Netty TCP 粘包和拆包 及解决方案
2021-03-12 23:31
标签:连接 netty final cal imp opened return hand bec 1 TCP 粘包和拆包基本介绍 对图的说明: 假设客户端分别发送了两个数据包 D1 和 D2 给服务端, 由于服务端一次读取到字节数是不确定的, 故可能存在以 4) 服务端分两次读取到了数据包, 第一次读取到了 D1 包的部分内容 D1_1, 第二次读取到了 D1 包的剩余部 分内容 D1_2 和完整的 D2 包。 2 TCP 粘包和拆包现象实例 (现象) 在编写 Netty 程序时, 如果没有做处理, 就会发生粘包和拆包的问题 3 TCP 粘包和拆包解决方案 1) 使用自定义协议 + 编解码器 来解决 1) 要求客户端发送 5 个 Message 对象, 客户端每次发送一个 Message 对象 MessageProtocol //协议包 MyClientHandler Netty TCP 粘包和拆包 及解决方案 标签:连接 netty final cal imp opened return hand bec 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cb1186512739/p/12774583.html
1) TCP 是面向连接的, 面向流的, 提供高可靠性服务。 收发两端(客户端和服务器端) 都要有一一成对的 socket,因此, 发送端为了将多个发给接收端的包, 更有效的发给对方, 使用了优化方法(Nagle 算法) , 将多次间隔较小且数据量小的数据, 合并成一个大的数据块, 然后进行封包。 这样做虽然提高了效率, 但是接收端就难于分辨出完整的数据包了, 因为面向流的通信是无消息保护边界的。
2) 由于 TCP 无消息保护边界, 需要在接收端处理消息边界问题, 也就是我们所说的粘包、 拆包问题, 看一张图
3) 示意图 TCP 粘包、 拆包图解
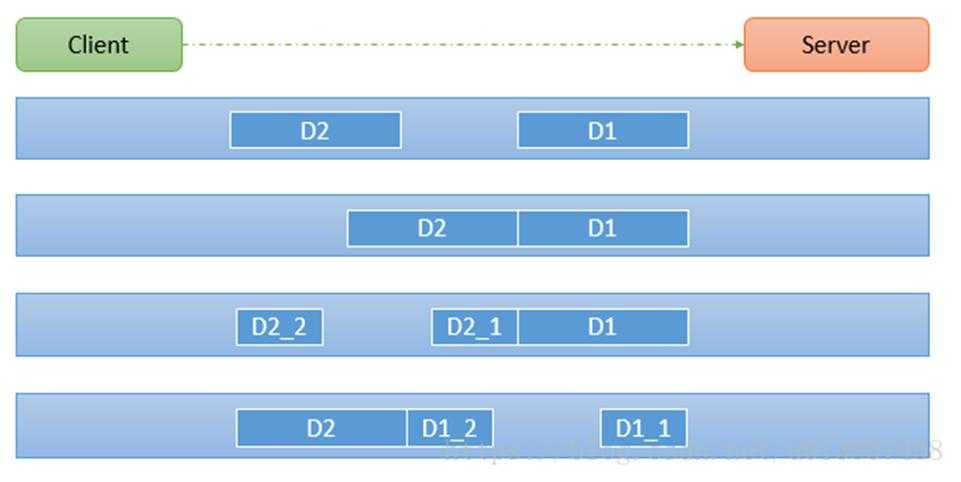
下四种情况:
1) 服务端分两次读取到了两个独立的数据包, 分别是 D1 和 D2, 没有粘包和拆包
2) 服务端一次接受到了两个数据包, D1 和 D2 粘合在一起, 称之为 TCP 粘包
3) 服务端分两次读取到了数据包, 第一次读取到了完整的 D1 包和 D2 包的部分内容, 第二次读取到了 D2 包 的剩余内容, 这称之为 TCP 拆包
看一个具体的实例:
MyClientHandler

import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
MyServerHandler


import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.UUID;
public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
2) 关键就是要解决 服务器端每次读取数据长度的问题, 这个问题解决, 就不会出现服务器多读或少读数据的问题, 从而避免的 TCP 粘包、 拆包 。
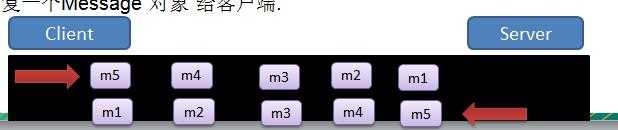
实列:
2) 服务器端每次接收一个 Message, 分 5 次进行解码, 每读取到 一个 Message , 会回复一个 Message 对象 给客
户端.


public class MessageProtocol {
private int len; //关键
private byte[] content;
public int getLen() {
return len;
}
public void setLen(int len) {
this.len = len;
} p
ublic byte[] getContent() {
return content;
} p
ublic void setContent(byte[] content) {
this.content = content;
}
}


import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
MyClient


import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new MyClientInitializer()); //自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MyClientInitializer


import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
public class MyClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer
MyServer


import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer()); //自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9994).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MyServerInitializer


import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
public class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer
MyServerHandler


import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.UUID;
//处理业务的handler
public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
MyMessageDecoder


import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ReplayingDecoder;
import java.util.List;
public class MyMessageDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder
MyMessageEncoder


import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
public class MyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder
文章标题:Netty TCP 粘包和拆包 及解决方案
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/63880.html