C# 泛型
2021-01-23 23:13
标签:eth 补充 需求 数字 reading monitor 复制 除了 delegate 一、什么是泛型 泛型是C#2.0推出的新语法,不是语法糖,而是2.0由框架升级提供的功能 我们在编写程序时,会经常遇到功能非常相似的模块,只是他们的处理数据不一样,但我们没有办法,只能分别写多个方法来做处理不同的数据类型。那么问题来了,有没有一种方法,用同一个方法处理传入不同种类型参数的方法呢?有人就会想到传入Object可以去处理,但是我们都知道Object有装箱拆箱的操作,那么在C#2.0泛型的出现就是专门来解决这个问题的。 二、为什么使用泛型 先来看下以前做法的例子: 结果: 从上面显示的结果中我们三个方法,除了传入的参数不同外,里面实现的功能都是一样的。在1.0版的时候,还没有泛型这个概念,哪怎么办呢。想想很多人会想到了OOP三大特性之一的继承,我们知道,C#语言中,Object是所有类型的基类,将上面的代码进行以下优化: 结果: 从上面的结果中我们可以看出,使用Object类型达到我们的要求,解决代码的可复用。可鞥有人问定的是Objcet类型,为什么可以传入int、string等类型呢?原因有二: 1、Objcet类型是一切类型的基类 2、通过继承,子类拥有父类一切属性和行为,任何父类初夏你的地方,都可以用子类代替(在C#中,子类不能继承父类中用private修饰的成员变量和成员方法) 但是上面的Objcet类型的方法又会带来另外一个问题:装箱和拆箱,会损耗性能。 微软在C#2.0的时候推出了泛型,可以很好的解决上面的问题。 三、泛型类型参数 在泛型类型或方法定义中,类型参数是在实例化泛型类型的一个变量是,客户端指定的特定类型占位符。泛型类(GenerictList 上面例子中的代码可以修改如下: 调用: 结果: 为什么泛型可以解决上面的问题呢? 泛型是延迟声明的:即定义的时候没有指定具体的参数类型,把参数类型的声明推迟到了调用的时候才指定参数类型。延迟思想在程序架构涉及的时候很受欢迎。例如:分布式缓存队列,EF的延迟加载等等。 泛型究竟是如何工作的呢? 控制台程序最终会编译成一个exe程序,exe被点击的时候,会经过JIT(即时编译器)的编译,最终会生成二进制代码,才能被计算机执行,泛型加入到语法以后,VS自带的编译器又做了升级,升级之后编译时遇到泛型,会做特殊的处理:生成占位符。再次经过JIT编译的时候,会把上面编译成的占位符替换成具体的数据类型,请看下面一个例子: 结果: 从上面的截图中可以看出:泛型在编译之后会生成占位符。 注意:占位符需要在英文输入法状态下才能输入,只需要按一次波浪线(数字1左边的键位)的键位即可,不需要按Shift键。 1。泛型性能问题 请看以下的例子,比较普通方法、Object参数类型的方法、泛型方法的性能。 添加一个Monitor类,让三种方法执行同样的操作,比较用时长短: Main()方法调用: 从结果中可以看出:泛型方法的新能最高,其次时普通方法,Object方法的新能最低。 四、泛型类 除了方法可以泛型之外,类也是可以的是泛型的,例如: Main()方法中调用 除了可以有泛型类,也可以有泛型接口,例如: 也可以有泛型委托: 注意: 1、泛型在声明的时候可以不指定具体的类型,但是在使用的时候必须指定具体类型,例如: 如果子类也是泛型的,那么继承的时候可以不指定具体类型,例如: 2、类实现泛型接口也是这种情况,例如: 五、泛型约束 先来看看下面的一个例子: 定义一个People类,里面有属性和方法: 在Main()方法里面实例化: 这时有一个需求:需要打印出Id和Name属性的值,将ShowObject()方法修改如下: 但是这样修改报错了:object类里面没有Id和Name属性,可能会有人说,强制类型转换一下就行了啊: 这样修改以后,代码不会报错了,这时我们在Main()方法里面调用: 可以看出程序报错了,因为Japanese没有继承自People,这里类型转换的时候失败了。