
});
this.failCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
// 判断 x 的值是普通值还是promise对象
// 如果是普通值 直接调用resolve
// 如果是promise对象 查看promsie对象返回的结果
// 再根据promise对象返回的结果 决定调用resolve 还是调用reject
resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject)
}catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0)
});
}
});
return promsie2;
}
finally (callback) {
return this.then(value => {
return MyPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value);
}, reason => {
return MyPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => { throw reason })
})
}
catch (failCallback) {
return this.then(undefined, failCallback)
}
static all (array) {
let result = [];
let index = 0;
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
function addData (key, value) {
result[key] = value;
index++;
if (index === array.length) {
resolve(result);
}
}
for (let i = 0; i ) {
let current = array[i];
if (current instanceof MyPromise) {
// promise 对象
current.then(value => addData(i, value), reason => reject(reason))
}else {
// 普通值
addData(i, array[i]);
}
}
})
}
static resolve (value) {
if (value instanceof MyPromise) return value;
return new MyPromise(resolve => resolve(value));
}
}
function resolvePromise (promsie2, x, resolve, reject) {
if (promsie2 === x) {
return reject(new TypeError(‘Chaining cycle detected for promise #
文章标题:函数式编程与JS异步编程、手写Promise
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/40340.html