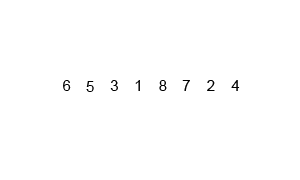算法设计与分析——排序
2021-03-12 00:36
标签:order line NPU 最小 anti ges new pack spec 关于排序的原文网址:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/21elementary/ 算法设计与分析——排序 标签:order line NPU 最小 anti ges new pack spec 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Monster-su/p/14512684.html选择排序(Selection sort)
思想
package sort;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Selection {
// This class should not be instantiated.
private Selection() { }
/**
* Rearranges the array in ascending order, using the natural order.
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int n = a.length;
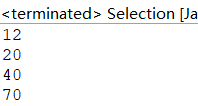
for (int i = 0; i 运行结果
插入排序(Insertion sort)
思想:
package sort;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Insertion {
// This class should not be instantiated.
private Insertion() { }
/**
* Rearranges the array in ascending order, using the natural order.
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int n = a.length;
for (int i = 1; i 0 && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--) {
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
assert isSorted(a, 0, i);
}
assert isSorted(a);
}
/**
* Rearranges the subarray a[lo..hi) in ascending order, using the natural order.
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param lo left endpoint (inclusive)
* @param hi right endpoint (exclusive)
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
for (int i = lo + 1; i lo && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--) {
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
}
assert isSorted(a, lo, hi);
}
/**
* Rearranges the array in ascending order, using a comparator.
* @param a the array
* @param comparator the comparator specifying the order
*/
public static void sort(Object[] a, Comparator comparator) {
int n = a.length;
for (int i = 1; i 0 && less(a[j], a[j-1], comparator); j--) {
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
assert isSorted(a, 0, i, comparator);
}
assert isSorted(a, comparator);
}
/**
* Rearranges the subarray a[lo..hi) in ascending order, using a comparator.
* @param a the array
* @param lo left endpoint (inclusive)
* @param hi right endpoint (exclusive)
* @param comparator the comparator specifying the order
*/
public static void sort(Object[] a, int lo, int hi, Comparator comparator) {
for (int i = lo + 1; i lo && less(a[j], a[j-1], comparator); j--) {
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
}
assert isSorted(a, lo, hi, comparator);
}
// return a permutation that gives the elements in a[] in ascending order
// do not change the original array a[]
/**
* Returns a permutation that gives the elements in the array in ascending order.
* @param a the array
* @return a permutation {@code p[]} such that {@code a[p[0]]}, {@code a[p[1]]},
* ..., {@code a[p[n-1]]} are in ascending order
*/
public static int[] indexSort(Comparable[] a) {
int n = a.length;
int[] index = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i 0 && less(a[index[j]], a[index[j-1]]); j--)
exch(index, j, j-1);
return index;
}
/***************************************************************************
* Helper sorting functions.
***************************************************************************/
// is v 运行结果

希尔排序(Shellsort)
思想
package sort;
public class Shell {
// This class should not be instantiated.
private Shell() { }
/**
* Rearranges the array in ascending order, using the natural order.
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int n = a.length;
// 3x+1 increment sequence: 1, 4, 13, 40, 121, 364, 1093, ...
int h = 1;
while (h = 1) {
// h-sort the array
for (int i = h; i = h && less(a[j], a[j-h]); j -= h) {
exch(a, j, j-h);
}
}
assert isHsorted(a, h);
h /= 3;
}
assert isSorted(a);
}
/***************************************************************************
* Helper sorting functions.
***************************************************************************/
// is v 运行结果

归并排序(Mergesort)
思想
package sort;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Merge {
// This class should not be instantiated.
private Merge() { }
// stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 ..hi] using aux[lo .. hi]
private static void merge(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) {
// precondition: a[lo .. mid] and a[mid+1 .. hi] are sorted subarrays
assert isSorted(a, lo, mid);
assert isSorted(a, mid+1, hi);
// copy to aux[]
for (int k = lo; k mid) a[k] = aux[j++];
else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++];
else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++];
else a[k] = aux[i++];
}
// postcondition: a[lo .. hi] is sorted
assert isSorted(a, lo, hi);
}
// mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi]
private static void sort(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int hi) {
if (hi mid) index[k] = aux[j++];
else if (j > hi) index[k] = aux[i++];
else if (less(a[aux[j]], a[aux[i]])) index[k] = aux[j++];
else index[k] = aux[i++];
}
}
/**
* Returns a permutation that gives the elements in the array in ascending order.
* @param a the array
* @return a permutation {@code p[]} such that {@code a[p[0]]}, {@code a[p[1]]},
* ..., {@code a[p[N-1]]} are in ascending order
*/
public static int[] indexSort(Comparable[] a) {
int n = a.length;
int[] index = new int[n];
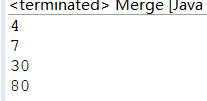
for (int i = 0; i 运行结果
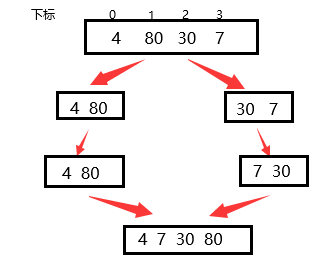
过程树状图
动态演示图