js实现图的遍历之广度优先搜索
2021-01-16 14:15
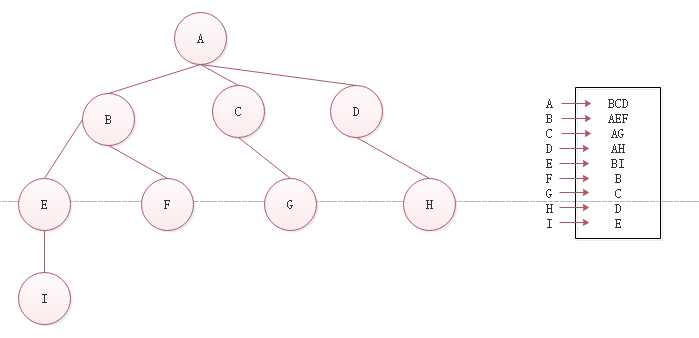
标签:default pre res 结果 ++ this loading 广度优先搜索 white 1.图 图是一种非线性数据结构,是网络模型的抽象模型,图是一组由边连接的节点。 2.图的组成 一个图G = (V,E),V:一组顶点,E:一组边 3.强连通图 任何两个节点,它们之间都有路径到达,称为强连通图 4.邻接矩阵 5.领接表 6.字典 我采用是领接表的方法,所以这里我采用字典来存储,每个顶点和每个顶点所对应的边。 7.创建图 8.图中添加节点 9.结果 10.广度优先搜索(BFS) 图遍历算法的思想是必须追踪每个第一次访问的节点,并且追踪有哪些节点还没有被完全探索。BFS和DFS都需要指出第一个被访问的节点 这里用三种颜色,来表示节点访问状态。 白色:表示节点还没有访问 灰色:节点访问过,但是还没有完全探索过 黑色:节点访问过,已完全探索过 使用一个Colors变量来存储三种颜色 初始化所有节点颜色,参数为一个数组,返回一个对象 BFS代码 结果 11.改进版BFS 结果 12.所有代码 js实现图的遍历之广度优先搜索 标签:default pre res 结果 ++ this loading 广度优先搜索 white 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/MySweetheart/p/13376360.html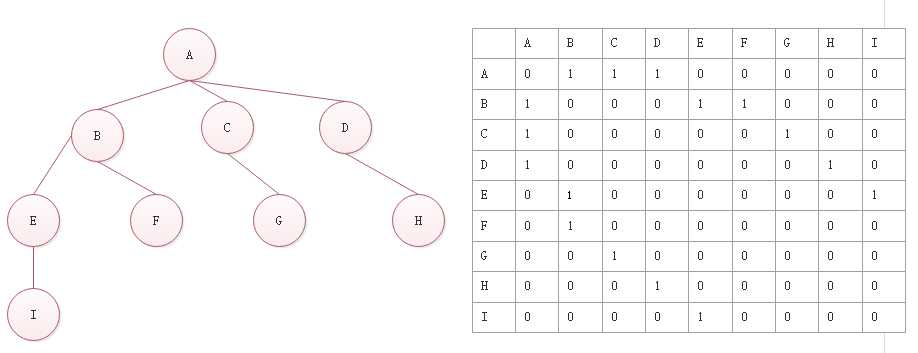
function defaultToString(item){
if(item == null){
return ‘null‘;
}
if(item == undefined){
return ‘undefined‘;
}
if(typeof item == ‘string‘ || item instanceof String){
return item;
}
return `${item}`;
}
//这个类专门用来保存节点点值和相邻的节点
class ValuePair{
constructor(key,value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
//字典类
class Dictionary{
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString){//接受外面的函数
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;//这里把所有的键名全部转换字符串,方便检索
this.table = {};//专门存储数据
}
set(key,value){//设置节点和相邻的节点的方法
if(key != null && value != null){
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
this.table[tableKey] = new ValuePair(key,value);//{键名:{key:键名;value:相邻的节点}}
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key){//返回节点所相连的节点
const valuePair = this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
return valuePair == null?undefined:valuePair.value;
}
hasKey(key){//判断字典中有没有这个节点
return this.table[this.toStrFn(key)] != null;
}
remove(key){//移除这个节点
if(this.hasKey(key)){
delete this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
return true;
}
return false;
}
clear(){//清除字典的所有内容
this.table = {};
}
size(){//返回字典的节点的个数
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
isEmpty(){//判断字典是否为空
return this.size() === 0;
}
keys(){//获取字典的所有的节点的方法
return this.keyValues().map(valuePair => valuePair.key);
}
keyValues(){//获取字典的所有的边的方法
const valuePair = [];
for(let key in this.table){
if(this.hasKey(key)){
valuePair.push(key);
}
}
return valuePair;
}
}
class Graph{
constructor(isDirected = false){
this.isDirected = isDirected;//是否为有向图
this.vertices = [];//存储所有节点
this.adjList = new Dictionary();//用字典来存储邻接表
}
addVertex(v){//添加顶点
if(!this.vertices.includes(v)){
this.vertices.push(v);
this.adjList.set(v,[]);//使用字典的set方法,来存储节点,和邻接节点,这里邻接节点会有很多,所以用数组来存储
}
}
addEdge(v,w){//给节点添加它的邻接节点
if(!this.vertices.includes(v)){
this.addVertices(v);
}
if(!this.vertices.includes(w)){
this.addVertices(w);
}
this.adjList.get(v).push(w);//{key:v;value:[]},在v所对应的数组里面push它的邻接节点
