2. kubeadm部署kubernetes集群— kubernetes入门到实战【入门+进阶篇】
2021-02-19 13:18
标签:jpg 编译 初始化 server 受限 部署 tables tools vim 要学习kubernetes,首先需要有一个kubernetes集群,社区为了满足不同场景下,提供了不同的安装方法以适应各种场景需求,常见方法有: 对于学习环境,Katacoda提供了一个在线的MiniKube环境,只需在控制台启用即可使用,当然也可以将MiniKube下载到本地使用。对于生产环境,推荐使用二进制安装或者Kubeadm,新版kubeadm目前已将kubernetes管理组件以pod的形式部署在集群中,不管用哪种方式,受限于GFW,大部分镜像下载,大家自行补脑和解决,本文以离线的方式安装部署。 【环境准备】 1、设置主机名,其他两个节点类似设置 2、设置hosts文件,其他两个节点设置相同内容 3、设置SSH无密码登录,并通过ssh-copy-id将公钥拷贝到对端 1、下载docker的yum源 2、设置cgroup driver类型为systemd 3、启动docker服务并验证,可以通过docker info查看docker安装的版本等信息 1、安装kubernetes源,国内可以使用阿里的kubernetes源,速度会快一点 2、安装kubeadm,kubelet,kubectl,会自动安装几个重要依赖包:socat,cri-tools,cni等包 3、设置iptables网桥参数 4、重新启动kubelet服务,使配置生效 1、从cos中下载kubernetes安装镜像,并通过docker load命令将镜像导入到环境中 2、检查镜像列表 1、 kubeadm初始化集群,需要设置初始参数 通过kubeadm init --apiserver-advertise-address 10.254.100.101 --apiserver-bind-port 6443 --kubernetes-version 1.14.1 --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16安装命令,显示了kubeadm安装过程中的一些重要步骤:下载镜像,生成证书,生成配置文件,配置RBAC授权认证,配置环境变量,安装网络插件指引,添加node指引配置文件。 2、生成kubectl环境配置文件 3、添加node节点,将另外两个节点加入到集群中,复制上述的添加节点命令到指定节点添加即可。 4、安装网络plugin,kubernetes支持多种类型网络插件,要求网络支持CNI插件即可,CNI是Container Network Interface,要求kubernetes的中pod网络访问方式: 不同的CNI plugin支持的特性有所差别。kubernetes支持多种开源的网络CNI插件,常见的有flannel、calico、canal、weave等,flannel是一种overlay的网络模型,通过vxlan隧道方式构建tunnel网络,实现k8s中网络的互联,后续在做介绍,如下是安装过程: 5、通过上述输出可知道,部署flannel 需要RBAC授权,配置configmap和daemonset,其中Daemonset能够适配各种类型的CPU架构,默认安装了多个,一般是adm64即可,可以将上述的url下载编辑,保留kube-flannel-ds-amd64这个daemonset即可,或者将其删除 6、此时再验证node的安装情况,所有节点均已显示为Ready状态,安装完毕! 1、验证node状态,获取当前安装节点,可以查看到状态, 角色,启动市场,版本, 2、查看kubernetse服务组件状态,包括scheduler,controller-manager,etcd 3、查看pod的情况,master中的角色包括kube-apiserver,kube-scheduler,kube-controller-manager,etcd,coredns以pods形式部署在集群中,worker节点的kube-proxy也以pod的形式部署。实际上pod是以其他控制器如daemonset的形式控制的。 使用kubectl和kubernetes交互时候可以使用缩写模式也可以使用完整模式,如kubectl get nodes和kubectl get no能实现一样的效果,为了提高工作效率,可以使用命令补全的方式加快工作效率。 1、生成kubectl bash命令行补全shell 2、加载shell环境变量,使配置生效 3、校验命令行补全,命令行中输入kubectl get co再按TAB键就能自动补全了 除了支持命令行补全之外,kubectl还支持命令简写,如下是一些常见的命令行检测操作,更多通过kubectl api-resources命令获取,SHORTNAMES显示的是子命令中的简短用法。 2. kubeadm部署kubernetes集群— kubernetes入门到实战【入门+进阶篇】 标签:jpg 编译 初始化 server 受限 部署 tables tools vim 原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/happylab/24971381.1 kubernetes安装概述
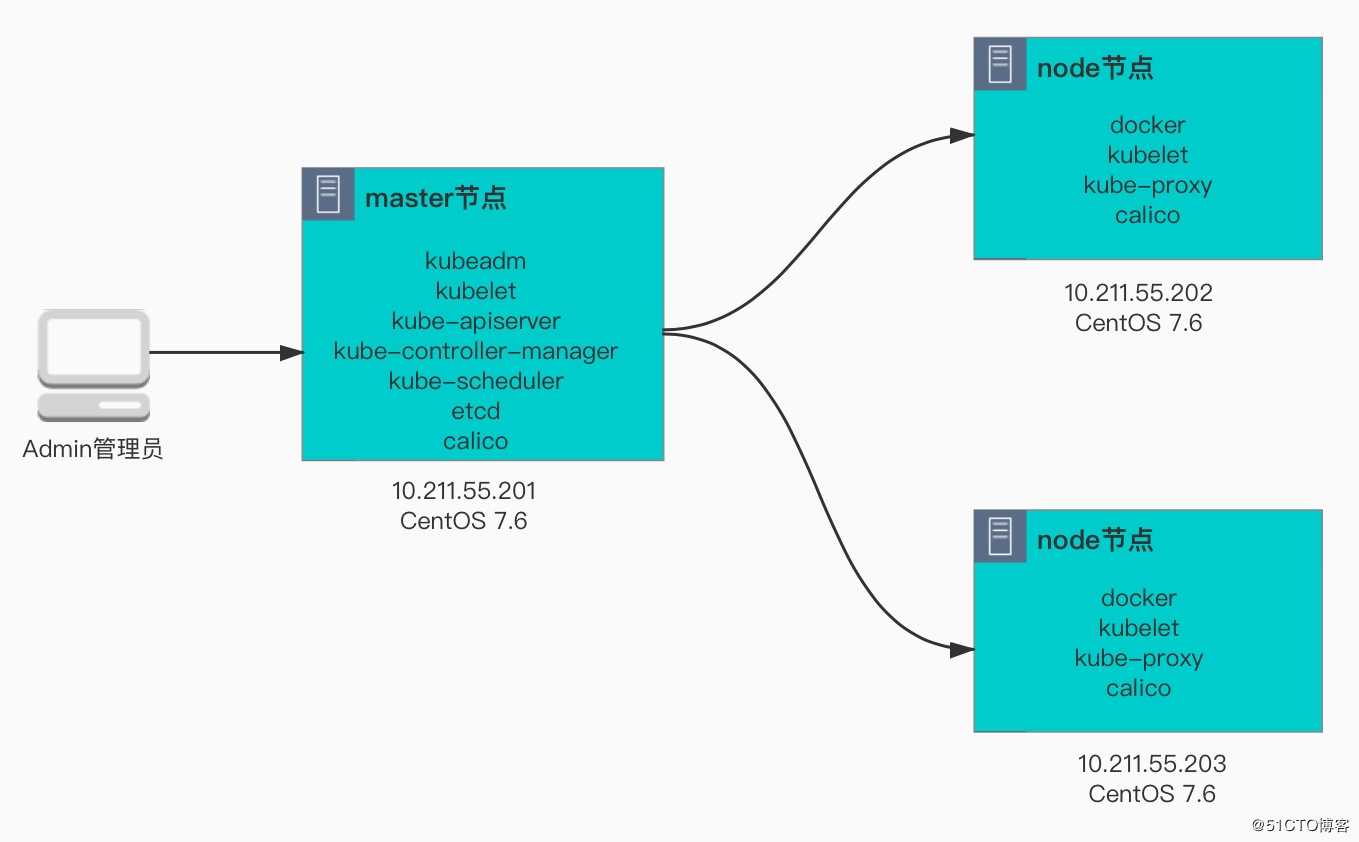
1.2 kubernetes环境说明
