Spring的Bean管理
2021-02-03 07:16
标签:initial rod handler 增强 files equals rop double repos Spring的Bean管理 标签:initial rod handler 增强 files equals rop double repos 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jessekkk/p/12804876.htmlSpring工厂类介绍
Spring工厂类
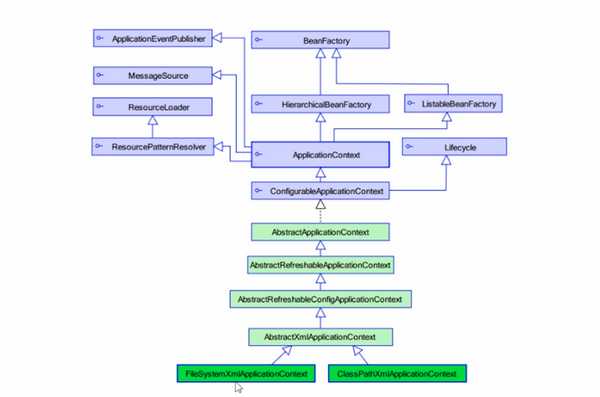
Example
@Test
/**
* 传统方式开发
*/
public void demo1(){
//UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
//设置属性:
userService.setName("张三");
userService.sayHello();
}
@Test
/**
* Spring的方式实现
*/
public void demo2(){
//创建Spring的工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类
UserService userService = (UserService)applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.sayHello();
}
@Test
/**
* 读取磁盘系统中的配置文件
*/
public void demo3(){
//创建Spring的工厂类:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("c:\\applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类
UserService userService = (UserService)applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.sayHello();
}
@Test
/**
* 传统方式的工厂类:BeanFactory
*/
public void demo4(){
//创建工厂类:
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
//通过工厂获得类:
UserService userService = (UserService)beanFactory.getBean("userService");
userService.sayHello();
}
@Test
/**
* 传统方式的工厂类:BeanFactory
*/
public void demo5(){
//创建工厂类:
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("c:\\applicationContext.xml"));
//通过工厂获得类:
UserService userService = (UserService)beanFactory.getBean("userService");
userService.sayHello();
}
Spring的Bean管理-XML方式(上)
Bean的实例化三种方式

方式一
package com.jesse.ioc.demo2;
/**
* Bean的实例化的三种方式:采用无参数的构造方法的方式
*/
public class Bean1 {
public Bean1(){
System.out.println("Bean1被实例化了...");
}
}
@Test
public void demo1(){
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实例:
Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1)applicationContext.getBean("bean1");
}
方式二
package com.jesse.ioc.demo2;
/**
* Bean的实例化三种方式:静态工厂实例化方式
*/
public class Bean2 {
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo2;
/**
* Bean2的静态工厂
*/
public class Bean2Factory {
public static Bean2 createBean2(){
System.out.println("Bean2Factory已经执行");
return new Bean2();
}
}
@Test
public void demo2(){
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实例:
Bean2 bean2 = (Bean2)applicationContext.getBean("bean2");
}
方式三
package com.jesse.ioc.demo2;
/**
* Bean的实例化三种方式:实例工厂实例化
*/
public class Bean3 {
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo2;
public class Bean3Factory {
public Bean3 createBean3(){
System.out.println("Bean3Factory执行了...");
return new Bean3();
}
}
@Test
public void demo3(){
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实例:
Bean3 bean3 = (Bean3)applicationContext.getBean("bean3");
}
Bean的常用配置

Bean的作用域

Example
package com.jesse.ioc.demo3;
public class Person {
}
@Test
public void demo1() {
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实例:
Person person1 = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");
Person person2 = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person1);
System.out.println(person2);
}
Bean的生命周期的配置
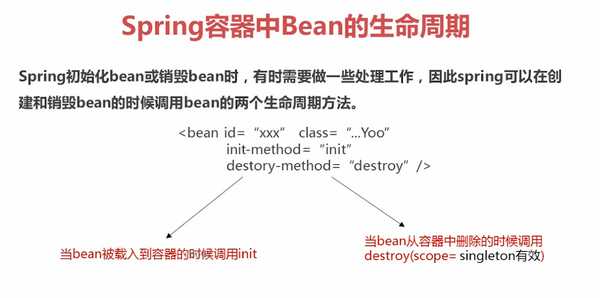
package com.jesse.ioc.demo3;
public class Man {
public Man(){
System.out.println("Man被实例化了...");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("Man被初始化了...");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("Man被销毁了...");
}
}
@Test
public void demo2() {
//创建工厂
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实例:
Man man = (Man) applicationContext.getBean("man");
System.out.println(man);
applicationContext.close();
}
Bean的生命周期的完整过程
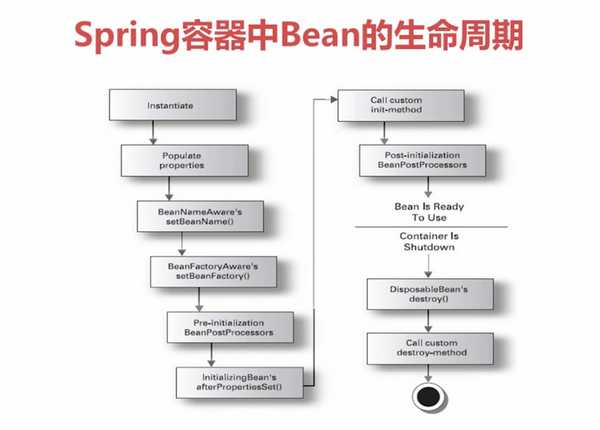


