java_多线程 (二)
2021-03-05 01:27
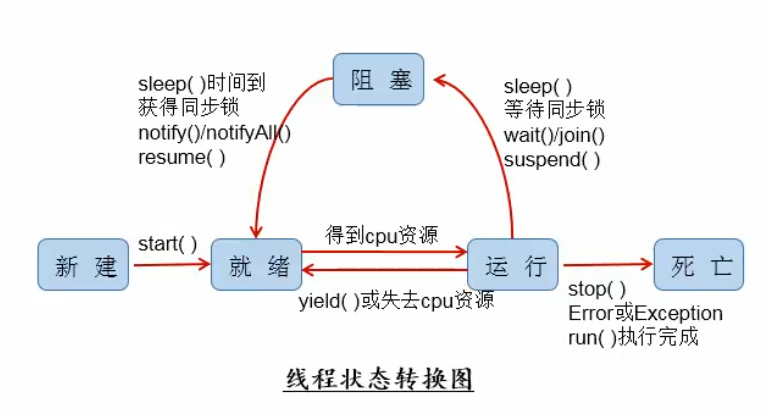
标签:style 解决办法 extend logs img runnable setname 接口 == 1.创建多线程的第二种方式 2.用第二种方式 , 实现多个窗口同时买票 3.线程的生命周期 4.两种创建线程方式的选择 5.解决多线程的线程安全问题(方式一 : 同步代码块) 6.解决多线程的线程安全问题(方式二 : 同步方法) java_多线程 (二) 标签:style 解决办法 extend logs img runnable setname 接口 == 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Anonymity-zhang/p/14334074.html//创建多线程的第二种方式 : 实现runnable接口
//1.创建子类实现runnable接口
class MyThread implements Runnable{
//2.重写run()
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i ) {
if (i % 2 ==0){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
public class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3.创建实现类的对象
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
//4.将实现类作为参数放到Thread的构造器中,创建Thread对象
Thread thread = new Thread(myThread);
//5.调用start()
thread.start();
}
}
//多线程案例2 : 三个窗口卖票
class Window implements Runnable{
//票数 100 , 注意这里不需要加static
private int ticket=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if (ticket > 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖票 , 票号为:"+ticket);
ticket--;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
}
public class WindowTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Window w = new Window();
// 100号票被重复消费的问题
Thread t1 = new Thread(w);
Thread t2 = new Thread(w);
Thread t3 = new Thread(w);
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}


//用同步代码块 , 解决extends Thread 的线程安全问题
class Window3 extends Thread{
private static int ticket=100;
//需要创建一个对象来充当锁 , 且必须唯一 : static
private static Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//方式一 : 同不代码块
//this : 代表 -> 锁 , 这里的锁必须是唯一的
//this在implements Tunnable方式中可以用 , 但是在这里不能用
synchronized(obj) {
if (ticket > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖票 , 票号为:" + ticket);
ticket--;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class WindowTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Window3 w1 = new Window3();
Window3 w2 = new Window3();
Window3 w3 = new Window3();
w1.setName("窗口1");
w2.setName("窗口2");
w3.setName("窗口3");
w1.start();
w2.start();
w3.start();
}
}
//多线程案例 : 买票 -> implements Runnable
//问题 : 重票 & 错票
//解决办法 : 1.同步代码块 2. 同步方法
class Window2 implements Runnable{
//票数 100 , 注意这里不需要加static
private int ticket=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//方式一 : 同不代码块
//this : 代表 -> 锁 , 这里的锁必须是唯一的, 这个this代表Window2 , 而Window2我们只创建了一次,所以可以用
synchronized(this) {
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖票 , 票号为:" + ticket);
ticket--;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class WindowTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Window2 w = new Window2();
// 100号票被重复消费的问题
Thread t1 = new Thread(w);
Thread t2 = new Thread(w);
Thread t3 = new Thread(w);
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
//同步方法
class Window4 extends Thread{
private static int ticket=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//方式二: 同步方法
show();
if (ticket){
break;
}
}
}
private static synchronized void show(){ //static : 表示只加载一次 , 这里的锁默认为当前类的对象 : Window4.class
if (ticket > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖票 , 票号为:" + ticket);
ticket--;
}
}
}
public class WindowTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Window4 w1 = new Window4();
Window4 w2 = new Window4();
Window4 w3 = new Window4();
w1.setName("窗口1");
w2.setName("窗口2");
w3.setName("窗口3");
w1.start();
w2.start();
w3.start();
}
}
//用同步方法 解决 implements Runnable 的线程安全问题
class Window5 implements Runnable{
//票数 100 , 注意这里不需要加static
private int ticket=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
show();
if (ticket){
break;
}
}
}
private synchronized void show(){ //因为Window5只创建一次 , 所以这里不需要static , 且当前的 默认锁为 : this
if (ticket > 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖票 , 票号为:"+ticket);
ticket--;
}
}
}
public class WindowTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Window5 w = new Window5();
// 100号票被重复消费的问题
Thread t1 = new Thread(w);
Thread t2 = new Thread(w);
Thread t3 = new Thread(w);
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}