13、JAVA常见类(Scanner类、String类)
2021-02-02 16:16
标签:两种 class 区别 堆内存 new 中间 ++ case 条件 录入整数的方法 next和nextLine方法的区别 nextLine()方法 String类的构造方法 String类介绍 1、Java程序中所有的字符串字面值("abc")都可以作为此类的实例实现;(可以调用方法) 2、字符串是常量,它们的值在创建后不能更改。 String类的面试题 String类的方法 与判断相关的方法 与获取相关的方法 与转换相关的方法 与替换有关的方法 练习题 13、JAVA常见类(Scanner类、String类) 标签:两种 class 区别 堆内存 new 中间 ++ case 条件 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/shawnyue-08/p/12808111.htmlScanner类
Scanner(InputStream source)
构造一个新的 Scanner ,产生从指定输入流扫描的值。
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//Scanner对象必须是新的,否则第一次录入的是非整数时,下一次循环if的条件表达式永远为false
if (sc.hasNextInt()) {
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(num);
break;
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的数据类型不正确,请重新输入。");
}
}
}
}
class MyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int index = 3;
while (index-- > 0) {
if (sc.hasNextLine()) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
//录入一行字符串,遇到空格会录入进s,nextLine方法的结束符只是Enter键,即nextLine()方法返回的是Enter键之前的
//所有字符,它是可以得到带空格的字符串的
System.out.println("s = " + s);
}
}
/*
I am a student. Do you think so?
s = I am a student. Do you think so?
哈哈,nextLine()方法的结束符只有enter键
s = 哈哈,nextLine()方法的结束符只有enter键
果然是这样,空格可以录入吧 Tab也可以录入吧 果然可以
s = 果然是这样,空格可以录入吧 Tab也可以录入吧 果然可以
*/
/*
Enter
s =
Enter
s =
Enter
s =
*/
/*
nextLine()会录入Enter键之前的所有字符
*/
}
}
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int times = 10;
while (times-- > 0) {
if (sc.hasNext()) {
String next = sc.next();
//next()读取到有效字符后才可以结束输入,对输入有效字符之前遇到的空格键、Tab键或Enter键等结束符,
//next()方法会自动将其去掉,只有在输入有效字符之后,next()方法才将其后输入的空格键、Tab键或Enter键等视为分隔符或结束符
//next()不会读取空格、Tab、Enter
System.out.println("next = " + next);
}
}
/*
