Java基础之异常
2021-03-04 22:29
标签:cep except cts demo exce 程序 就会 extends rgs 异常 try。。。。catch throw throws Objects 判断非空 finally 有try或catch先走try或catch finally后走 自定义异常 Java基础之异常 标签:cep except cts demo exce 程序 就会 extends rgs 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/qj696/p/14333108.htmlpublic class Demo02Exception {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建int类型的数组,并赋值
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
int e = getElement(arr,3);
System.out.println(e);
}
/*
定义一个方法,获取数组指定索引处的元素
参数:
int[] arr
int index
*/
public static int getElement(int[] arr,int index){
int ele = arr[index];
return ele;
}
}
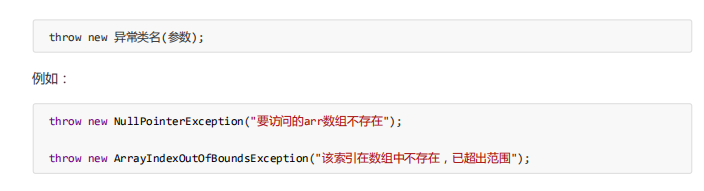
try...catch:异常处理的第二种方式,自己处理异常
格式:
try{
可能产生异常的代码
}catch(定义一个异常的变量,用来接收try中抛出的异常对象){
异常的处理逻辑,异常异常对象之后,怎么处理异常对象
一般在工作中,会把异常的信息记录到一个日志中
}
...
catch(异常类名 变量名){
}
注意:
1.try中可能会抛出多个异常对象,那么就可以使用多个catch来处理这些异常对象
2.如果try中产生了异常,那么就会执行catch中的异常处理逻辑,执行完毕catch中的处理逻辑,继续执行try...catch之后的代码
如果try中没有产生异常,那么就不会执行catch中异常的处理逻辑,执行完try中的代码,继续执行try...catch之后的代码
*/
public class Demo01TryCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
//可能产生异常的代码
readFile("d:\\a.tx");
System.out.println("资源释放");
}catch (IOException e){//try中抛出什么异常对象,catch就定义什么异常变量,用来接收这个异常对象
//异常的处理逻辑,异常异常对象之后,怎么处理异常对象
//System.out.println("catch - 传递的文件后缀不是.txt");
/*
Throwable类中定义了3个异常处理的方法
String getMessage() 返回此 throwable 的简短描述。
String toString() 返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串。
void printStackTrace() JVM打印异常对象,默认此方法,打印的异常信息是最全面的
*/
//System.out.println(e.getMessage());//文件的后缀名不对
//System.out.println(e.toString());//重写Object类的toString java.io.IOException: 文件的后缀名不对
//System.out.println(e);//java.io.IOException: 文件的后缀名不对
/*
java.io.IOException: 文件的后缀名不对
at com.itheima.demo02.Exception.Demo01TryCatch.readFile(Demo01TryCatch.java:55)
at com.itheima.demo02.Exception.Demo01TryCatch.main(Demo01TryCatch.java:27)
*/
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("后续代码");
}
/*
如果传递的路径,不是.txt结尾
那么我们就抛出IO异常对象,告知方法的调用者,文件的后缀名不对
*/
public static void readFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
if(!fileName.endsWith(".txt")){
throw new IOException("文件的后缀名不对");
}
System.out.println("路径没有问题,读取文件");
}
}
public class Demo03Throw {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int[] arr = null;
int[] arr = new int[3];
int e = getElement(arr,3);
System.out.println(e);
}
/*
定义一个方法,获取数组指定索引处的元素
参数:
int[] arr
int index
以后(工作中)我们首先必须对方法传递过来的参数进行合法性校验
如果参数不合法,那么我们就必须使用抛出异常的方式,告知方法的调用者,传递的参数有问题
注意:
NullPointerException是一个运行期异常,我们不用处理,默认交给JVM处理
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException是一个运行期异常,我们不用处理,默认交给JVM处理
