Spring 循环依赖
2021-03-19 18:24
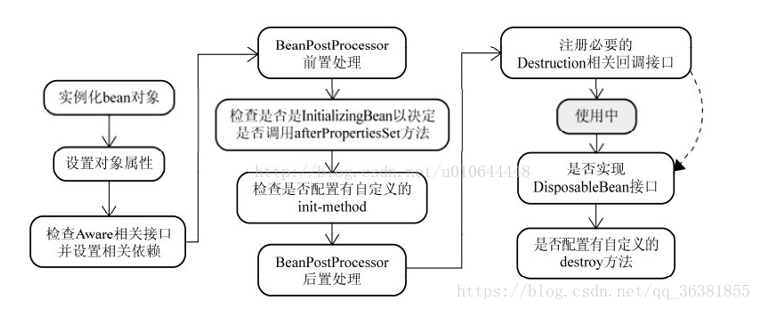
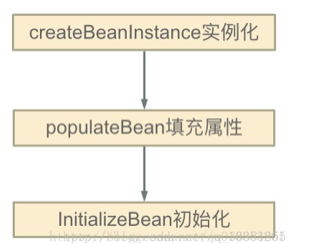
标签:create let 引用 init detail 属性 ebean details string 1. 如果是在构造方式中循环依赖,则直接报错 2. Setter 方式不会报错,因为Spring分两步,先调用无参构造方法实例化Bean对象,将实例化结束的对象放到一个Map中,然后才会设置对象属性,结合我们的实例来看,,当Spring实例化了Class A、Class B,紧接着会去设置对象的属性,此时Class A依赖Class B,就会去Map中取出存在里面的单例B对象,以此类推,不会出来循环的问题。 3. Spring的循环依赖的理论依据其实是基于Java的引用传递,当我们获取到对象的引用时,对象的field或属性是可以延后设置的(但是构造器必须是在获取引用之前)。 Spring的单例对象的初始化主要分为三步: ①:createBeanInstance:实例化,其实也就是 调用对象的构造方法实例化对象 ②:populateBean:填充属性,这一步主要是多bean的依赖属性进行填充 ③:initializeBean:调用spring xml中的init() 方法。 从上面讲述的单例bean初始化步骤我们可以知道,循环依赖主要发生在第一、第二步。也就是构造器循环依赖和field循环依赖。 那么我们要解决循环引用也应该从初始化过程着手,对于单例来说,在Spring容器整个生命周期内,有且只有一个对象,所以很容易想到这个对象应该存在Cache中,Spring为了解决单例的循环依赖问题,使用了三级缓存。三级缓存源码主要指: 三级缓存怎么使用参照: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35165000/article/details/108185093 Spring 循环依赖 标签:create let 引用 init detail 属性 ebean details string 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Ivyduan/p/13940636.html@Component
public class A {
public A(B b) {
}
}
@Component
public class B {
public B(A a) {
}
}
Description:
The dependencies of some of the beans in the application context form a cycle:
┌─────┐
| a defined in file [C:\A-project\customer\configuration\A.class]
↑ ↓
| b defined in file [C:\A-project\customer\configuration\B.class]
└─────┘
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
private final Map