I am a student, she is my girlfriend. do you think so?
next = I
next = am
next = a
next = student,
next = she
next = is
next = my
next = girlfriend.
next = do
next = you
*/
/*
I am a student.
next = I
next = am
next = a
next = student.
She is my girlfriend, do
next = She
next = is
next = my
next = girlfriend,
next = do
you think so?
next = you
*/
}
}
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String next = sc.next();
String s = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("next = " + next + ", s = " + s);
/*
前面有空格,在next下不会录入 该nextLine了
next = 前面有空格,在next下不会录入, s = 该nextLine了
*/
/*
next()只会录入有效字符,有效字符之前的空格、Tab、Enter都不会录入,开始录入有效字符之后,一旦遇到空格、Tab将作为分隔符,一旦遇到Enter将作为结束符
nextLine()会录入回车符前面的所有字符,包括空格、Tab,Enter是nextLine()的结束符
*/
}
}
class MyDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String next = sc.next();
String s = sc.nextLine();
String s1 = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("next = " + next + " , s = " + s + " , s1 = " + s1);
/*
home
next = home , s =
输入完home后直接回车
next()读不到回车的,而是将回车作为结束符,并且留给了nextLine(),nextLine()毫不客气,直接读入,然后结束
*/
/*
如果要录入Enter键后面的字符串,建议在后面再加一条nextLine()
*/
/*
next
s1读取的我
next = next , s = , s1 = s1读取的我
*/
}
}
String类
String()
String(String original)
String(byte[] bytes)
//字节数组
String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
//字节数组的一部分
String(char[] value)
//字符数组
String(char[] value, int offset, int count)
//字符数组的一部分
package org.westos.demo;
/**
* 1、String类的构造方法
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/26 19:29
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String();
//空参的构造方法
System.out.println(s1);
//
//打印对象,默认调用toString方法
byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101};