这样会造成类型不安全的问题。那么怎么解决类型不安全的问题呢?那就是使用泛型约束。 所谓的泛型约束,实际上就是约束的类型T。使T必须遵循一定的规则。比如T必须继承自某个类,或者T必须实现某个接口等等。那么怎么给泛型指定约束?其实也很简单,只需要where关键字,加上约束的条件。 泛型约束总共有五种。 1、基类约束 上面打印的方法约束T类型必须是People类型。 注意: 基类约束时,基类不能是密封类,即不能是sealed类。sealed类表示该类不能被继承,在这里用作约束就无任何意义,因为sealed类没有子类。 2、接口约束 3、引用类型约束 class 引用类型约束保证T一定是引用类型的。 4、值类型约束 struct 值类型约束保证T一定是值类型的。 5、无参数构造函数约束 new() 泛型约束也可以同时约束多个,例如: 注意:有多个泛型约束时,new()约束一定是在最后。 如果泛型有多个参数,且都要进行约束,则可以按以下进行: 六、泛型的协变(out)和逆变(in)(只能运用到接口或者委托) 让泛型运用起来更方便,为了补充泛型 协变和逆变是在.NET 4.0的时候出现的,只能放在接口或者委托的泛型参数前面,out 协变covariant,用来修饰返回值;in:逆变contravariant,用来修饰传入参数。 先看下面的一个例子: 定义一个Animal类: 然后在定义一个Cat类继承自Animal类: 在Main()方法可以这样调用: 那么问题来了:下面的一句代码是不是正确的呢? 可能有人会认为是正确的:因为一只Cat属于Animal,那么一群Cat也应该属于Animal啊。但是实际上这样声明是错误的:因为List 这时就可以用到协变和逆变了。 F12查看定义: 可以看到,在泛型接口的T前面有一个out关键字修饰,而且T只能是返回值类型,不能作为参数类型,这就是协变。使用了协变以后,左边声明的是基类,右边可以声明基类或者基类的子类。 协变除了可以用在接口上面,也可以用在委托上面: 除了使用.NET框架定义好的以为,我们还可以自定义协变,例如: 使用自定义的协变: 在来看看逆变。 在泛型接口的T前面有一个In关键字修饰,而且T只能方法参数,不能作为返回值类型,这就是逆变。请看下面的自定义逆变: 使用自定义逆变: 协变和逆变也可以同时使用,看看下面的例子: 使用: 七、泛型缓存 在前面我们学习过,类中的静态类型无论实例化多少次,在内存中只会有一个。静态构造函数只会执行一次。在泛型类中,T类型不同,每个不同的T类型,都会产生一个不同的副本,所以会产生不同的静态属性、不同的静态构造函数,请看下面的例子: 然后新建一个测试类,用来测试GenericCache类的执行顺序: Main()方法里面调用 结果: 从上面的截图中可以看出,泛型会为不同的类型都创建一个副本,所以静态构造函数会执行5次。 而且每次静态属性的值都是一样的。利用泛型的这一特性,可以实现缓存。 注意:只能为不同的类型缓存一次。泛型缓存比字典缓存效率高。泛型缓存不能主动释放 C# 泛型 标签:eth 补充 需求 数字 reading monitor 复制 除了 delegate 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/IT-Ramon/p/12061043.html
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public class CommonMethod
{
///