root@VM_100_101_centos ~# hostnamectl set-hostname node-1
root@VM_100_101_centos ~# hostname
node-1root@node-1 ~# vim /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain
10.211.55.201 node-1
10.211.55.202 node-2
10.211.55.203 node-3#生成密钥对
root@node-1 .ssh# ssh-keygen -P ‘‘
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:zultDMEL8bZmpbUjQahVjthVAcEkN929w5EkUmPkOrU root@node-1
The key‘s randomart image is:
+---RSA 2048----+
| .=O=+=o.. |
| o+o..+.o+ |
| .oo=. o. o |
| . . * oo .+ |
| oSOo.E . |
| oO.o. |
| o++ . |
| . .o |
| ... |
+----SHA256-----+
#拷贝公钥到node-2和node-3节点
root@node-1 .ssh# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub node-2:
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host ‘node-1 (10.254.100.101)‘ can‘t be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:jLUH0exgyJdsy0frw9R+FiWy+0o54LgB6dgVdfc6SEE.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:f4:86:a8:0e:a6:03:fc:a6:04:df:91:d8:7a:a7:0d:9e.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@node-1‘s password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh ‘node-2‘"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.1.3 安装docker
# wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo[root@node-1 ~]# cat > /etc/docker/daemon.json {
> "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
> "log-driver": "json-file",
> "log-opts": {
> "max-size": "100m"
> },
> "storage-driver": "overlay2",
> "storage-opts": [
> "overlay2.override_kernel_check=true"
> ]
> }
> EOF[root@node-1 ~]# systemctl restart docker
[root@node-1 ~]# systemctl enable docker1.4 安装kubeadm组件
[root@node-1 ~]#cat /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF[root@node-1 ~]# yum install kubeadm kubectl kubelet --disableexcludes=kubernetes -y[root@node-1 ~]# cat /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
> net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
> net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
> EOF
[root@node-1 ~]# sysctl --system,然后使用sysctl -a|grep 参数的方式验证是否生效[root@node-1 ~]# systemctl restart kubelet
[root@node-1 ~]# systemctl enable kubelet1.5 导入kubernetes镜像
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i etcd:3.3.10.tar
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i pause:3.1.tar
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i coredns:1.3.1.tar
