标签:sel nan eal src 总数 obj 方式 就会 不同的
一.什么是泛型
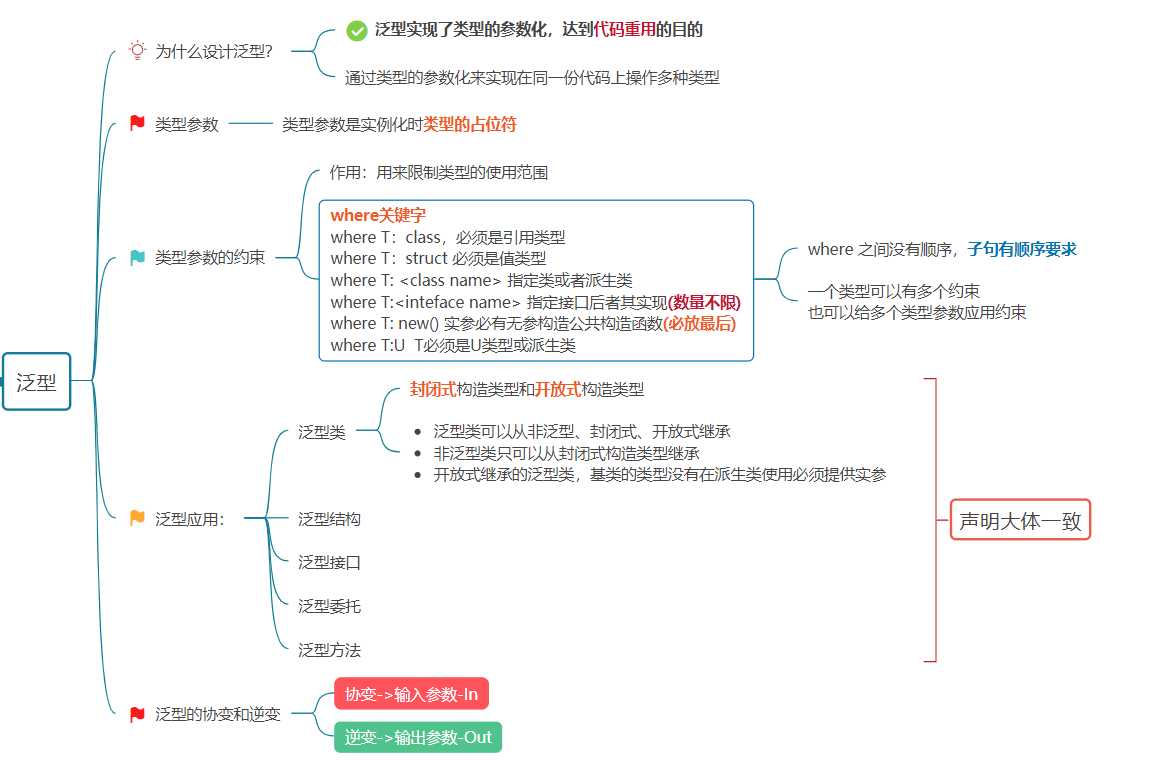
泛型(Generic)是C#语言2.0、通用语言运行时(CLR)2.0、.NET Framework2.0推出来的新特性。
泛型为.NET框架引入类型参数(Type Parameters)的概念。类型参数使得设计类和方法时,不必确定一个或多个参具体数。
具体的参数类型可延迟到声明和使用时再确定。避免了运行时类型转换或装箱操作的代价和风险。
二.泛型的使用和对比
2.1.CommandMethod(普通方法)
1 ///
2 /// 打印一个Int值
3 ///
4 /// 因为方法声明的时候,写死了参数类型
5 ///
6 ///
7 public static void ShowInt(int iParameter)
8 {
9 Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(CommonMethod).Name, iParameter.GetType().Name, iParameter);
10
11 }
12 ///
13 /// 打印一个string值
14 ///
15 ///
16 public static void ShowString(string sParameter)
17 {
18 Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(CommonMethod).Name, sParameter.GetType().Name, sParameter);
19 }
20 ///
21 /// 打印一个DateTime值
22 ///
23 ///
24 public static void ShowDateTime(DateTime dtParameter)
25 {
26 Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(CommonMethod).Name, dtParameter.GetType().Name, dtParameter);
27 }
2.2.ObjectMethod(基类方法)
1 ///
2 /// 打印一个object值
3 ///
4 /// object引用类型 假如传个值类型 会有装箱拆箱 性能损失
5 /// 类型不安全
6 ///
7 ///
8 public static void ShowObject (object oParameter)
9 {
10 Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(CommonMethod).Name, oParameter.GetType().Name, oParameter);
11
12 //Console.WriteLine($"{((People)oParameter).Id}_{((People)oParameter).Name}");
13 }
2.3.GenericMethod(泛型方法)
1 ///
2 /// 2.0推出的新语法
3 /// 一个方法满足不同参数类型 做相同的事
4 ///
5 /// 延迟声明:把参数类型的声明推迟到调用
6 /// 不是语法糖,而是由框架升级提供的功能
7 ///
8 /// 没有写死参数类型,调用的时候才指定的类型
9 ///
10 /// T/S 不要用关键字 也不要跟别的类型冲突
11 ///
12 public static void Show(T tParameter)
13 {
14 Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(GenericMethod).Name, tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter.ToString());
15 }
2.3调用
1 int iValue = 123;
2 string sValue = "456";
3 DateTime dtValue = DateTime.Now;
4 object oValue = "789";
5 Console.WriteLine("*********普通方法************");
6 CommonMethod.ShowInt(iValue);
7 CommonMethod.ShowString(sValue);
8 CommonMethod.ShowDateTime(dtValue);
9 CommonMethod.ShowObject(oValue);
10
11 Console.WriteLine("*********通过Object************");//.NET Framework1.0 1.1
