Spring(DI,AOP) 理解(一)
2021-02-14 19:16
标签:span 依赖注入 style on() ack 基于 pre 方法 imp 感觉自己的spring理解的不好.所以重新开始学习. 这篇文章主要是来理解DI(依赖注入),Aop(切面) 一.DI(依赖注入,这里没有涉及到注释.只是用xml文件和Bean的方法来注册pojo,) 依赖注入就是将创建bean对象的权利交给spring框架(控制反转) 然后用Applicationcontext.getBean() 来获取对象. 容器:spring容器创建对象,管理对象,并负责管理对象的生命周期. 容器有两种 BeanFactiory ..ApplicationContext ..多的就不解释了,BeanFactiory 比较low,这里使用ApplicaitonContext ApplicaitonContext: 1 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:以基于文件系统的XML配置文件创建ApplicationContext实例。 2 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:以类加载路径下的XML配置文件创建的ApplicationContext实例 3 XmlWebApplicationContext:从web应用下的一个或者多个xml配置文件加载创建ApplicationContext实例 4 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 从一个或者多个基于java的配置类中加载Spring ApplicaitonContext实例 5 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 基于一个或者多个java的配置类来创建spring web 的应用上下文 二. Aop :面向切面编程.(将复用性很强的模块抽离出来,然后通过配置,将抽离出来的模块(比如日志模块),覆盖到其他需要日志模块的服务上) 一个项目假设有讲师服务,学生服务,计费服务.......还有日志模块,安全模块,事务模块 讲师服务,学生服务,计费服务 每一个服务都需要与日志模块,安全模块,事务模块 进行耦合.....如果这个样子,,每一个服务里面的代码不能够专注于解决本服务的问题.需要调用日志模块,安全模块,事务模块的代码. 这样,代码的复用性会很低,耦合性很高. 创建一个Person类...里面有一个doSomething方法 创建一个Play类 type 表示可以做的事情 测试Aop的一个类 装配bean的xml 用javaBean来装配对象 测试Main类 这些代码虽然很简单,却让我认识清楚了DI和Aop的作用 Spring(DI,AOP) 理解(一) 标签:span 依赖注入 style on() ack 基于 pre 方法 imp 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ly12/p/12722110.html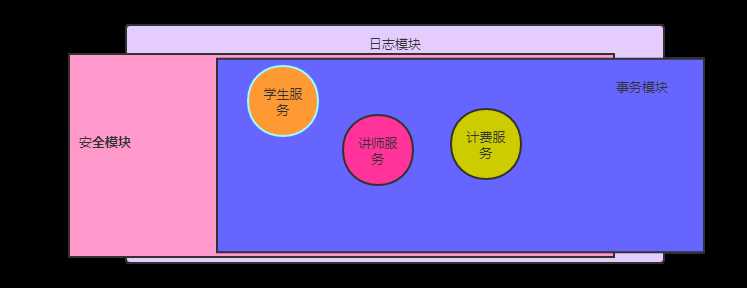
package com.start.demo;
/**
* 男孩,女孩,工程师,程序员....
*/
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Play play;
public Person(Play p) {
this.play = p;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
void doSomething() {
System.out.println(" we can play " + play.getType() +"together");
}
}
package com.start.demo;
/**
* 各种活动,,玩游戏,读书,看电视.....
*/
public class Play {
private String type="computer game";
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
package com.start.demo;
/**
* 这个类是用来测试Aop.在切点之前,之后,分别调用对应的方法
*/
public class Asker {
private String name;
void doSomethingBefore(){
System.out.println("what can we do ");
}
void doSomethingAfter(){
System.out.println("that‘s fine");
}
}
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
bean id="person" class="com.start.demo.Person">
constructor-arg ref="play"/>
bean>
bean id="play" class="com.start.demo.Play"/>
bean id="asker" class="com.start.demo.Asker"/>
aop:config>
aop:aspect ref="asker">
aop:pointcut id="personPointcut"
expression="execution(* *.doSomething())"/>
aop:before pointcut-ref="personPointcut" method="doSomethingBefore"/>
aop:after pointcut-ref="personPointcut" method="doSomethingAfter"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>
package com.start.confBean;
import com.start.demo.Person;
import com.start.demo.Play;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class PersonConf {
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person(play());
}
@Bean
public Play play() {
return new Play();
}
}
package com.start.demo;
import com.start.confBean.PersonConf;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext appcontext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); //从beans.xml 文件获取ApplicaitonContext
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PersonConf.class);//PersonConf.java 文件获取ApplicaitonContext
// Person person1 = annotationApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class); //获取bean ,直接指定Bean 为Person
// Person person = (Person) appcontext.getBean("person");//获取bean person 为配置文件里面的 id
Person pers = (Person) appcontext.getBean("person");
pers.doSomething();
}
}
上一篇:web api 本地测试
下一篇:Java-泛型的作用
文章标题:Spring(DI,AOP) 理解(一)
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/55303.html