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i flannel:v0.11.0-amd64.tar
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i kube-apiserver:v1.14.1.tar
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i kube-controller-manager:v1.14.1.tar
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i kube-scheduler:v1.14.1.tar
[root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image load -i kube-proxy:v1.14.1.tar [root@node-1 v1.14.1]# docker image list
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
k8s.gcr.io/kube-proxy v1.14.1 20a2d7035165 3 months ago 82.1MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-apiserver v1.14.1 cfaa4ad74c37 3 months ago 210MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-scheduler v1.14.1 8931473d5bdb 3 months ago 81.6MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager v1.14.1 efb3887b411d 3 months ago 158MB
quay.io/coreos/flannel v0.11.0-amd64 ff281650a721 6 months ago 52.6MB
k8s.gcr.io/coredns 1.3.1 eb516548c180 6 months ago 40.3MB
k8s.gcr.io/etcd 3.3.10 2c4adeb21b4f 8 months ago 258MB
k8s.gcr.io/pause 3.1 da86e6ba6ca1 19 months ago 742kB1.6 kubeadm初始化集群
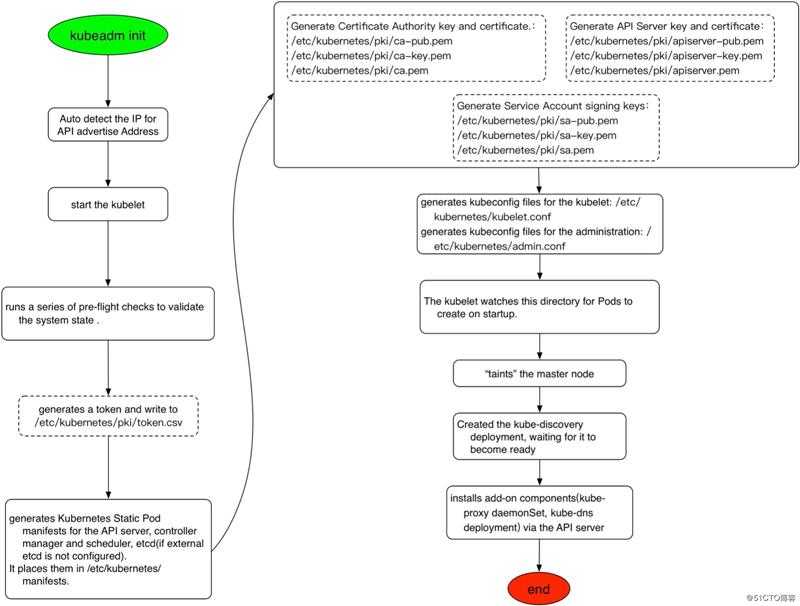
[root@node-1 ~]# kubeadm init --apiserver-advertise-address 10.254.100.101 --apiserver-bind-port 6443 --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.14.1
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING SystemVerification]: this Docker version is not on the list of validated versions: 18.03.1-ce. Latest validated version: 18.09
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using ‘kubeadm config images pull‘#下载镜像
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"#生成CA等证书
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [node-1 kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 10.254.100.101]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [node-1 localhost] and IPs [10.254.100.101 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [node-1 localhost] and IPs [10.254.100.101 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"#生成master节点静态pod配置文件
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 18.012370 seconds
[upload-config] storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.14" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --experimental-upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node node-1 as control-plane by adding the label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=‘‘"