*/
public static int getElement(int[] arr,int index){
/*
我们可以对传递过来的参数数组,进行合法性校验
如果数组arr的值是null
那么我们就抛出空指针异常,告知方法的调用者"传递的数组的值是null"
*/
if(arr == null){
throw new NullPointerException("传递的数组的值是null");
}
/*
我们可以对传递过来的参数index进行合法性校验
如果index的范围不在数组的索引范围内
那么我们就抛出数组索引越界异常,告知方法的调用者"传递的索引超出了数组的使用范围"
*/
if(indexarr.length-1){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("传递的索引超出了数组的使用范围");
}
int ele = arr[index];
return ele;
}
}


public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
readFile("c:\\a.tx");
System.out.println("后续代码");
}
/*
定义一个方法,对传递的文件路径进行合法性判断
如果路径不是"c:\\a.txt",那么我们就抛出文件找不到异常对象,告知方法的调用者
注意:
FileNotFoundException是编译异常,抛出了编译异常,就必须处理这个异常
可以使用throws继续声明抛出FileNotFoundException这个异常对象,让方法的调用者处理
*/
public static void readFile(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{
if(!fileName.equals("c:\\a.txt")){
throw new FileNotFoundException("传递的文件路径不是c:\\a.txt");
}
/*
如果传递的路径,不是.txt结尾
那么我们就抛出IO异常对象,告知方法的调用者,文件的后缀名不对
*/
if(!fileName.endsWith(".txt")){
throw new IOException("文件的后缀名不对");
}
System.out.println("路径没有问题,读取文件");
}
}
public class Demo04Objects {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method(null);
}
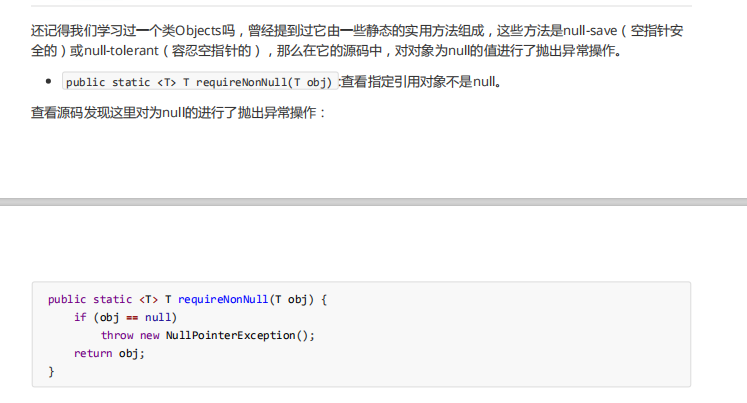
public static void method(Object obj){
//对传递过来的参数进行合法性判断,判断是否为null
/*if(obj == null){
throw new NullPointerException("传递的对象的值是null");
}*/
//Objects.requireNonNull(obj);
Objects.requireNonNull(obj,"传递的对象的值是null");
}
}


public class Fu {
public void show01() throws NullPointerException,ClassCastException{}
public void show02() throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{}
public void show03() throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{}
public void show04() {} 没有异常
}
class Zi extends Fu{
//子类重写父类方法时,抛出和父类相同的异常
public void show01() throws NullPointerException,ClassCastException{}
//子类重写父类方法时,抛出父类异常的子类
public void show02() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{}
//子类重写父类方法时,不抛出异常
public void show03() {}
/*
父类方法没有抛出异常,子类重写父类该方法时也不可抛出异常。
*/
//public void show04() throws Exception{}
//此时子类产生该异常,只能捕获处理,不能声明抛出
public void show04() { 此处必能抛出异常只能try catch
try {
throw new Exception("编译期异常");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
package com.itheima.demo03.Exception;
import java.util.List;
/*
异常的注意事项
*/
public class Demo01Exception {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
多个异常使用捕获又该如何处理呢?
1. 多个异常分别处理。
2. 多个异常一次捕获,多次处理。
3. 多个异常一次捕获一次处理。
*/
//1. 多个异常分别处理。
/* try {
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(arr[3]);//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
try{
List