public static void ShowObject(object oParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(CommonMethod), oParameter.GetType().Name, oParameter);
}

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public class GenericMethod
{
///


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int iValue = 123;
string sValue = "456";
DateTime dtValue = DateTime.Now;
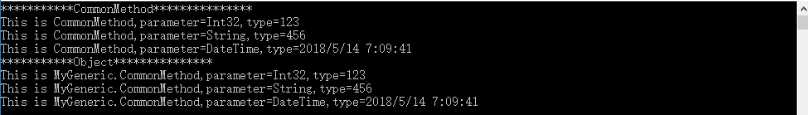
Console.WriteLine("***********CommonMethod***************");
CommonMethod.ShowInt(iValue);
CommonMethod.ShowString(sValue);
CommonMethod.ShowDateTime(dtValue);
Console.WriteLine("***********Object***************");
CommonMethod.ShowObject(iValue);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(sValue);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(dtValue);
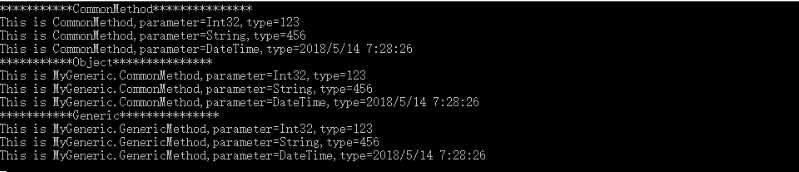
Console.WriteLine("***********Generic***************");
GenericMethod.Show

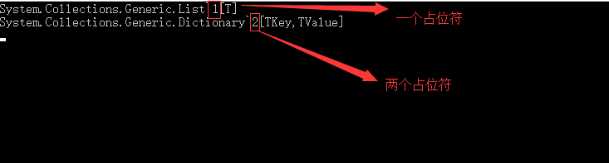
Console.WriteLine(typeof(List));
Console.WriteLine(typeof(Dictionary));

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public class Monitor
{
public static void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("****************Monitor******************");
{
int iValue = 12345;
long commonSecond = 0;
long objectSecond = 0;
long genericSecond = 0;
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i (iValue);
}
watch.Stop();
genericSecond = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
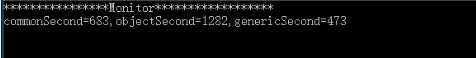
Console.WriteLine("commonSecond={0},objectSecond={1},genericSecond={2}"
, commonSecond, objectSecond, genericSecond);
}
}
#region PrivateMethod
private static void ShowInt(int iParameter)
{
//do nothing
}
private static void ShowObject(object oParameter)
{
//do nothing
}
private static void Show


class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Monitor.Show();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
///


// T是int类型
GenericClass


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
///

public delegate void SayHi

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
///


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
///


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
///

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public interface ISports
{
void Pingpang();
}
public interface IWork
{
void Work();
}
public class People
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Hi()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hi");
}
}
public class Chinese : People, ISports, IWork
{
public void Tradition()
{
Console.WriteLine("仁义礼智信,温良恭俭让");
}
public void SayHi()
{
Console.WriteLine("吃了么?");
}
public void Pingpang()
{
Console.WriteLine("打乒乓球...");
}
public void Work()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
public class Hubei : Chinese
{
public Hubei(int version)
{ }
public string Changjiang { get; set; }
public void Majiang()
{
Console.WriteLine("打麻将啦。。");
}
}
public class Japanese : ISports
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Hi()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hi");
}
public void Pingpang()
{
Console.WriteLine("打乒乓球...");
}
}
}

People people = new People()
{
Id = 123,
Name = "走自己的路"
};
Chinese chinese = new Chinese()
{
Id = 234,
Name = "晴天"
};
Hubei hubei = new Hubei(123)
{
Id = 345,
Name = "流年"
};
Japanese japanese = new Japanese()
{
Id = 7654,
Name = "werwer"
};

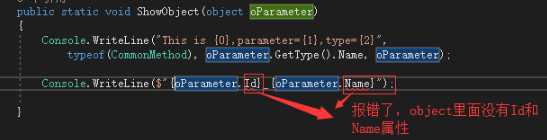

public static void ShowObject(object oParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(CommonMethod), oParameter.GetType().Name, oParameter);
Console.WriteLine($"{((People)oParameter).Id}_{((People)oParameter).Name}");
}

