MVC URL Routing 深入与使用URL最佳实践
2021-02-09 23:15
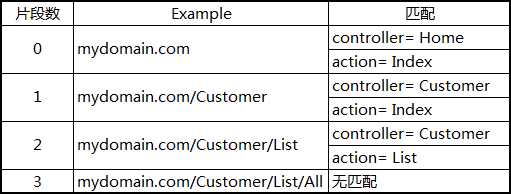
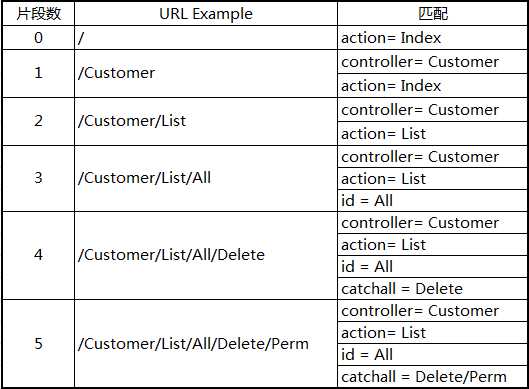
标签:global mapr form col bapi width 其他 resource ring 1.前言 我们知道在ASP.NET Web Forms中,一个URL请求往往对应一个aspx页面,一个aspx页面就是一个物理文件,它包含对请求的处理。 而在ASP.NET MVC中,一个URL请求是由对应的一个Controller中的Action来处理的,由URL Routing来告诉MVC如何定位到正确的Controller和Action。 总的来说,URL Routing包含两个主要功能:解析URL 和 生成URL,本文将围绕这两个大点进行讲解。 2.URL ROUTING的定义方式 http://mysite.com/Admin/Index 在域名的后面,默认使用“/”来对URL进行分段。路由系统通过类似于 {controller}/{action} 格式的字符串可以知道这个URL的 Admin 和 Index 两个片段分别对应Controller和Action的名称。 默认情况下,路由格式中用“/”分隔的段数是和URL域名的后面的段数是一致的,比如,对于{controller}/{action} 格式只会匹配两个片段。如下表所示: URL路由是在MVC工程中的App_Start文件夹下的RouteConfig.cs文件中的RegisterRoutes方法中定义的,下面是创建一个空MVC项目时系统生成的一个简单URL路由定义: 静态方法RegisterRoutes是在Global.asax.cs文件中的Application_Start方法中被调用的,除了URL路由的定义外,还包含其他的一些MVC核心特性的定义: RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes方法中传递的是 RouteTable 类的静态 Routes 属性,返回一个RouteCollection的实例。其实,“原始”的定义路由的方法可以这样写: 创建Route对象时用了一个URL格式字符串和一个MvcRouteHandler对象作为构造函数的参数。不同的ASP.NET技术有不同的RouteHandler,MVC用的是MvcRouteHandler。 这种写法有点繁琐,一种更简单的定义方法是: 这种方法简洁易读,一般我们都会用这种方法定义路由。 3.示例准备 4.给片段变量定义默认值 各种匹配情况: 5.定义静态片段 并不是所有的片段都是用来作为匹配变量的,比如,我们想要URL加上一个名为Public的固定前缀,那么我们可以这样定义: routes.MapRoute("", "Public/{controller}/{action}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }); 这样,请求的URL也需要一个Public前缀与之匹配。我们也可以把静态的字符串放在大括号以外的任何位置,如: routes.MapRoute("", "X{controller}/{action}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" }); 在一些情况下这种定义非常有用。比如当你的网站某个链接已经被用户普遍记住了,但这一块功能已经有了一个新的版本,但调用的是不同名称的controller,那么你把原来的controller名称作为现在controller的别名。这样,用户依然使用他们记住的URL,而导向的却是新的controller。如下使用Shop作为Home的一个别名: routes.MapRoute("ShopSchema", "Shop/{action}", new { controller = "Home" }); 6.自定义片段变量 自定义片段变量的定义和取值 contrlloer和action片段变量对MVC来说有着特殊的意义,在定义一个路由时,我们必须有这样一个概念:contrlloer和action的变量值要么能从URL中匹配得到,要么由默认值提供,总之一个URL请求经过路由系统交给MVC处理时必须保证contrlloer和action两个变量的值都有。当然,除了这两个重要的片段变量,我们也可从通过自定义片段变量来从URL中得到我们想要的其它信息。如下自定义了一个名为Id的片段变量,而且给它定义了默认值: 我们在HomeController中增加一个名为CustomVariable的ACtion来演示一下如何取自定义的片段变量: 可以通过 RouteData.Values[segment] 来取得任意一个片段的变量值。 7.将自定义片段变量作为Action方法的参数 我们可以将自定义的片段变量当作参数传递给Action方法,如下所示: 效果和上面是一样的,只不过这样省去了用 RouteData.Values[segment] 的方式取自定义片段变量的麻烦。这个操作背后是由模型绑定来做的。 8.指定自定义片段变量为可选 指定自定片段变量为可选,即在URL中可以不用指定片段的值。如下面的定义将Id定义为可选: 定义为可选以后,需要对URL中没有Id这个片段值的情况进行处理,如下: 当Id是整型的时候,参数的类型需要改成可空的整型(即int? id)。 为了省去判断参数是否为空,我们也可以把Action方法的id参数也定义为可选,当没有提供Id参数时,Id使用默认值,如下所示: routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = "DefaultId" }); 9. 定义可变数量的自定义片段变量 我们可以通过 catchall 片段变量加 * 号前缀来定义匹配任意数量片段的路由。如下所示: 这个路由定义的匹配情况如下所示: 使用*catchall,将匹配的任意数量的片段,但我们需要自己通过“/”分隔catchall变量的值来取得独立的片段值。 10. 路由约束 MVC URL Routing 深入与使用URL最佳实践 标签:global mapr form col bapi width 其他 resource ring 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/youguess/p/13055834.html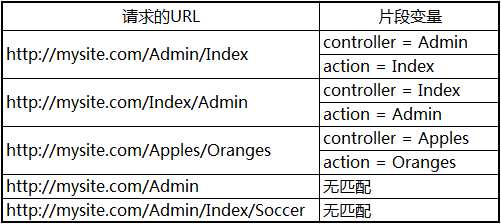