if(!this.isDirected){//有向图就不添加
this.adjList.get(w).push(v);
}
}
getVertices(){//返回所有节点
return this.vertices;
}
getAdjList(){//返回存储邻接表的字典
return this.adjList;
}
toString(){//打印邻接表
let s =‘‘;
for(let i = 0; i this.vertices.length; i++){
s+=`${this.vertices[i]}->`;
let value = this.adjList.get(this.vertices[i]);
for(let j =0; j ){
s+=`${value[j]}`;
}
s+="\n";
}
return s;
}
}
const printVertex = (value) => console.log(value);
const myVertices = [‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘, ‘D‘, ‘E‘, ‘F‘, ‘G‘, ‘H‘, ‘I‘];
const graph = new Graph();
for (let i = 0; i ) {
graph.addVertex(myVertices[i]);
}
graph.addEdge(‘A‘, ‘B‘);
graph.addEdge(‘A‘, ‘C‘);
graph.addEdge(‘A‘, ‘D‘);
graph.addEdge(‘C‘, ‘D‘);
graph.addEdge(‘C‘, ‘G‘);
graph.addEdge(‘D‘, ‘G‘);
graph.addEdge(‘D‘, ‘H‘);
graph.addEdge(‘B‘, ‘E‘);
graph.addEdge(‘B‘, ‘F‘);
graph.addEdge(‘E‘, ‘I‘);

Colors={
WHITE:0,//还没有访问的
GREY:1,//已经访问过的,但是还没有完全探索的
BLACK:2 //已经访问过的,并且已经全部探索过的
}
const initializeColor = vertices =>{
const color = {};
for(let i =0; i ){
color[vertices[i]] = Colors.WHITE;
}
return color;
}
const breadthFirstSearch = (graph,startVertex,callback)=>{
const vertices = graph.getVertices();
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();
let color = initializeColor(vertices);
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(startVertex);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
let v = queue.dequeue();
color[v] = Colors.GREY;
let neighbor = adjList.get(v);
for(let i = 0; i ){
let w = neighbor[i];
if(color[w] == Colors.WHITE){//还没有访问,就执行
queue.enqueue(w);
color[w] = Colors.GREY;
}
}
color[v] = Colors.BLACK;
if(callback){
callback(v);
}
}
}

class Stack{
constructor(){
this.item = {};
this.count = 0;
}
push(key){
this.item[this.count] = key;
this.count++;
}
pop(){
if(this.isEmpty()){
return ‘stack is null‘;
}
this.count--;
let result = this.item[this.count];
delete this.item[this.count];
return result;
}
isEmpty(){
return this.size() === 0;
}
size(){
return this.count;
}
peek(){
return this.item[this.count-1];
}
}
const fromVertex = myVertices[0];
for(let i = 1; i ){
const vertice = myVertices[i];
const path = new Stack();
for(let v = vertice; v != fromVertex; v = shortestPathA.predecessors[v]){
path.push(v);
}
path.push(fromVertex);
let s = path.pop();
while(!path.isEmpty()){
s += `->${path.pop()}`;
}
console.log(s);
}
//用来表示每个节点的颜色
Colors={
WHITE:0,//还没有访问的
GREY:1,//已经访问过的,但是还没有完全探索的
BLACK:2 //已经访问过的,并且已经全部探索过的
}
//初始化节点的颜色,让它们都为白色,vertices是一个数组,专门用来存储节点
const initializeColor = vertices =>{
const color = {};
for(let i =0; i ){
color[vertices[i]] = Colors.WHITE;
}
return color;
}
class Queue{
constructor(){
this.queue = {};
this.lowerCast = 0;
