Java装饰模式
2021-01-20 11:16
标签:类方法 结构型模式 end out inf 缺点 sele cache 很多 这种模式创建了一个装饰类,用来包装原有的类,并在保持类方法签名完整性的前提下,提供了额外的功能。 介绍 何时使用:在不想增加很多子类的情况下扩展类。 如何解决:将具体功能职责划分,同时继承装饰者模式。 关键代码: 1、Component 类充当抽象角色,不应该具体实现。 2、修饰类引用和继承 Component 类,具体扩展类重写父类方法。 优点:装饰类和被装饰类可以独立发展,不会相互耦合,装饰模式是继承的一个替代模式,装饰模式可以动态扩展一个实现类的功能。 缺点:多层装饰比较复杂。 使用场景: 1、扩展一个类的功能。 2、动态增加功能,动态撤销。 注意事项:可代替继承。 Component:定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态的添加职责 ConcreteComponent: 定义一个对象,可以给这个对象添加一些职责 Decorator:维持一个指向Component对象的指针,并定义一个与Component接口一致的接口 ConcreteDecoratorA,ConcreteDecoratorB。。。CD等:向组件添加职责 我们通过下面的实例来演示装饰器模式的用法,给图像修饰比如上色、装框、然后打印。 1. 定义一个抽象类: 2. 创建抽象类的包装实现类。 3. 创建装饰类 4. 扩写具体实现的装饰类(上色,装框,打印,其实还接着加,比如售卖) ColorDecorator.java、FrameDecorator.java、PrintDecorator.java 5. 测试图像装饰效果: 输出效果: 只有0是原材料,123修饰 入库https://github.com/dongguangming/design-pattern/tree/master/src/code/decorator 链式写法长 和javafx.swing 开发中component的扩展开发也都用到了装饰模式 MyBatis框架中cache也有装饰的影子 Spring也有装饰,发挥的更牛叉(没有Bean就没有其他扩展):BeanDefinitionDecorator(要分开理解,BeanDefinition和Decorator),是Bean定义阶段的装饰,当然还有其他装饰比如装饰WebSocket 对象。 参考: 0. 装饰模式 https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E8%A3%85%E9%A5%B0%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F/10158540 1. 如何使用Decorator模式 http://www.uml.org.cn/sjms/20041655.htm 2. javax.swing.JScrollPane https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/swing/JScrollPane.html 4. The Decorator Pattern in Depth https://blogs.oracle.com/javamagazine/the-decorator-pattern-in-depth 5. Decorator Design Pattern in Java with Example https://www.java67.com/2013/07/decorator-design-pattern-in-java-real-life-example-tutorial.html?m=1 Java装饰模式 标签:类方法 结构型模式 end out inf 缺点 sele cache 很多 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dongguangming/p/12901589.html
你在山上看风景,看风景的人在山上看你。明月装饰了你的窗子,你装饰了别人的梦。
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern),别名又叫包装者模式(wapper),允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它是作为现有的类的一个包装,不同于代理。
意图:动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,装饰器模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
主要解决:一般我们为了扩展一个类经常使用继承方式实现,由于继承为类引入静态特征,并且随着扩展功能的增多,子类会很膨胀。
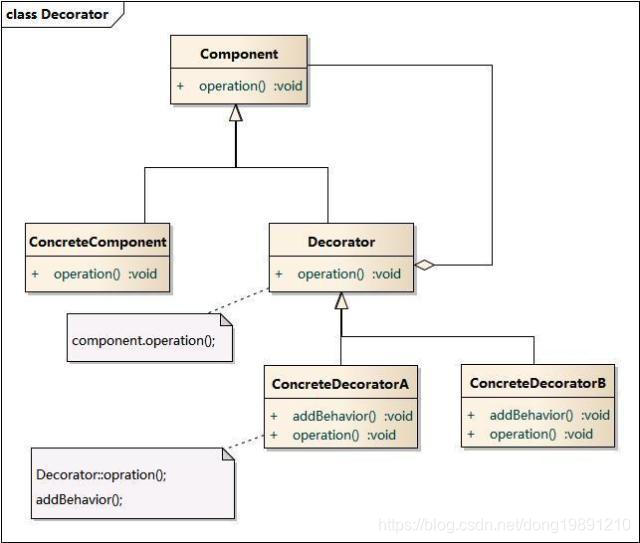
结构图
?
参与者:
/**
* @author dgm
* @describe "图片图像,同比Conpenent"
*/
public abstract class PhotoImage {
//图像描述
public abstract String getDescription();
}
/**
*
* @author dgm
* @describe "类比ConcreteComponent"
*/
public class PhotoImageWrapper extends PhotoImage {
// 图像标题
String title;
// 图片文件名
String fileName;
// 图像宽高
int pixWidth, pixHeight;
public PhotoImageWrapper() {
// Empty; used in Decorators.
