XML、JSON、YAML和ProtoBuf 渲染
2021-02-03 17:14
标签:返回 UNC 不同 mes std out serialize name pack 既然请求可以使用不同的content-type,响应也如此。通常响应会有html,text,plain,json和xml等。 gin提供了很优雅的渲染方法。 使用SecureJSON可以防止json劫持,如果返回的数据是数组,则会默认在返回值前加上 在不同的域中使用 JSONP 从一个服务器请求数据。如果请求参数中存在 callback,添加 callback 到 response body 。 使用 AsciiJSON 生成仅有 ASCII 字符的 JSON,非 ASCII 字符将会被转义 。 XML、JSON、YAML和ProtoBuf 渲染 标签:返回 UNC 不同 mes std out serialize name pack 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yzg-14/p/13143980.html1. JSON/XML/YAML/ProtoBuf渲染
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin/testdata/protoexample"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// gin.H is a shortcut for map[string]interface{}
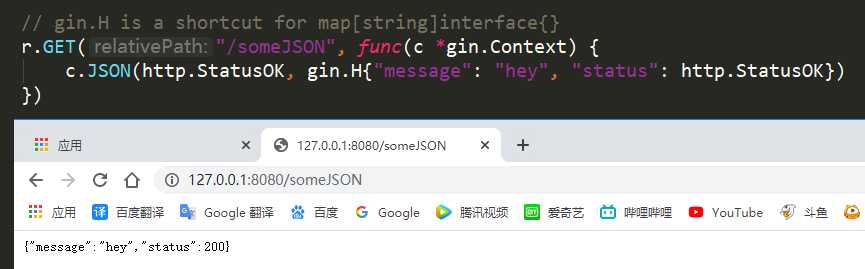
r.GET("/someJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "hey", "status": http.StatusOK})
})
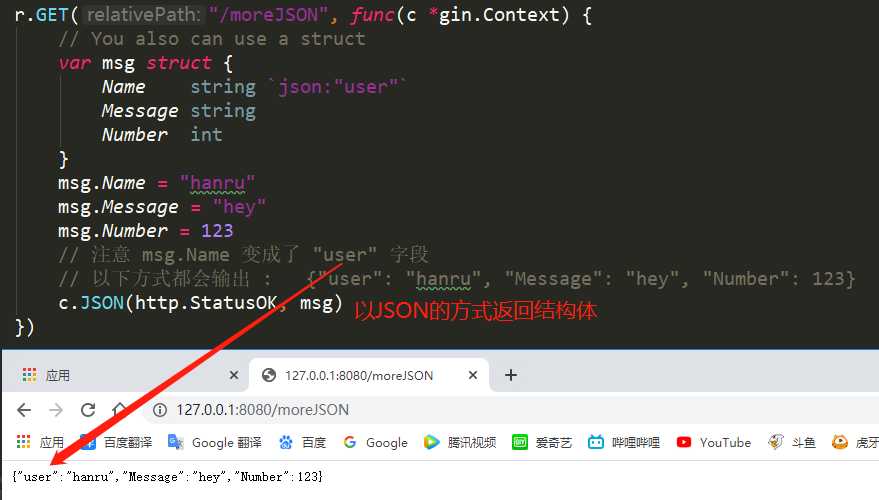
r.GET("/moreJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
// You also can use a struct
var msg struct {
Name string `json:"user"`
Message string
Number int
}
msg.Name = "hanru"
msg.Message = "hey"
msg.Number = 123
// 注意 msg.Name 变成了 "user" 字段
// 以下方式都会输出 : {"user": "hanru", "Message": "hey", "Number": 123}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, msg)
})
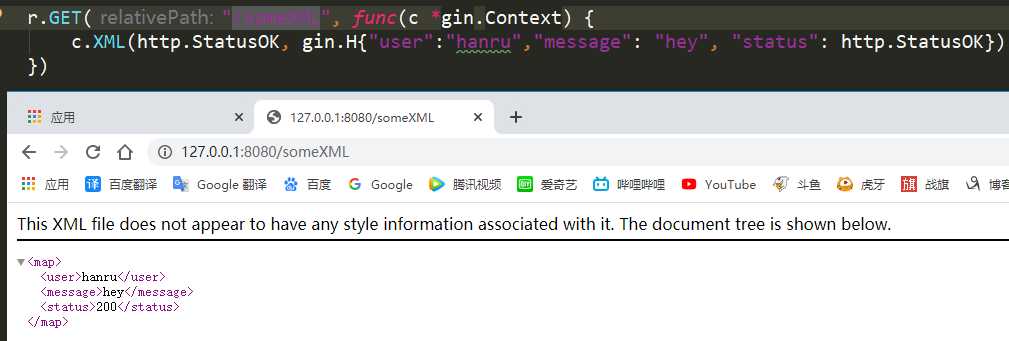
r.GET("/someXML", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.XML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"user":"hanru","message": "hey", "status": http.StatusOK})
})
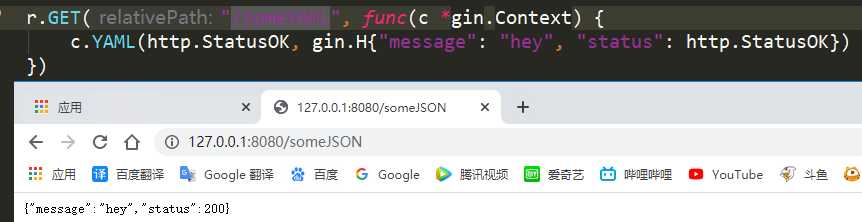
r.GET("/someYAML", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.YAML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "hey", "status": http.StatusOK})
})
r.GET("/someProtoBuf", func(c *gin.Context) {
reps := []int64{int64(1), int64(2)}
label := "test"
// The specific definition of protobuf is written in the testdata/protoexample file.
data := &protoexample.Test{
Label: &label,
Reps: reps,
}
// Note that data becomes binary data in the response
// Will output protoexample.Test protobuf serialized data
c.ProtoBuf(http.StatusOK, data)
})
// Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}
1.1 JSON
1.2 XML
1.3 YAML
2. SecureJSON
"while(1)"func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// 可以自定义返回的json数据前缀
// r.SecureJsonPrefix(")]}‘,\n")
r.GET("/someJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
names := []string{"lena", "austin", "foo"}
// 将会输出: while(1);["lena","austin","foo"]
c.SecureJSON(http.StatusOK, names)
})
// Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}
3. JSONP
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/JSONP?callback=x", func(c *gin.Context) {
data := map[string]interface{}{
"foo": "bar",
}
//callback 是 x
// 将会输出 : x({\"foo\":\"bar\"})
c.JSONP(http.StatusOK, data)
})
// 监听并服务于 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}
4. AsciiJSON
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/someJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
data := map[string]interface{}{
"lang": "GO语言",
"tag": "
",
}
// 将会输出 : {"lang":"GO\u8bed\u8a00","tag":"\u003cbr\u003e"}
c.AsciiJSON(http.StatusOK, data)
})
// 监听并服务于 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}
上一篇:PHP实验四
文章标题:XML、JSON、YAML和ProtoBuf 渲染
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/50505.html