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node node-1 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: r8n5f2.9mic7opmrwjakled
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles#配置RBAC授权
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube #配置环境变量配置文件
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at: #安装网络插件
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 10.254.100.101:6443 --token r8n5f2.9mic7opmrwjakled \ #添加节点命令,优先记录下来
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:16e383c8abff6233021331944080087f0514ddd15d96c65d19443b0af02d64ab [root@node-1 ~]# mkdir /root/.kube
[root@node-1 ~]# cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf /root/.kube/config
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node-1 NotReady master 6m29s v1.14.1[root@node-3 ~]# kubeadm join 10.254.100.101:6443 --token r8n5f2.9mic7opmrwjakled > --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:16e383c8abff6233021331944080087f0514ddd15d96c65d19443b0af02d64ab
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING SystemVerification]: this Docker version is not on the list of validated versions: 18.03.1-ce. Latest validated version: 18.09
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with ‘kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -oyaml‘
[kubelet-start] Downloading configuration for the kubelet from the "kubelet-config-1.14" ConfigMap in the kube-system namespace
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run ‘kubectl get nodes‘ on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
以此类推到node-2节点添加即可,添加完之后通过kubectl get nodes验证,此时由于还没有安装网络plugin,
所有的node节点均显示NotReady状态:
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node-1 NotReady master 16m v1.14.1
node-2 NotReady 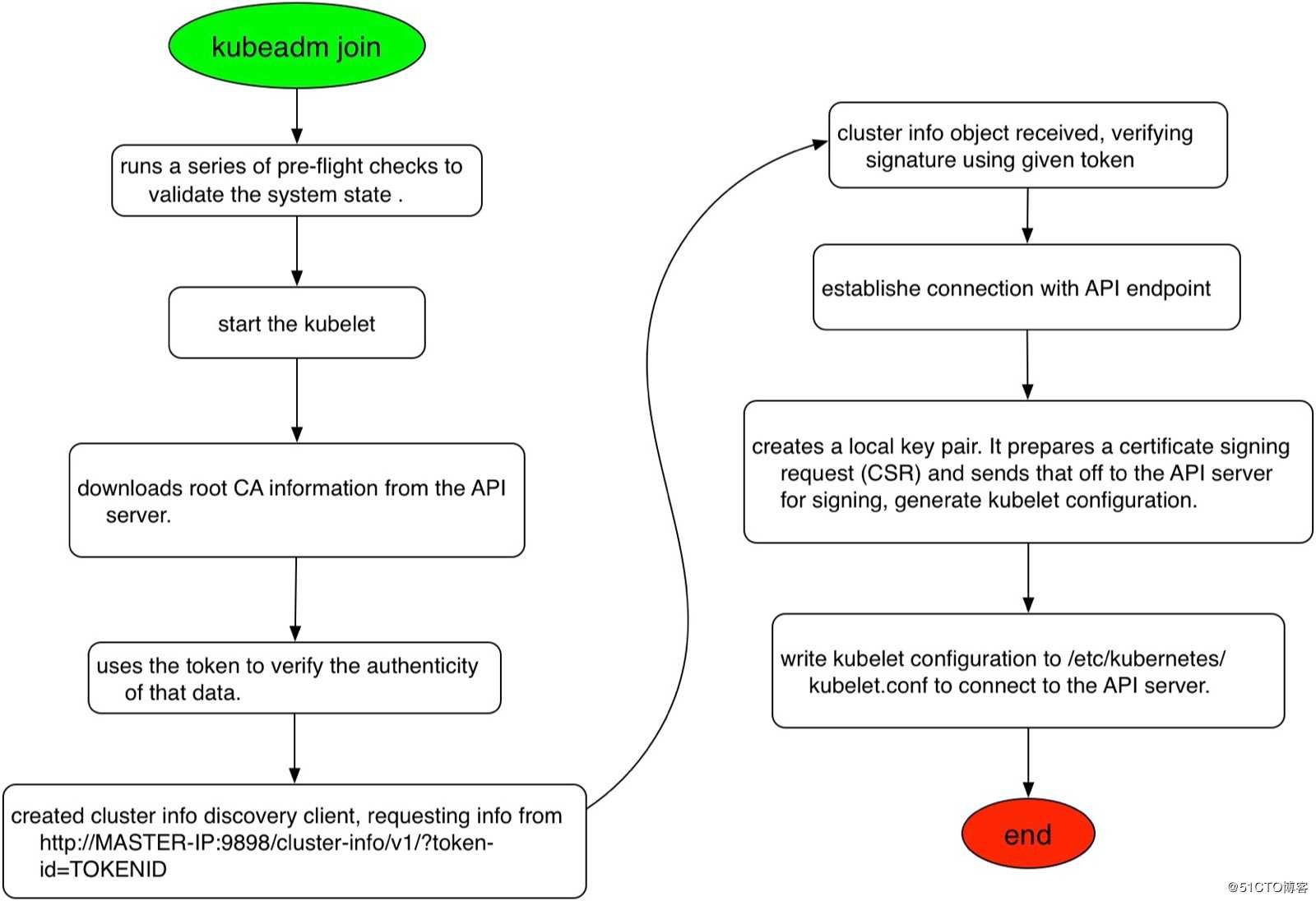
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/62e44c867a2846fefb68bd5f178daf4da3095ccb/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
podsecuritypolicy.extensions/psp.flannel.unprivileged created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
serviceaccount/flannel created
configmap/kube-flannel-cfg created
daemonset.extensions/kube-flannel-ds-amd64 created
daemonset.extensions/kube-flannel-ds-arm64 created