this.biggerCast = 0;
}
enqueue(key){
this.queue[this.biggerCast] = key;
this.biggerCast++;
}
dequeue(){
if(this.isEmpty())return;
let item = this.queue[this.lowerCast];
delete this.queue[this.lowerCast];
this.lowerCast++;
return item;
}
isEmpty(){
return this.size() === 0;
}
size(){
return this.biggerCast - this.lowerCast;
}
}
function defaultToString(item){
if(item == null){
return ‘null‘;
}
if(item == undefined){
return ‘undefined‘;
}
if(typeof item == ‘string‘ || item instanceof String){
return item;
}
return `${item}`;
}
//这个类专门用来保存节点点值和相邻的节点
class ValuePair{
constructor(key,value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
//字典类
class Dictionary{
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString){//接受外面的函数
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;//这里把所有的键名全部转换字符串,方便检索
this.table = {};//专门存储数据
}
set(key,value){//设置节点和相邻的节点的方法
if(key != null && value != null){
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
this.table[tableKey] = new ValuePair(key,value);//{键名:{key:键名;value:相邻的节点}}
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key){//返回节点所相连的节点
const valuePair = this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
return valuePair == null?undefined:valuePair.value;
}
hasKey(key){//判断字典中有没有这个节点
return this.table[this.toStrFn(key)] != null;
}
remove(key){//移除这个节点
if(this.hasKey(key)){
delete this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
return true;
}
return false;
}
clear(){//清除字典的所有内容
this.table = {};
}
size(){//返回字典的节点的个数
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
isEmpty(){//判断字典是否为空
return this.size() === 0;
}
keys(){//获取字典的所有的节点的方法
return this.keyValues().map(valuePair => valuePair.key);
}
keyValues(){//获取字典的所有的边的方法
const valuePair = [];
for(let key in this.table){
if(this.hasKey(key)){
valuePair.push(key);
}
}
return valuePair;
}
}
class Graph{
constructor(isDirected = false){
this.isDirected = isDirected;//是否为有向图
this.vertices = [];//存储所有节点
this.adjList = new Dictionary();//用字典来存储邻接表
}
addVertex(v){//添加顶点
if(!this.vertices.includes(v)){
this.vertices.push(v);
this.adjList.set(v,[]);//使用字典的set方法,来存储节点,和邻接节点,这里邻接节点会有很多,所以用数组来存储
}
}
addEdge(v,w){//给节点添加它的邻接节点
if(!this.vertices.includes(v)){
this.addVertices(v);
}
if(!this.vertices.includes(w)){
this.addVertices(w);
}
this.adjList.get(v).push(w);//{key:v;value:[]},在v所对应的数组里面push它的邻接节点
if(!this.isDirected){//有向图就不添加
this.adjList.get(w).push(v);
}
}
getVertices(){//返回所有节点
return this.vertices;
}
getAdjList(){//返回存储邻接表的字典
return this.adjList;
}
toString(){//打印邻接表
let s =‘‘;
for(let i = 0; i this.vertices.length; i++){
s+=`${this.vertices[i]}->`;
let value = this.adjList.get(this.vertices[i]);
for(let j =0; j ){
s+=`${value[j]}`;
}
s+="\n";