String s2 = new String(bytes);
//字节数组
System.out.println(s2.toString());
//abcde
String s3 = new String(bytes, 1, 3);
//字节数组的一部分,byte[],int offset,int length
System.out.println(s3);
//bcd
char[] chars = {‘S‘, ‘h‘, ‘a‘, ‘w‘, ‘n‘, ‘Y‘, ‘u‘, ‘e‘};
String s4 = new String(chars);
//字符数组
System.out.println(s4);
//ShawnYue
String s5 = new String(chars, 0, 5);
//字符数组的一部分,char[],int offset,int length
System.out.println(s5);
//Shawn
}
}
class MyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int length = "abc".length();
//获取字符串的长度
System.out.println(length);
//3
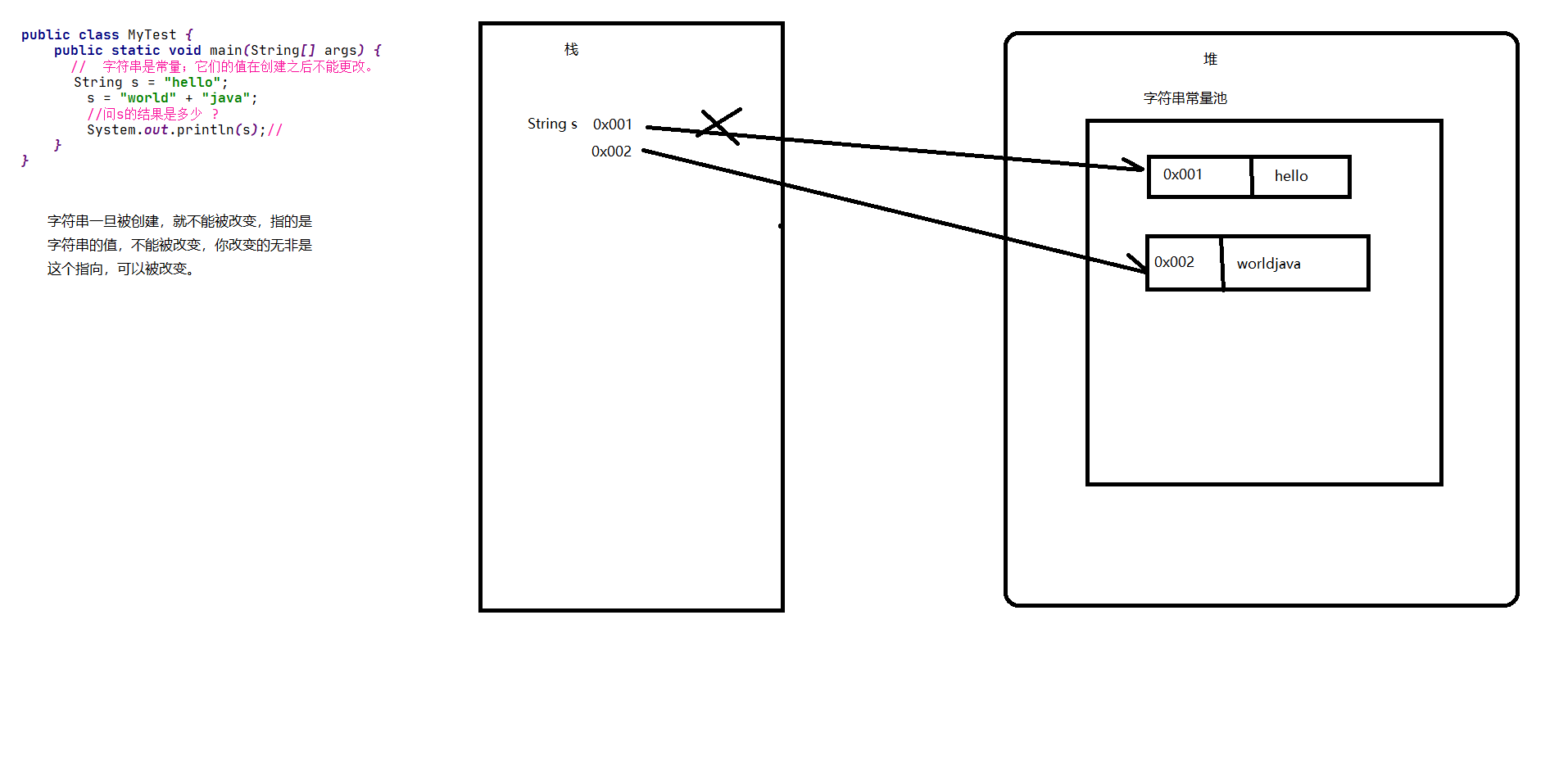
String s = "hello";
//存储在字符串常量池
s = "world" + "java";
//字面量 + 字面量,还在字符串常量池
System.out.println(s);
//s引用可以变,但是字符串的值不能改变
}
}
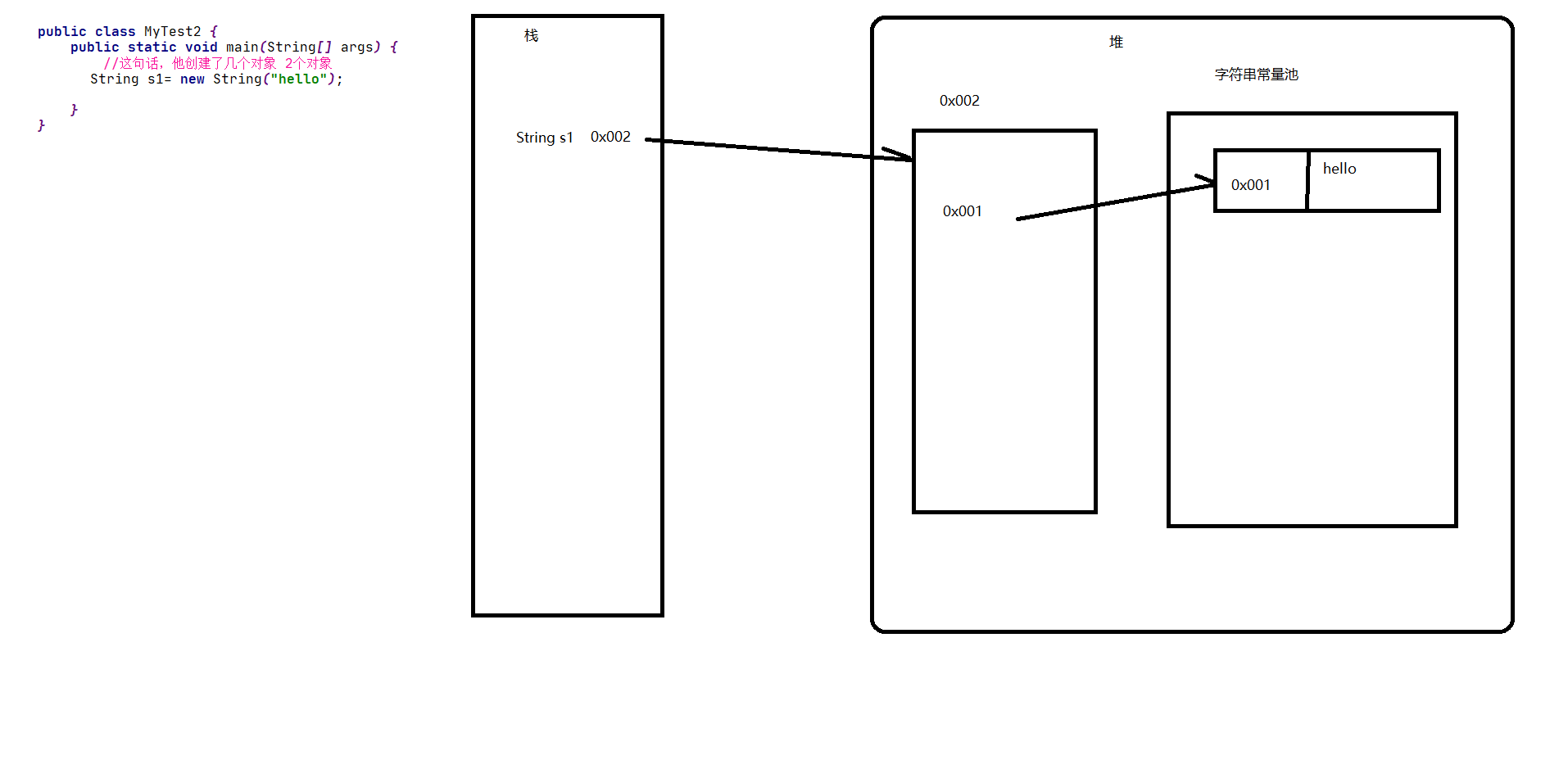
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hello_world = new String("hello");
//这句代码创建了几个对象,2个
}
}
package org.westos.demo;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/29 18:53
*/
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("Hello World");
String s2 = new String("Hello World");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
//false
//判断对象地址,每new一个对象都是在堆内存开辟一块空间
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
//true
//判断对象内容
String s3 = new String("Hello World");
String s4 = "Hello World";
System.out.println(s3 == s4);
//false
//判断对象地址,一个在堆区,一个在字符串常量池,当然不等
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));
//true
//判断对象内容
String s5 = "Hello World";
String s6 = "Hello World";
System.out.println(s5 == s6);
//true
//判断对象地址,两个都在字符串常量池,地址相同
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));
//true
//判断对象内容
}
}
String s1 = "hello" 和 String s2 = new String("hello") 两种方式创建对象的区别?