daemonset.extensions/kube-flannel-ds-arm created
daemonset.extensions/kube-flannel-ds-ppc64le created
daemonset.extensions/kube-flannel-ds-s390x created#查看flannel安装的daemonsets
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get daemonsets -n kube-system
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
kube-flannel-ds-amd64 3 3 3 3 3 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64 2m34s
kube-flannel-ds-arm 0 0 0 0 0 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=arm 2m34s
kube-flannel-ds-arm64 0 0 0 0 0 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=arm64 2m34s
kube-flannel-ds-ppc64le 0 0 0 0 0 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=ppc64le 2m34s
kube-flannel-ds-s390x 0 0 0 0 0 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=s390x 2m34s
kube-proxy 3 3 3 3 3 [root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node-1 Ready master 29m v1.14.1
node-2 Ready 1.7 验证kubernetes组件
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node-1 Ready master 46m v1.14.1
node-2 Ready [root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get componentstatuses
NAME STATUS MESSAGE ERROR
scheduler Healthy ok
controller-manager Healthy ok
etcd-0 Healthy {"health":"true"} [root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-fb8b8dccf-hrqm8 1/1 Running 0 50m
coredns-fb8b8dccf-qwwks 1/1 Running 0 50m
etcd-node-1 1/1 Running 0 48m
kube-apiserver-node-1 1/1 Running 0 49m
kube-controller-manager-node-1 1/1 Running 0 49m
kube-proxy-lfckv 1/1 Running 0 38m
kube-proxy-x5t6r 1/1 Running 0 50m
kube-proxy-x8zqh 1/1 Running 0 36m
kube-scheduler-node-1 1/1 Running 0 49m1.8 配置kubectl命令补全
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl completion bash >/etc/kubernetes/kubectl.sh
[root@node-1 ~]# echo "source /etc/kubernetes/kubectl.sh" >>/root/.bashrc
[root@node-1 ~]# cat /root/.bashrc
# .bashrc
# User specific aliases and functions
alias rm=‘rm -i‘
alias cp=‘cp -i‘
alias mv=‘mv -i‘
# Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
source /etc/kubernetes/kubectl.sh #添加环境变量配置[root@node-1 ~]# source /etc/kubernetes/kubectl.sh [root@node-1~]# kubectl get co componentstatuses configmaps controllerrevisions.apps
[root@node-1~]# kubectl get componentstatuses
参考文档
文章标题:2. kubeadm部署kubernetes集群— kubernetes入门到实战【入门+进阶篇】
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/57537.html