12 /*为什么可以传string、int、datetime、class等的原因
13 1. object类型是一切类型的父类
14 2. 通过继承,子类拥有父类的一切属性和行为;任何父类出现的地方,都可以用子类来代替
15 */
16 CommonMethod.ShowObject(iValue);
17 CommonMethod.ShowObject(sValue);
18 CommonMethod.ShowObject(dtValue);
19
20 Console.WriteLine("***********通过泛型***************");
21 GenericMethod.Showint>(iValue);//需要指定类型参数
22 GenericMethod.Showstring>(sValue);//必须吻合
23 GenericMethod.Show(dtValue);//能省略自动推算
24 GenericMethod.Showobject>(oValue);
2.4.性能对比
1 ///
2 /// 性能监视类
3 ///
4 public class Monitor
5 {
6 public static void Show()
7 {
8 int iValue = 12345;
9 long commonSecond = 0;
10 long objectSecond = 0;
11 long genericSecond = 0;
12
13 {
14 //提供一组方法和属性,可用于准确地测量运行时间
15 Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
16 //开始或继续测量某个时间间隔的运行时间。
17 stopwatch.Start();
18 for (int i = 0; i 100000000; i++)
19 {
20 ShowInt(iValue);
21 }
22 // 停止测量某个时间间隔的运行时间。
23 stopwatch.Stop();
24 //获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位)。
25 commonSecond = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
26 }
27 {
28 Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
29 stopwatch.Start();
30 for (int i = 0; i 100000000; i++)
31 {
32 ShowObject(iValue);
33 }
34 stopwatch.Stop();
35 objectSecond = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
36 }
37 {
38 Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
39 stopwatch.Start();
40 for (int i = 0; i 100000000; i++)
41 {
42 Show(iValue);
43 }
44 stopwatch.Stop();
45 genericSecond = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
46 }
47
48 Console.WriteLine($"普通方法耗时:{commonSecond} Object方法耗时:{objectSecond} Generic方法耗时:{genericSecond}");
49 }
50
51 private static void ShowInt(int iParameter)
52 {
53
54 }
55
56 private static void ShowObject(object oParameter)
57 {
58
59 }
60
61 private static void Show(T tParameter)
62 {
63
64 }
65
66 #region Stopwatch详解
67 /*
68 获取以每秒计时周期数表示的计时器频率。此字段为只读。
69 public static readonly long Frequency;
70 指示计时器是否基于高分辨率性能计数器。此字段为只读。
71 public static readonly bool IsHighResolution;
72 初始化 System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch 类的新实例。
73 public Stopwatch();