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) {
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
protected void Application_Start() {
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
WebApiConfig.Register(GlobalConfiguration.Configuration);
FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
}
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) {
Route myRoute = new Route("{controller}/{action}", new MvcRouteHandler());
routes.Add("MyRoute", myRoute);
}
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) {
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}");
}
public class HomeController : Controller {
public ActionResult Index() {
ViewBag.Controller = "Home";
ViewBag.Action = "Index";
return View("ActionName");
}
}
public class CustomerController : Controller {
public ActionResult Index() {
ViewBag.Controller = "Customer";
ViewBag.Action = "Index";
return View("ActionName");
}
public ActionResult List() {
ViewBag.Controller = "Customer";
ViewBag.Action = "List";
return View("ActionName");
}
}
public class AdminController : Controller {
public ActionResult Index() {
ViewBag.Controller = "Admin";
ViewBag.Action = "Index";
return View("ActionName");
}
}
@{
Layout = null;
}
DOCTYPE html>
html>
head>
meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
title>ActionNametitle>
head>
body>
div>The controller is: @ViewBag.Controllerdiv>
div>The action is: @ViewBag.Actiondiv>
body>
html>
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) {
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}");
}
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" });
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
new{
controller = "Home",
action = "Index",
id = "DefaultId"});
});
publicActionResult CustomVariable() {
ViewBag.Controller = "Home";
ViewBag.Action = "CustomVariable";
ViewBag.CustomVariable = RouteData.Values["id"];
return View("ActionName");
}
public ActionResult CustomVariable(string id) {
ViewBag.Controller = "Home";
ViewBag.Action = "CustomVariable";
ViewBag.CustomVariable =id;
return View("ActionName");
}
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}", new {
controller = "Home",
action = "Index",
id=UrlParameter.Optional
});
public ActionResult CustomVariable(string id) {
ViewBag.Controller = "Home";
ViewBag.Action = "CustomVariable";
ViewBag.CustomVariable = id == null ? "
public ActionResult CustomVariable(string id = "DefaultId") {
ViewBag.Controller = "Home";
ViewBag.Action = "CustomVariable";
ViewBag.CustomVariable = id;
return View("ActionName");
}
routes.MapRoute("MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}",
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional });
上一篇:html基础
下一篇:websocket协议全双工协议
文章标题:MVC URL Routing 深入与使用URL最佳实践
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/53296.html