Java-链表知识梳理
2021-01-08 11:31
标签:pre 16px font let string 取数据 last inf turn 链表将每个对象存放在独立的节点中,每个节点还存放着序列中下一个节点的引用。在Java中,所有链表实际上都是双向链接的——即每个节点还存放着指向前驱节点的引用。 双向链表结构如下所示: 获取数据慢,需要遍历查找;插入和删除快,只需要修改前后的链接。 1、定义节点类: 2、实现单链表: 3、方法测试: 4、控制台输出: Java-链表知识梳理 标签:pre 16px font let string 取数据 last inf turn 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/happy2333/p/12966139.html 一、链表的概念:
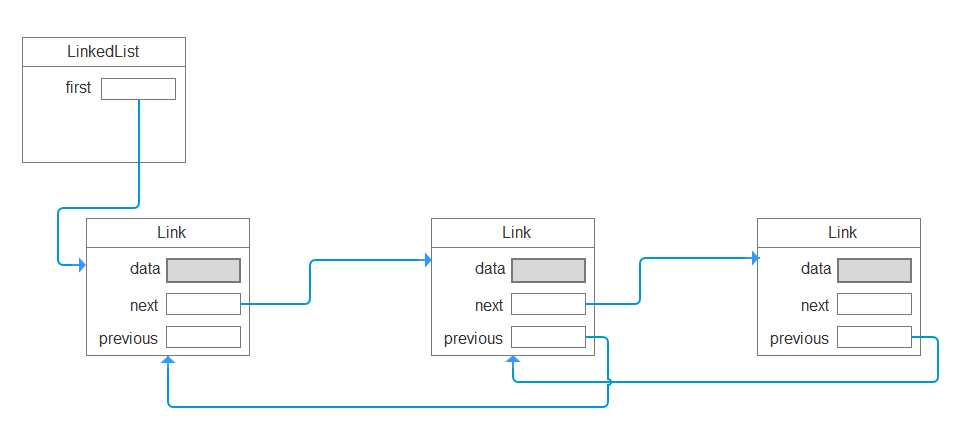
二、链表的特点:
三、单链表的实现:
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
public class SingleLinkedList {
ListNode head = null;
/**
* 添加头节点
*/
public void addHead(int x){
ListNode node = new ListNode(x);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
/**
* 添加尾节点
*/
public void addLast(int x){
ListNode node = new ListNode(x);
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = node;
}
/**
* 链表长度
*/
public int length(){
int length = 0;
ListNode tem = head;
while (tem != null){
length++;
tem = tem.next;
}
return length;
}
/**
* 打印节点值
*/
public void printNode(){
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null){
System.out.print(node.val+",");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 根据下标删除节点
* @param index
*/
public void deleteNode(int index){
ListNode node = head;
if (indexlength()){
System.out.println("下标错误!!!!");
return;
}else if (index == 0){
head = head.next;
}else {
for (int i = 1; i ) {
node = node.next;
}
//跳过index项的node
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList linkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
linkedList.addHead(2);
linkedList.addHead(3);
linkedList.addLast(1);
System.out.println("------添加节点------");
linkedList.printNode();
linkedList.deleteNode(1);
System.out.println("------删除节点-------");
linkedList.printNode();
System.out.println(linkedList.length()+"---节点长度----");
}
------添加节点------
3,2,1,
------删除节点-------
3,1,
2---节点长度----
上一篇:jq 删除数组中的某一项
下一篇:Spring事件的应用