74 获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间。
75 返回结果:
76 一个只读的 System.TimeSpan,用于表示当前实例测量得出的总运行时间。
77 public TimeSpan Elapsed { get; }
78 获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(以毫秒为单位)。
79 返回结果:
80 一个只读长整型,表示当前实例测量得出的总毫秒数。
81 public long ElapsedMilliseconds { get; }
82 获取当前实例测量得出的总运行时间(用计时器计时周期表示)。
83 返回结果:
84 一个只读长整型,表示当前实例测量得出的计时器计时周期的总数。
85 public long ElapsedTicks { get; }
86 获取一个指示 System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch 计时器是否在运行的值。
87 返回结果:
88 如果 System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch 实例当前正在运行,并且在对某个时间间隔的运行时间进行测量,则该值为 true;否则为 false。
89 public bool IsRunning { get; }
90 获取计时器机制中的当前最小时间单位数。
91 返回结果:
92 一个长整型,表示基础计时器机制中的计时周期计数器值。
93 public static long GetTimestamp();
94 对新的 System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch 实例进行初始化,将运行时间属性设置为零,然后开始测量运行时间。
95 返回结果:
96 刚刚开始测量运行时间的 System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch。
97 public static Stopwatch StartNew();
98 停止时间间隔测量,并将运行时间重置为零。
99 public void Reset();
100 停止时间间隔测量,将运行时间重置为零,然后开始测量运行时间。
101 public void Restart();
102 开始或继续测量某个时间间隔的运行时间。
103 public void Start();
104 停止测量某个时间间隔的运行时间。
105 public void Stop();
106 */
107 #endregion
108 }
109 }
2.6对比结果

三.泛型的原理
泛型在编译的时候,类型是不明确的,类型参数会被系统编译成占位符 (~),在运行时,Jit即时编译会根据程序中调用泛型方法时候给它指定的类型参数替换过来
四. 泛型类、泛型方法、泛型接口、泛型委托
1 ///
2 /// 泛型类
3 /// 一个类来满足不同的具体类型,来做相同的事
4 ///
5 public class GenericClass 6 {
7
8 }
9
10 public class GenericClasswhere T:People where S:Hunan
11 {
12
13 }
14
15 ///
16 /// 泛型接口
17 /// 一个接口来满足不同的具体类型的接口,来做相同的事
18 ///
19 public interface IGenericInterface//where T:People
20 {
21
22 }
23
24 public class CommonClass:GenericClassint>//使用泛型必须指定类型
25 {
26
27 }
28
29 public class GenericClassChild:GenericClass30 {
31
32 }
33
34 ///
35 /// 泛型委托
36 ///
37 ///
38 public delegate void GenericDelegate();
五.泛型约束
泛型定义中的 where 子句指定对用作泛型类型、方法、委托或本地函数中类型参数的参数类型的约束。
约束可指定接口、基类或要求泛型类型为引用、值或非托管类型。 它们声明类型参数必须具备的功能。
1 ///
2 /// 约束类
3 /// 泛型:不同的参数类型都能进来;任何类型都来进来,无法准确定位
4 /// 没有约束,也就没有自由
5 /// 泛型约束-----基类约束(不能是sealed)
6 /// 1.可以使用基类的一切属性方法---权利
7 /// 2.强制保证T一定是People或者People的子类
8 ///
9 ///
10 /// 为什么不能用int(Int32)?