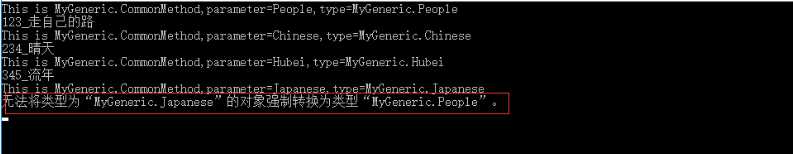
CommonMethod.ShowObject(people);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(chinese);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(hubei);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(japanese);
约束
s说明
T:结构
类型参数必须是值类型
T:类
类型参数必须是引用类型;这一点也适用于任何类、接口、委托或数组类型。
T:new()
类型参数必须具有无参数的公共构造函数。 当与其他约束一起使用时,new() 约束必须最后指定。
T:
类型参数必须是指定的基类或派生自指定的基类。
T:
类型参数必须是指定的接口或实现指定的接口。 可以指定多个接口约束。 约束接口也可以是泛型的。

///


///


///


///


///


public static void Show


public static void Show


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public class Animal
{
public int Id { get; set; }
}
}


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public class Cat :Animal
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}


static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 直接声明Animal类
Animal animal = new Animal();
// 直接声明Cat类
Cat cat = new Cat();
// 声明子类对象指向父类
Animal animal2 = new Cat();
// 声明Animal类的集合
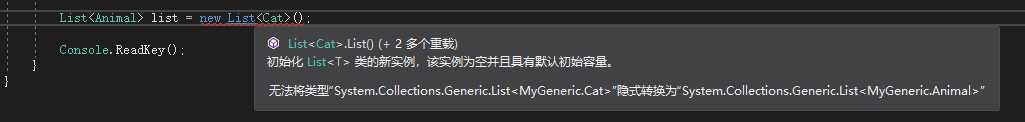
List listAnimal = new List();
// 声明Cat类的集合
List

List list = new List
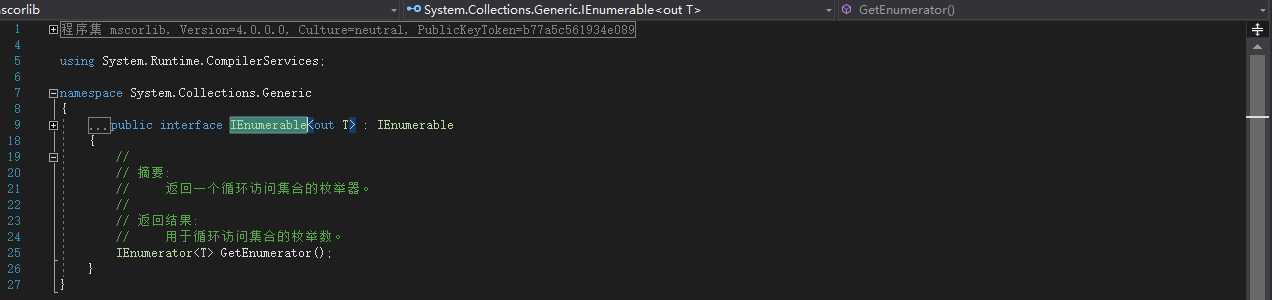
// 协变
IEnumerable List1 = new List();
IEnumerable List2 = new List
Func func = new Func

///

// 使用自定义协变
ICustomerListOut customerList1 = new CustomerListOut();
ICustomerListOut customerList2 = new CustomerListOut

///

// 使用自定义逆变
ICustomerListIn

///

IMyList

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public class GenericCache


using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyGeneric
{
public class GenericCacheTest
{
public static void Show()
{
for (int i = 0; i .GetCache());
Thread.Sleep(10);
Console.WriteLine(GenericCache

GenericCacheTest.Show();
