【SpringBoot】SpringBoot 入门
2021-01-14 03:11
标签:tag toc map ring init mpi single ++ 容器 SpringBoot来简化Spring应用开发,约定大于配置,去繁从简,just run就能创建一个独立的,产品级别的应用。 J2EE笨重的开发,繁多的配置、地下的开发效率、复杂的部署流程、第三方技术集成难度大。 Spring全家桶时代。 Spring Boot -> J2EE一站式解决方案 Spring Cloud ->分布式整体解决方案 https://spring.io/projects 可以访问spring的所有项目 intellij/eclipse 修改idea中的maven设置 maven设置:在setting.xml配置文件的profilers标签添加 实现一个功能:浏览器发送一个请求,并处理响应 将这个应用打成jar包,直接使用java -jar的命令来进行执行 SpringBoot的版本仲裁中心; 以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要版本号的,(没有在dependencies里面管理的依赖需要声明) spring-boot-starter-web: ? spring-boot-starter:spring-boot场景启动器,帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件; https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.2.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter 可以查看所有的启动器模块 Spring Boot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做出一个个的starter,只需要在项目里引入这些starter相关场景所需的依赖就会导入进来。 Spring Boot应用标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类,SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用。 ? 标注在某个类上表示这是一个Spring Boot的配置类 以前我们需要配置的东西,SpringBoot帮我们自动配置;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能;这样自动配置才能生效; @AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包 @Import({Registrar.class}) Spring的底层注解@Import,给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由Registrar; 将主配置类的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器 @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) 给容器中导入组件 AutoConfigurationImportSelector:需要导入哪些组件的选择器, 将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回;这些组件就会被添加到容器中 会给容器导入非常多的自动配置类;就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能等的工作。 从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效,帮我们进行自动配置工作;以前需要我们自己配置的东西,自动配置类帮我们做了。 J2EE的整体整合和配置都在autoconfig包下面。 IDE都支持使用Spring的项目创建向导快速创建一个SpringBoot项目 选择我们需要的模块;向导会联网创建Spring Boot项目 默认生成的Spring Boot项目; 【SpringBoot】SpringBoot 入门 标签:tag toc map ring init mpi single ++ 容器 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dream-to-pku/p/12944000.htmlSpringBoot 入门
一、背景
二、解决
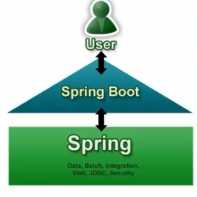
三、优点
四、环境准备
五、HelloWorld
1.创建一个maven工程
2.导入spring boot的相关依赖
3.编写一个主程序,启动Spring Boot的应用
package com.slp;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序,说明这是一个springboot程序
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldMainApplication {
/**
* 启动程序
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class,args);
}
}
4.编写实现
package com.slp.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}
5.测试
6.简化部署
六、Hello World探究
1.pom文件
1.1 父项目
1.2 导入的依赖
2.主程序类
package com.slp;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序,说明这是一个springboot程序
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldMainApplication {
/**
* 启动程序
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class,args);
}
}
2.1 @SpringBootApplication:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
2.2 @SpringBootConfiguration:Spring Boot的配置类:
2.3 @EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import({Registrar.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AutoConfigurationPackages.register(registry, (new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata)).getPackageName());
}
public static void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String... packageNames) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(BEAN)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(BEAN);
ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArguments = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
constructorArguments.addIndexedArgumentValue(0, addBasePackages(constructorArguments, packageNames));
} else {
GenericBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(AutoConfigurationPackages.BasePackages.class);
beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(0, packageNames);
beanDefinition.setRole(2);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN, beanDefinition);
}
}
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
}
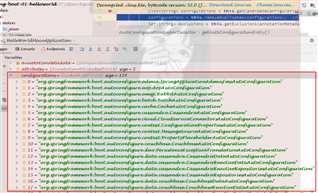
private static Map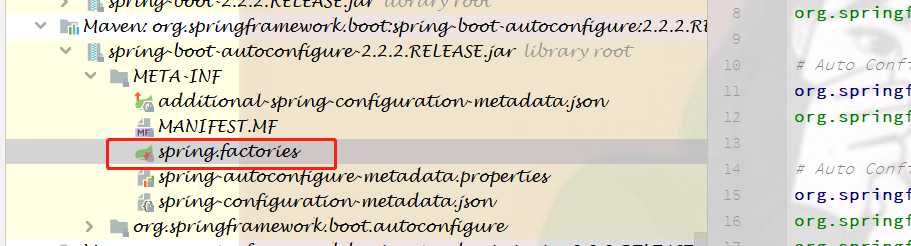
七、使用Spring Initializer快速创建Spring Boot项目
文章标题:【SpringBoot】SpringBoot 入门
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/41586.html