当我们采用"字符串字面值"这种方式来定义一个字符串的时候,他会先去字符串常量池去查找有没有有该字符串,如果没有,就构建这个字符串;如果有,就把字符串常量池中这个字符串的地址值,赋值给这个新的引用,从而栈区的两个变量指向同一块内存。
当采用new对象的方式时,同样先会去字符串常量池查看是否存在该字符串,如果不存在,则先在字符串常量池创建该字符串,然后再在堆区new一个String对象,指向字符串常量池的该字符串;如果存在,则直接在堆区new对象,指向字符串常量池的该字符串。
package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/27 18:41
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b1 = "abc".equals("ABC");
System.out.println(b1);
//false
//区分大小写
boolean b2 = "abc".equalsIgnoreCase("ABC");
System.out.println(b2);
//true
//不区分大小写
boolean empty = "".isEmpty();
System.out.println(empty);
//true
//判断字符串是否为空串
//boolean b3 = "".length() == 0;
boolean b3 = "abc".startsWith("a");
System.out.println(b3);
//true
//判断字符串是否是以"a"开头
boolean b4 = "abc".endsWith("c");
System.out.println(b4);
//true
//判断字符串是否是以"c"结尾
boolean b5 = "abcdefg".contains("cde");
System.out.println(b5);
//true
//判断字符串是否包含某个子串
}
}
/**
* 模拟登录,三次机会
*/
class MyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = "张三";
String password = "123456";
int index = 3;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (index-- > 0) {
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.next();
if (username.equals(name) && password.equals(pwd)) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误,请重新输入。你还有" + index + "次机会。");
}
}
}
/*
请输入用户名:
李四
请输入密码:
123456
用户名或密码错误,请重新输入。你还有2次机会。
请输入用户名:
王五
请输入密码:
123456
用户名或密码错误,请重新输入。你还有1次机会。
请输入用户名:
张三
请输入密码:
123456
登录成功
*/
}
package org.westos.demo;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/27 18:59
*/
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int length = "abc".length();
System.out.println(length);
//3
//获取字符串的长度
char c = "abcdefg".charAt(3);
System.out.println(c);
//d
//根据索引获取单个字符
int index = "abcdabcd".indexOf(‘c‘);
System.out.println(index);
//2
//获取单个字符第一次出现的索引
int index2 = "abcdabcd".indexOf(‘c‘, 3);
System.out.println(index2);
//6
//从fromIndex位置开始找单个字符第一次出现的索引
int index3 = "abcdabcd".indexOf("cd");
System.out.println(index3);
//2
//获取子串第一次出现的索引
int index4 = "abcdabcd".indexOf("cd", 3);
System.out.println(index4);
//6
//从fromIndex位置开始找子串第一次出现的索引
int index5 = "abcdabcd".indexOf(‘e‘);
System.out.println(index5);
//-1
//当没有找到时返回-1
}
}
class MyDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int index = "abcdabcd".lastIndexOf(‘d‘);
System.out.println(index);
//7
//从后向前查找单个字符第一次出现的索引
int index2 = "abcdabcd".lastIndexOf(‘d‘, 6);
System.out.println(index2);
//3
//从指定位置开始从后向前找单个字符第一次出现的索引
int index3 = "abcdabcd".lastIndexOf("bc");
System.out.println(index3);
//5
//从后向前查找子串第一次出现的索引
int index4 = "abcdabcd".lastIndexOf("bc", 4);
System.out.println(index4);
//1
//截取字符串
String s = "我在人民广场吃炸鸡,而此时此刻你在哪里?";
String substring = s.substring(0, 9);
System.out.println(substring);
//我在人民广场吃炸鸡
//[beginIndex, endIndex)
String substring1 = s.substring(3);
System.out.println(substring1);
//民广场吃炸鸡,而此时此刻你在哪里?