}
public PhotoImageWrapper(String title, String fileName) {
super();
this.title = title;
this.fileName = fileName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getDescription();
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getFileName() {
return fileName;
}
public void setFileName(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
public int getPixWidth() {
return pixWidth;
}
public void setPixWidth(int width) {
this.pixWidth = width;
}
public int getPixHeight() {
return pixHeight;
}
public void setPixHeight(int height) {
this.pixHeight = height;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return getTitle();
}
}
/**
*
* @author dgm
* @describe "图像装饰,类比Decorator"
*/
public abstract class ImageDecorator extends PhotoImage {
protected PhotoImage target;
public ImageDecorator(PhotoImage target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return target.getDescription();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getDescription();
}
}
public class ColorDecorator extends ImageDecorator {
String color;
public ColorDecorator(String color, PhotoImage target) {
super(target);
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return target.getDescription() + ", 上色(" + color + ")";
}
}
public class FrameDecorator extends ImageDecorator {
private String desc;
public FrameDecorator(String desc, PhotoImage target) {
super(target);
this.desc = desc;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return target.getDescription() + ", "+desc+", ";
}
}
/**
*
* @author dgm
* @describe "打印图像,类比ConcreteDecorator"
*/
public class PrintDecorator extends ImageDecorator {
private String desc;
private double printWidth, printHeight;
public PrintDecorator(String desc,double printWidth, double printHeight, PhotoImage target) {
super(target);
this.desc = desc;
this.printWidth = printWidth;
this.printHeight = printHeight;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return target.getDescription() + desc+ " " + String.format("(%4.1f x %4.1f in)", getPrintWidth(), getPrintHeight());
}
public double getPrintWidth() {
return printWidth;
}
public void setPrintWidth(double printWidth) {
this.printWidth = printWidth;
}
public double getPrintHeight() {
return printHeight;
}
public void setPrintHeight(double printHeight) {
this.printHeight = printHeight;
}
}
/**
*
* @author dgm
* @describe "装饰模式(装饰的是图片图像)测试"
*/
public class PhotoImageDecoratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
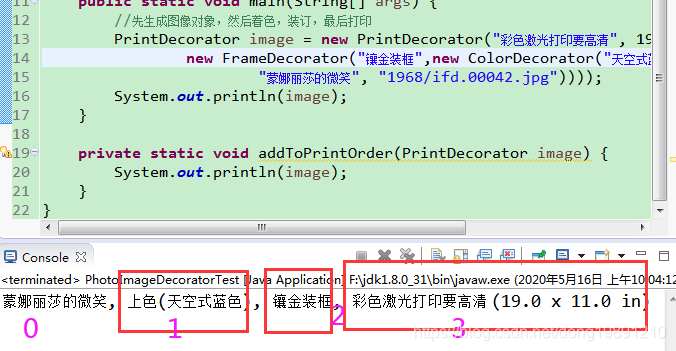
//先生成图像对象,然后着色,装订,最后打印
PrintDecorator image = new PrintDecorator("彩色激光打印要高清", 19, 11,
new FrameDecorator("镶金装框",new ColorDecorator("天空式蓝色", new PhotoImageWrapper(
"蒙娜丽莎的微笑", "1968/ifd.00042.jpg"))));
System.out.println(image);
}
private static void addToPrintOrder(PrintDecorator image) {
System.out.println(image);
}
}
?
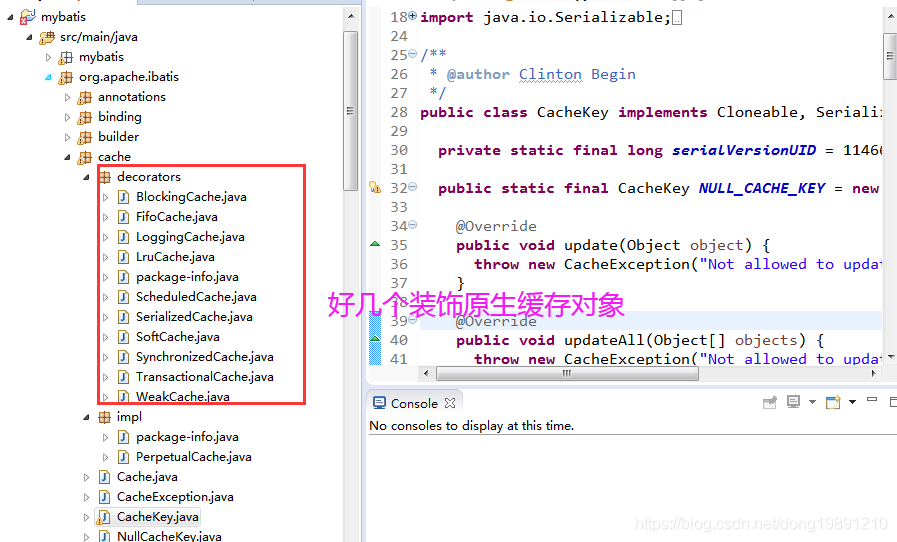
案例: 比如原生jdk中io流就用到了装饰模式,装饰一个流
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("f:\\InstallCert.java");
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
InputStream in = new DataInputStream(bis);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//将文本打印到控制台
System.out.println(line);
}
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("f:\\InstallCert.java")))));
?
装饰模式,特别于日志、缓存、io流等场景太合适不过了!!!
特别注意它和其他几种模式的区别:

小结: 如果你想给原生对象添加额外的行为职责,又不想变它,就可以使用该模式,那就装饰它原生对象, 使用场景颇多,具体自己发挥去,走自己的路,然别人去说吧
3. Decorator Design Pattern Applied https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2014/08/decorator-design-pattern-applied.html
下一篇:C++类与对象