package com.jesse.ioc.demo3;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class Man implements BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("第二步:设置属性");
this.name = name;
}
public Man(){
System.out.println("第一步:初始化...");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("第七步:Man被初始化了...");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("第十一步:Man被销毁了...");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("第三步:设置Bean的名称" + s);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第四步:了解工厂的信息");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第六步:属性设置后");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("第九步:执行业务方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第十步:执行Spring的销毁方法");
}
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo3;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第五步:初始化前方法...");
return o;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第八步:初始化后方法...");
return o;
}
}
@Test
public void demo2() {
//创建工厂
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实例:
Man man = (Man) applicationContext.getBean("man");
man.run();
applicationContext.close();
}
BeanPostProcessor的作用(演示如何增强类方法)
package com.jesse.ioc.demo3;
public interface UseDao {
public void findAll();
public void save();
public void update();
public void delete();
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo3;
public class UseDaoImpl implements UseDao {
@Override
public void findAll() {
System.out.println("查询用户...");
}
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("保存用户...");
}
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("修改用户...");
}
@Override
public void delete() {
System.out.println("删除用户...");
}
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo3;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//System.out.println("第五步:初始化前方法...");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//System.out.println("第八步:初始化后方法啊...");
if ("useDao".equals(beanName)){
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("save".equals(method.getName())){
System.out.println("权限校验==========");
return method.invoke(bean,args);
}
return method.invoke(bean,args);
}
});
return proxy;
}else {
return bean;
}
}
}
@Test
public void demo3() {
//创建工厂
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//通过工厂获得类的实例:
UseDao useDao = (UseDao) applicationContext.getBean("useDao");
useDao.findAll();
useDao.save();
useDao.update();
useDao.delete();
}
Spring的Bean管理-XML方式(下)
属性注入的方式

构造方法的属性注入

package com.jesse.ioc.demo4;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
‘}‘;
}
}
@Test
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = (User)applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
set方法的属性注入

package com.jesse.ioc.demo4;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Cat cat;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
", cat=" + cat +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo4;
public class Cat {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
}
@Test
public void demo2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person)applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
p名称空间的属性注入

xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
SpEL的属性注入

package com.jesse.ioc.demo4;
public class Category {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Category{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo4;
public class ProductInfo {
public Double calculatePrice(){
return Math.random() * 199;
}
}
package com.jesse.ioc.demo4;
public class Product {
private String name;
private Double price;
private Category category;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Category getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(Category category) {
this.category = category;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", price=" + price +
", category=" + category +
‘}‘;
}
}
@Test
public void demo3(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Product product = (Product)applicationContext.getBean("product");
System.out.println(product);
}
复杂类型的属性注入

package com.jesse.ioc.demo5;
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionBean {
private String[] arrs; //数组类型
private Listpackage com.jesse.ioc.demo5;
import com.jesse.ioc.demo4.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo5 {
@Test
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CollectionBean collectionBean = (CollectionBean)applicationContext.getBean("collectionBean");
System.out.println(collectionBean);
}
}
Spring的Bean管理-注解方式
Bean的管理

package com.jesse.demo1;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* Spring的Bean管理的注解方式:
*/
//@Component("userService")
@Service("userService")
public class UserService {
public String sayHello(String name){
return "Hello" + name;
}
}
package com.jesse.demo1;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo1 {
@Test
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
String s = userService.sayHello("张三");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
属性注入的注解


package com.jesse.demo1;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* Spring的Bean管理的注解方式:
*/
//@Component("userService")
@Service("userService")
public class UserService {
@Value("米饭")
private String something;
/* @Autowired
@Qualifier("userDao")*/
@Resource(name = "userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
public String sayHello(String name){
return "Hello" + name;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat:"+something);
}
public void save(){
System.out.println("Service中保存用户...");
userDao.save();
}
}
package com.jesse.demo1;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDao {
public void save(){
System.out.println("DAO中保存用户...");
}
}
@Test
public void demo3(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.save();
}
其他注解
@PostConstruct和@PreDestory

package com.jesse.demo2;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
@Component("bean1")
public class Bean1 {
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("initBean...");
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("say....");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("destoryBean...");
}
}
@Test
public void demo1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) applicationContext.getBean("bean1");
bean1.say();
applicationContext.close();
}
@Scope

package com.jesse.demo2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("bean2")
@Scope("prototype")
public class Bean2 {
}
@Test
public void demo2(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Bean2 bean1 = (Bean2) applicationContext.getBean("bean2");
Bean2 bean2 = (Bean2) applicationContext.getBean("bean2");
System.out.println(bean1 == bean2);
}
Spring的XML和注解整合开发

package com.jesse.demo3;
public class CategoryDao {
public void save(){
System.out.println("CategoryDao中的save方法执行了...");
}
}
package com.jesse.demo3;
public class ProductDao {
public void save(){
System.out.println("ProductDao的save方法执行了...");
}
}
package com.jesse.demo3;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class ProductService {
@Resource(name = "categoryDao")
private CategoryDao categoryDao;
@Resource(name = "productDao")
private ProductDao productDao;
/* public void setCategoryDao(CategoryDao categoryDao) {
this.categoryDao = categoryDao;
}
public void setProductDao(ProductDao productDao) {
this.productDao = productDao;
}*/
public void save(){
System.out.println("ProductService的save方法执行了...");
categoryDao.save();
productDao.save();
}
}
package com.jesse.demo3;
import com.jesse.demo2.Bean2;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo3 {
@Test
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ProductService productService = (ProductService)applicationContext.getBean("productService");
productService.save();
}
}
上一篇:Java 多线程三、线程间的通信
下一篇:Python中with的用法