Python格式化输出
2021-03-10 14:30
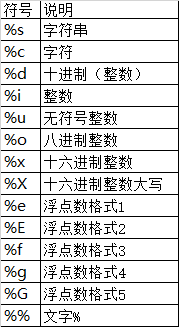
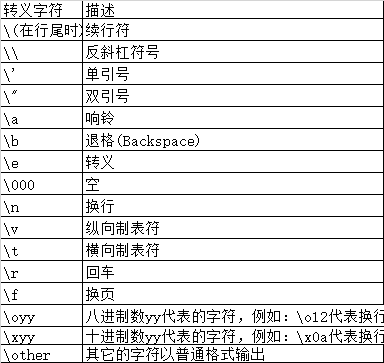
标签:默认 lte 多个 %x tool ima 区域 alt mat 1、整数的输出 2、浮点数输出 (2)内置round() round(number[, ndigits]) 注:“.5”这个是一个“坑”,且python2和python3出来的接口有时候是不一样的,尽量避免使用round()函数吧 3、字符串输出 4、 其他 字符串格式代码如下 (2)常用转义字符如下 二、format用法 相对基本格式化输出采用‘%’的方法,format()功能更强大,该函数把字符串当成一个模板,通过传入的参数进行格式化,并且使用大括号‘{}’作为特殊字符代替‘%’ 使用方法由两种:b.format(a)和format(a,b)。 1、基本用法 (1)不带编号,即“{}” (2)带数字编号,可调换顺序,即“{1}”、“{2}” (3)带关键字,即“{a}”、“{tom}” 2、进阶用法 (1) 右对齐、^ 中间对齐、= (只用于数字)在小数点后进行补齐 (2)取位数“{:4s}”、"{:.2f}"等 3、多个格式化 Python格式化输出 标签:默认 lte 多个 %x tool ima 区域 alt mat 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/maybach/p/14148649.html
%o —— oct 八进制
%d —— dec 十进制
%x —— hex 十六进制1 >>> print(‘%o‘ % 20)
2 24
3 >>> print(‘%d‘ % 20)
4 20
5 >>> print(‘%x‘ % 20)
6 14
(1)格式化输出
%f ——保留小数点后面六位有效数字
%.3f,保留3位小数位
%e ——保留小数点后面六位有效数字,指数形式输出
%.3e,保留3位小数位,使用科学计数法
%g ——在保证六位有效数字的前提下,使用小数方式,否则使用科学计数法
%.3g,保留3位有效数字,使用小数或科学计数法

1 >>> print(‘%f‘ % 1.11) # 默认保留6位小数
2 1.110000
3 >>> print(‘%.1f‘ % 1.11) # 取1位小数
4 1.1
5 >>> print(‘%e‘ % 1.11) # 默认6位小数,用科学计数法
6 1.110000e+00
7 >>> print(‘%.3e‘ % 1.11) # 取3位小数,用科学计数法
8 1.110e+00
9 >>> print(‘%g‘ % 1111.1111) # 默认6位有效数字
10 1111.11
11 >>> print(‘%.7g‘ % 1111.1111) # 取7位有效数字
12 1111.111
13 >>> print(‘%.2g‘ % 1111.1111) # 取2位有效数字,自动转换为科学计数法
14 1.1e+03


参数:
number - 这是一个数字表达式。
ndigits - 表示从小数点到最后四舍五入的位数。默认值为0。
返回值
该方法返回x的小数点舍入为n位数后的值。
round()函数只有一个参数,不指定位数的时候,返回一个整数,而且是最靠近的整数,类似于四舍五入,当指定取舍的小数点位数的时候,一般情况也是使用四舍五入的规则,但是碰到.5的情况时,如果要取舍的位数前的小数是奇数,则直接舍弃,如果是偶数则向上取舍。

1 >>> round(1.1125) # 四舍五入,不指定位数,取整
2 1
3 >>> round(1.1135,3) # 取3位小数,由于3为奇数,则向下“舍”
4 1.113
5 >>> round(1.1125,3) # 取3位小数,由于2为偶数,则向上“入”
6 1.113
7 >>> round(1.5) # 无法理解,查阅一些资料是说python会对数据进行截断,没有深究
8 2
9 >>> round(2.5) # 无法理解
10 2
11 >>> round(1.675,2) # 无法理解
12 1.68
13 >>> round(2.675,2) # 无法理解
14 2.67
15 >>>


%s
%10s——右对齐,占位符10位
%-10s——左对齐,占位符10位
%.2s——截取2位字符串
%10.2s——10位占位符,截取两位字符串

1 >>> print(‘%s‘ % ‘hello world‘) # 字符串输出
2 hello world
3 >>> print(‘%20s‘ % ‘hello world‘) # 右对齐,取20位,不够则补位
4 hello world
5 >>> print(‘%-20s‘ % ‘hello world‘) # 左对齐,取20位,不够则补位
6 hello world
7 >>> print(‘%.2s‘ % ‘hello world‘) # 取2位
8 he
9 >>> print(‘%10.2s‘ % ‘hello world‘) # 右对齐,取2位
10 he
11 >>> print(‘%-10.2s‘ % ‘hello world‘) # 左对齐,取2位
12 he




1 >>> print(‘{} {}‘.format(‘hello‘,‘world‘)) # 不带字段
2 hello world
3 >>> print(‘{0} {1}‘.format(‘hello‘,‘world‘)) # 带数字编号
4 hello world
5 >>> print(‘{0} {1} {0}‘.format(‘hello‘,‘world‘)) # 打乱顺序
6 hello world hello
7 >>> print(‘{1} {1} {0}‘.format(‘hello‘,‘world‘))
8 world world hello
9 >>> print(‘{a} {tom} {a}‘.format(tom=‘hello‘,a=‘world‘)) # 带关键字
10 world hello world




1 >>> print(‘{} and {}‘.format(‘hello‘,‘world‘)) # 默认左对齐
2 hello and world
3 >>> print(‘{:10s} and {:>10s}‘.format(‘hello‘,‘world‘)) # 取10位左对齐,取10位右对齐
4 hello and world
5 >>> print(‘{:^10s} and {:^10s}‘.format(‘hello‘,‘world‘)) # 取10位中间对齐
6 hello and world
7 >>> print(‘{} is {:.2f}‘.format(1.123,1.123)) # 取2位小数
8 1.123 is 1.12
9 >>> print(‘{0} is {0:>10.2f}‘.format(1.123)) # 取2位小数,右对齐,取10位
10 1.123 is 1.12




1 >>> print(‘{0:b}‘.format(3))
2 11
3 >>> print(‘{:c}‘.format(20))
4
5 >>> print(‘{:d}‘.format(20))
6 20
7 >>> print(‘{:o}‘.format(20))
8 24
9 >>> print(‘{:x}‘.format(20))
10 14
11 >>> print(‘{:e}‘.format(20))
12 2.000000e+01
13 >>> print(‘{:g}‘.format(20.1))
14 20.1
15 >>> print(‘{:f}‘.format(20))
16 20.000000
17 >>> print(‘{:n}‘.format(20))
18 20
19 >>> print(‘{:%}‘.format(20))
20 2000.000000%
21 >>>

下一篇:springboot elk