}
return s;
}
}
const myVertices = [‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘, ‘D‘, ‘E‘, ‘F‘, ‘G‘, ‘H‘, ‘I‘];
const graph = new Graph();
for (let i = 0; i ) {
graph.addVertex(myVertices[i]);
}
graph.addEdge(‘A‘, ‘B‘);
graph.addEdge(‘A‘, ‘C‘);
graph.addEdge(‘A‘, ‘D‘);
graph.addEdge(‘C‘, ‘D‘);
graph.addEdge(‘C‘, ‘G‘);
graph.addEdge(‘D‘, ‘G‘);
graph.addEdge(‘D‘, ‘H‘);
graph.addEdge(‘B‘, ‘E‘);
graph.addEdge(‘B‘, ‘F‘);
graph.addEdge(‘E‘, ‘I‘);
console.log( graph.toString());
const breadthFirstSearch = (graph,startVertex,callback)=>{
const vertices = graph.getVertices();
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();
let color = initializeColor(vertices);
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(startVertex);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
let v = queue.dequeue();
color[v] = Colors.GREY;
let neighbor = adjList.get(v);
for(let i = 0; i ){
let w = neighbor[i];
if(color[w] == Colors.WHITE){//还没有访问,就执行
queue.enqueue(w);
color[w] = Colors.GREY;
}
}
color[v] = Colors.BLACK;
if(callback){
callback(v);
}
}
}
const printVertex = (value) => console.log(value);
breadthFirstSearch(graph,myVertices[0],printVertex);
const BFS = (graph,startVertex) =>{
const vertices = graph.getVertices();//获取图的所有节点
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();//获取图的字典
const color = initializeColor(vertices);//初始化每个节点的颜色
const queue = new Queue();
const distance = {};
const predecessors = {};
queue.enqueue(startVertex);//把顶点放入队列
for(let i = 0; i ){
distance[vertices[i]] = 0;
predecessors[vertices[i]] = null;
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
let u = queue.dequeue();
color[u] = Colors.GREY;
let neighbor = adjList.get(u);
for(let j =0; j ){
let w = neighbor[j]
if(color[w] == Colors.WHITE){
queue.enqueue(w);
distance[w] = distance[u]+1;
predecessors[w] = u;
}
}
color[u] = Colors.BLACK;
}
return {
distance,
predecessors
}
}
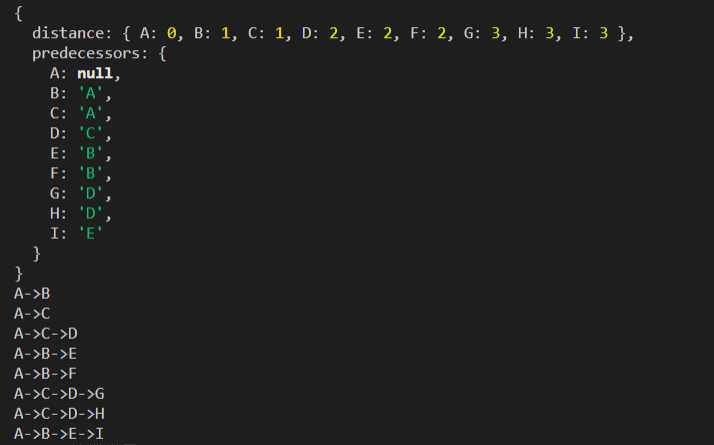
const shortestPathA = BFS(graph,myVertices[0]);
console.log(shortestPathA);
class Stack{
constructor(){
this.item = {};
this.count = 0;
}
push(key){
this.item[this.count] = key;
this.count++;
}
pop(){
if(this.isEmpty()){
return ‘stack is null‘;
}
this.count--;
let result = this.item[this.count];
delete this.item[this.count];
return result;
}
isEmpty(){
return this.size() === 0;
}
size(){
return this.count;
}
peek(){
return this.item[this.count-1];
}
}
const fromVertex = myVertices[0];
for(let i = 1; i ){
const vertice = myVertices[i];
const path = new Stack();
for(let v = vertice; v != fromVertex; v = shortestPathA.predecessors[v]){
path.push(v);
}
path.push(fromVertex);
let s = path.pop();
while(!path.isEmpty()){
s += `->${path.pop()}`;
}
console.log(s);
}