Java 多线程
2021-03-14 13:40
标签:image 提交 lang str mic down 线程状态 check inter Thread类使用静态代理实现,Thread构造函数接收一个实现Runnable接口的类作为代理类 Callable是线程池的方式创建线程,可以获取到执行函数的返回值,还可以在执行时抛出异常 线程的六种状态 ... 等待唤醒机制: wait()和sleep() 多个线程操作同一个数据,解决:添加锁 Arraylist线程安全 Juc的线程安全集合 Java 多线程 标签:image 提交 lang str mic down 线程状态 check inter 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiongyungang/p/12495740.html创建线程
方式一:继承Thread
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i 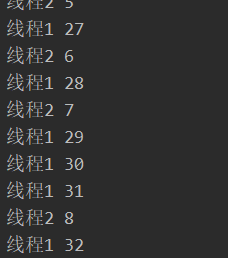
方式二: 实现Runnable接口。
Thread类本身继承自Runnable接口
public class DeamonDemo implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0;i方式三:实现Callable接口
public class TestCallable守护线程
DeamonDemo d = new DeamonDemo();
Thread d1 = new Thread(d);
Thread d2 = new Thread(d);
d1.setDaemon(true); // 设置守护线程
d2.setDaemon(true);
d1.start();
d2.start();
for(int i = 0;i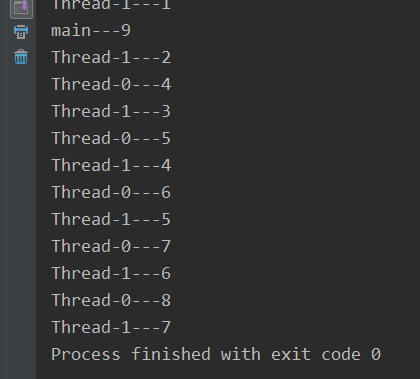
设置线程优先级
PriorityDemo p = new PriorityDemo();
Thread tp1 = new Thread(p);
Thread tp2 = new Thread(p);
Thread tp3 = new Thread(p);
tp1.setName("xyg");
tp2.setName("wdf");
tp3.setName("OoO");
tp1.setPriority(10); // 最高优先级
tp2.setPriority(1);
tp3.setPriority(1);
tp1.start();
tp2.start();
tp3.start();

线程状态
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i
thread = TIMED_WAITING
thread = TIMED_WAITING
thread = RUNNABLE
thread = RUNNABLE
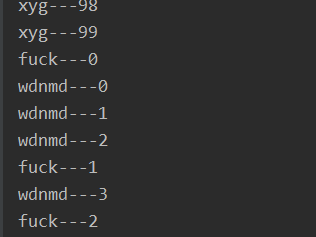
thread = TERMINATED线程加入 join
JoinDemo p = new JoinDemo();
Thread tp1 = new Thread(p);
Thread tp2 = new Thread(p);
Thread tp3 = new Thread(p);
tp1.setName("xyg");
tp2.setName("fuck");
tp3.setName("wdnmd");
tp1.setPriority(10);
tp2.setPriority(1);
tp3.setPriority(1);
tp1.start();
try {
tp1.join(); // 其他线程等待该线程终止
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
tp2.start();
tp3.start();
线程等待和唤醒
public synchronized void set(String name, int age) {
//如果有数据则等待
if (flag) {
try {
wait(); // 线程等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//设置值
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
// 修改标记
flag = true;
notify();// 线程唤醒
}
...
public synchronized void get(){
//如果没有数据就等待
if(!flag){
try {
wait(); // 线程等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(name+" "+age);
//修改标记
flag=false;
notify(); // 线程唤醒
}
线程暂停
public void run() {
for(int i = 0;i线程安全
同步代码块
...
public void run() {
if (x%2==0) {
//同步代码块
synchronized (this) {// 多个线程使用同一个锁对象
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + (ticket--) + "张票。");
}
}
}
方法锁
public void run() {
check();
}
...
//同步方法
//同步方法的锁对象是this对象
//静态同步方法的锁对象是 类名.class Class类型对象
private synchronized void check() {
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + (ticket--) + "张票。");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayListpublic class JucList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList重用锁 ReentrantLock