//[beginIndex, arr.length)
//遍历字符串
for (int i = 0; i = ‘a‘ && c = ‘A‘ && c package org.westos.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/27 20:09
*/
public class MyTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] bytes = "abcdefg".getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
//[97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103]
//把一个字符串转换为字节数组
String s = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(s);
//abcdefg
//把字节数组转换为字符串
int length = "我".getBytes().length;
System.out.println(length);
//3
//一个中文汉字UTF-8编码为3Byte
char[] chars = "abcdefg".toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars));
//[a, b, c, d, e, f, g]
//字符串转为字符数组
String s1 = new String(chars);
String s9 = String.valueOf(chars);
System.out.println(s1);
//abcdefg
//字符数组转字符串
String s2 = String.valueOf(12);
//int
String s3 = String.valueOf(12L);
//long
String s4 = String.valueOf(12.0);
//double
String s5 = String.valueOf(12.0f);
//float
String a = String.valueOf(‘a‘);
//char
String s6 = String.valueOf(true);
//boolean
String s7 = String.valueOf(chars);
//char[]
String s8 = String.valueOf(new Object());
//Object
}
}
class MyDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcdefg".toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s);
//ABCDEFG
//小写字母转大写字母
String s1 = "ABCDEFG".toLowerCase();
System.out.println(s1);
//abcdefg
//把大写字母转换为小写
String s2 = "abcd".concat("efg");
System.out.println(s2);
//abcdefg
//字符串拼接
}
}
class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
把字符串的首字母转大写,其余字母转小写
*/
String s = "aBCDEFG";
String concat = String.valueOf(s.charAt(0)).toUpperCase().concat(s.substring(1).toLowerCase());
System.out.println(concat);
//Abcdefg
}
}
package org.westos.demo;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/27 20:43
*/
public class MyTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "奥利奥和薯愿是我的伙伴。";
String replace = s.replace(‘和‘, ‘与‘);
System.out.println(replace);
//奥利奥与薯愿是我的伙伴。
//替换单个字符
String replace1 = s.replace("奥利奥", "三只松鼠").replace("薯愿", "乐事");
System.out.println(replace1);
//三只松鼠和乐事是我的伙伴。
//替换字符串
String str = " 前面有空格,后面有空格 ";
String trim = str.trim();
System.out.println(trim);
//前面有空格,后面有空格
//去掉字符串的两端空格
int i = "abc".compareTo("ABC");
System.out.println(i);
//32 ‘a‘ = 97, ‘A‘ = 65
//大于
//比较字符串:按照ASCII码表来比的
int j = "abc".compareTo("abcdef");
System.out.println(j);
//-3
//如果ASCII码表不能比较出来,那么比较长度
int k = "abc".compareToIgnoreCase("ABCDEF");
System.out.println(k);
//-3
//不区分大小写
}
}
package org.westos.test;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/27 21:01
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = " zha ng san ";
//去除字符串左端的空格
int left = 0;
int right = username.length();
char[] value = username.toCharArray();
char target = ‘ ‘;
while ((left package org.westos.test;
/**
* @author lwj
* @date 2020/4/30 11:34
*/
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//把数组中的数据按照指定个格式拼接成一个字符串
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
String res = "[";
for (int i = 0; i class MyDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//字符串反转,键盘录入abc,反转结果cba
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要反转的字符串:");
String source = sc.nextLine();
char[] value = source.toCharArray();
String target = "";
int index = 0;
int length = value.length - 1;
while (index class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//统计大串中小串出现的次数"woaijavawozhenaijavawozhendeaijavawozhendehenaijavaxinbuxinwoaijavagun”中java出现了5次
String source = "woaijavawozhenaijavawozhendeaijavawozhendehenaijavaxinbuxinwoaijavagun";
String target = "java";
int count = 0;
int start = 0;
int end = source.length();
while (start
下一篇:Java中遍历Set集合的方法
文章标题:13、JAVA常见类(Scanner类、String类)
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/50041.html