11 ///“int”不是有效的约束。作为约束使用的类型必须是接口、非密封类或类型参数 而Int32是密封类(sealed)
12 ///
13 public class Constraint
14 {
15 public static void Show(T tParameter)
16 where T : People,ISports,IWork,new()//基类约束
17 {
18 Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(GenericMethod).Name, tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter.ToString());
19
20 Console.WriteLine($"{tParameter.Id}_{tParameter.Name}");
21 tParameter.Hi();
22 tParameter.Pingpang();
23 tParameter.Work();
24 }
25
26 ///
27 /// 为什么不用基类
28 ///
29 ///
30 public static void ShowBase(People tParameter)//因为约束可以叠加 更灵活
31 {
32 Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}", typeof(GenericMethod).Name, tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter.ToString());
33 Console.WriteLine($"{tParameter.Id}_{tParameter.Name}");
34 tParameter.Hi();
35 }
36
37 public static T InterfaceGet(T t)
38 where T : ISports //接口约束
39 {
40 t.Pingpang();
41 return t;
42 }
43
44 public static T ClassGet(T t)
45 where T : class //引用类型约束:保证引用类型
46 {
47 T tNew = null;
48 return t;
49 }
50
51 public static T StructGet(T t)
52 where T : struct //值类型约束
53 {
54 T tNew = default(T); //会根据T的不同 赋予默认值
55 return t;
56 }
57
58 public static T NewGet(T t)
59 where T : new() //无参数构造函数约束
60 {
61 T tNew = new T();
62 return t;
63 }
64 }
六.协变和逆变
可变性是以一种类型安全的方式,将一个对象当做另一个对象来使用。如果不能将一个类型替换为另一个类型,那么这个类型就称之为:不变量。
协变和逆变是两个相互对立的概念:
- 如果某个返回的类型可以由其派生类型替换,那么这个类型就是支持协变的
- 如果某个参数类型可以由其基类替换,那么这个类型就是支持逆变的
1 ///
2 /// .NET 4.0出现的
3 /// 只能放在接口或者委托的泛型参数前面
4 /// out 协变covariant 修饰返回值
5 /// in 逆变contravariant 修饰传入参数
6 ///
7 public class CCTest
8 {
9 public static void Show()
10 {
11 {
12 Bird bird1 = new Bird();
13 Bird bird2 = new Sparrow();
14 Sparrow sparrow = new Sparrow();
15 //Sparrow sparrow=new Bird();//不合理 鸟不一定是麻雀
16 }
17
18 {
19 List birdList1 = new List();
20 //两个不同的类型 没有父子关系
21 //List birdList2 = new List();//应该可以 一堆麻雀是一堆鸟
22 //在.NET Core中需要引用System.Linq;
23 List birdList3 = new List().Select(c => (Bird)c).ToList();
24 }
25
26 {
27 //协变
28 IEnumerable birdList1 = new List();//接口
29 IEnumerable birdList2 = new List();
30 Func func = new Func(() => null);//委托
31 //自定义
32 ICustomerListOut customerList1 = new CustomerListOut();
33 ICustomerListOut customerList2 = new CustomerListOut();
34 }
35
36 {
37 //逆变
38 ICustomerListIn customerList1 = new CustomerListIn();
39 ICustomerListIn customerList2 = new CustomerListIn();
40 ICustomerListIn customerList3 = new CustomerListIn();
41 customerList3.Show(new Bird());
42 customerList3.Show(new Sparrow());
43 Action action = new Action((Bird i) => { });
44 }
45
46 {
47 IMyList myList1 = new MyList();
48 IMyList myList2 = new MyList();//协变
49 IMyList myList3 = new MyList();//逆变
50 IMyList myList4 = new MyList();//逆变+协变
51 }
52 }
53 }
54
55 ///
56 /// 鸟类
57 ///
58 public class Bird
59 {
60 public int Id { get; set; }
61 }
62 ///
63 /// 麻雀类
64 ///
65 public class Sparrow : Bird
66 {
67 public string Name { get; set; }
68 }
69 ///
70 /// in 逆变 只能做参数
71 ///
72 ///
73 public interface ICustomerListInin T>
74 {
75 void Show(T t);
76
77 //T Get(); 逆变,不能作为返回值,只能把它当成参数
78 }
79
80 public class CustomerListIn : ICustomerListIn 81 {
82 public void Show(T t)
83 {
84
85 }
86
87 //public T Get()
88 //{
89 // return default(T);
90 //}
91 }
92 ///
93 /// out 协变 只能是返回结果
94 ///
95 ///
96 public interface ICustomerListOutout T>
97 {
98 T Get();
99
100 //void Show(T t); 只能放在返回值,不能放在参数
101 }
102
103 public class CustomerListOut : ICustomerListOut104 {
105 public T Get()
106 {
107 return default(T);
108 }
109
110 //public void Show(T t)
111 //{
112
113 //}
114 }
115
116 public interface IMyListin inT,out outT>
117 {
118 void Show(inT t);
119
120 outT Get();
121
122 outT Do(inT t);
123
124 //out 只能是返回值 in只能是参数
125
126 }
127
128 public class MyList : IMyList129 {
130 public T2 Do(T1 t)
131 {
132 Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name);
133 Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name);
134 return default(T2);
135 }
136
137 public T2 Get()
138 {
139 Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name);
140 return default(T2);
141 }
142
143 public void Show(T1 t)
144 {
145 Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name);
146 }
147 }
七.泛型缓存
1 public class GenericCacheTest
2 {
3 public static void Show()
4 {
5 for (int i = 0; i 5; i++)
6 {
7 Console.WriteLine(GenericCacheint>.GetCache());
8 Thread.Sleep(10);
9 Console.WriteLine(GenericCachelong>.GetCache());
10 Thread.Sleep(10);
11 Console.WriteLine(GenericCache.GetCache());
12 Thread.Sleep(10);
13 Console.WriteLine(GenericCachestring>.GetCache());
14 Thread.Sleep(10);
15 Console.WriteLine(GenericCache.GetCache());
16 Thread.Sleep(10);
17 }
18 }
19 }
20 ///
21 /// 字典缓存:静态属性常驻内存
22 ///
23 public class DictionaryCache
24 {
25 private static Dictionarystring> _TypeTimeDictionary = null;
26
27 static DictionaryCache()
28 {
29 Console.WriteLine("This is Dictionary 静态构造函数");
30 _TypeTimeDictionary = new Dictionarystring>();
31 }
32
33 public static string GetCache()
34 {
35 Type type = typeof(Type);
36 if (!_TypeTimeDictionary.ContainsKey(type))
37 {
38 _TypeTimeDictionary[type] = string.Format("{0}_{1}",typeof(T).FullName,DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss fff"));
39 }
40 return _TypeTimeDictionary[type];
41 }
42 }
43 ///
44 /// 每个不同的T,都会生成一份不同的副本
45 /// 适合不同类型,需要缓存一份数据的场景,效率高
46 /// 不能主动释放
47 ///
48 ///
49 public class GenericCache50 {
51 private static string _TypeTime = "";
52 static GenericCache()
53 {
54 Console.WriteLine("This is GenericCache 静态构造函数");
55 _TypeTime = string.Format("{0}_{1}", typeof(T).FullName, DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss fff"));
56 }
57
58 public static string GetCache()
59 {
60 return _TypeTime;
61 }
62 }
63 /*
64 * 为什么不用字典缓存?
65 * 字典缓存是一种哈希分布的,找数据的时候需要把Key进行哈希 找到内存地址 然后才能找到数据 数据如果过多 范围就会很大 造成性能浪费
66 * 而泛型缓存,每一个都是独立的 不同的实体产生一个不同的副本,副本就存在CPU那,已经存在即时编译器里面去,如果需要找不同的类 直接在内存拿、寻址
67 * 而字典缓存需要去计算去寻址
68 *
69 * 泛型生命周期:永远都不释放
70 */
八.泛型缓存
C#泛型(Generic)
标签:sel nan eal src 总数 obj 方式 就会 不同的
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/vic-tory/p/12148153.html

