02-Introduction to Kubernetes.md
2021-03-22 20:25
标签:mat cluster 组件 ranch local nes 节点 ret ack Introduction to Kubernetes Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Kubernetes由google创建,后捐给CNCF,功能包含: The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) is one of the projects hosted by the Linux Foundation. CNCF aims to accelerate the adoption of containers, microservices, and cloud-native applications. ReplicationControllers已经不推荐使用, ReplicaSets support both equality- and set-based selectors, whereas ReplicationControllers only support equality-based Selectors. Currently, this is the only difference. ReplicaSets 可以用于控制pod,但是功能有限,推荐使用Deployments,它自动创建 ReplicaSet,用于控制pod。 DeploymentController是master node的组件之一,用来确定现状和需求是否一致,并且提供滚动更新和回滚的功能。在滚动更新时,DeploymentController会创建一个新的ReplicaSet B。 可以给不同的团队建立不同的Namespaces来控制资源。 k8s集群建立以后,默认有4个ns: 可以给ns分配Resource Quotas k8s包含2种用户:Normal Users(集群外管理,User/Client Certificates等)和Service Accounts(集群中管理),当然,也支持匿名访问和模拟用户访问 https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/authentication/#authentication-strategies Service在逻辑上对Pod进行了分组并定义了访问Pod的策略,避免直接访问pod带来的一系列问题。 Services can expose single Pods, ReplicaSets, Deployments, DaemonSets, and StatefulSets. service会根据满足条件的pod自动创建和管理 endpoint(eg. 10.0.1.3:5000) 所有工作节点都运行一个名为kube-proxy的守护进程,该守护进程监视主节点上的API server以了解服务和端点的添加和删除。 两种: 提供 CNAME 功能,可以像这样访问服务:my-database.example.com,当在同一个ns下时,也可以通过 my-database 访问 可以通过如下3种方式定义: csi 创建ConfigMap的两种方式: 使用 envFrom 来加载所有的配置到环境变量,或者使用 env 来加载特定 key 到环境变量,或者使用 configMap 挂载到 volume 使用 使用Secrets,避免将密码等机密信息放到yaml文件中。但是请注意,Secrets是以明文的形式存储在etcd中,所以需要限制user对etcd的访问权限。 创建Secrets: 通过 data 或 stringData 创建: An Ingress is a collection of rules that allow inbound connections to reach the cluster Services. Ingress configures a Layer 7 HTTP/HTTPS load balancer for Services and provides the following: An Ingress Controller is an application watching the Master Node‘s API server for changes in the Ingress resources and updates the Layer 7 Load Balancer accordingly Unlike Labels, annotations are not used to identify and select objects. Annotations can be used to: We can set the following types of quotas per Namespace: a specific type of Pod running on all nodes at all times. 新功能也支持用nodeSelectors and node affinity rules在指定的node上跑pod. 另外 DaemonSets 也支持 rolling updates and rollbacks. statefulset 02-Introduction to Kubernetes.md 标签:mat cluster 组件 ranch local nes 节点 ret ack 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/windchen/p/12697076.htmlWelcome
Chapter 1. From Monolith to Microservices
Chapter 2. Container Orchestration
Chapter 3. Kubernetes
Chapter 4. Kubernetes Architecture
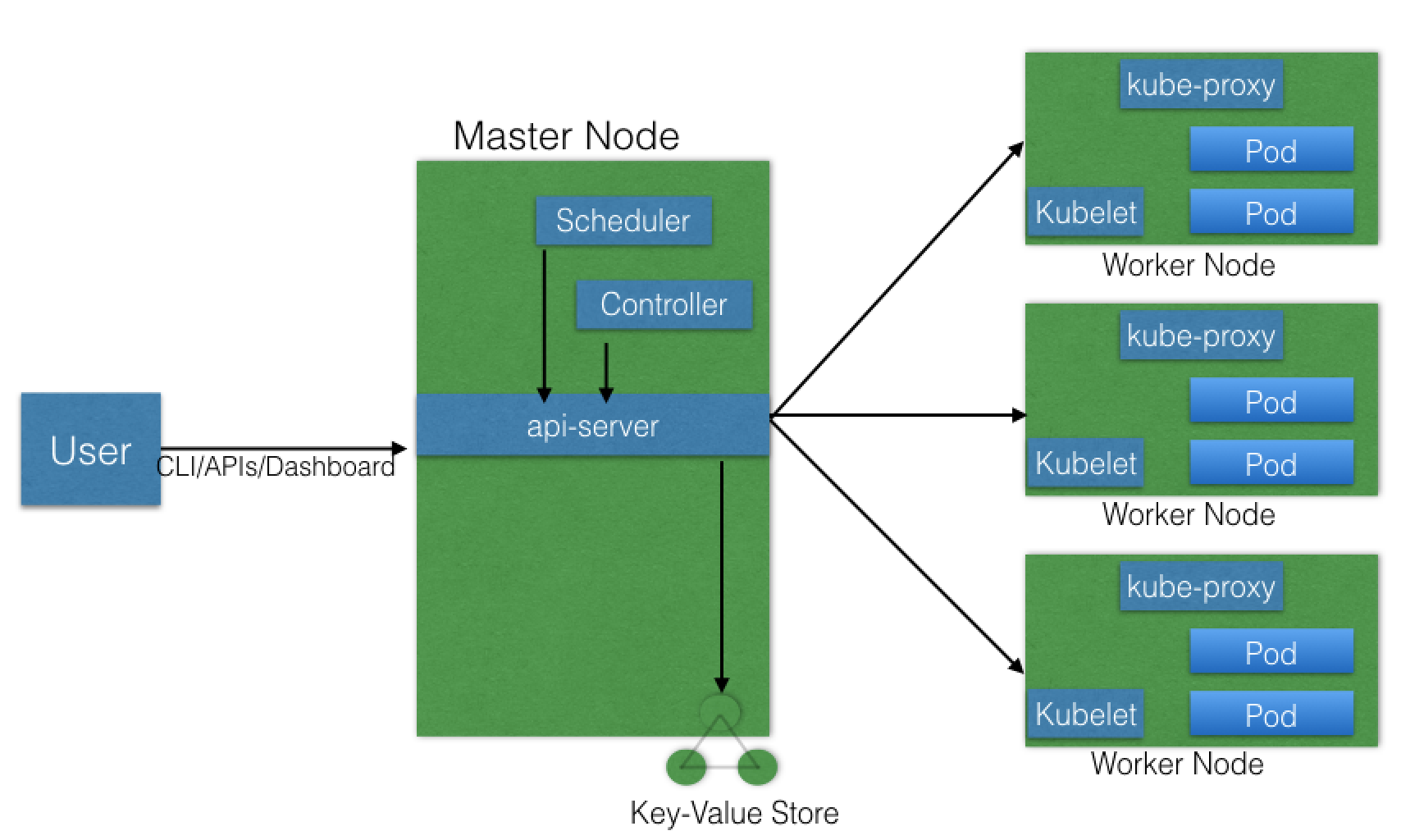
Networking Challenges
Chapter 4. Kubernetes Architecture
Chapter 5. Installing Kubernetes
Chapter 6. Minikube - A Local Single-Node Kubernetes Cluster
Chapter 7. Accessing Minikube
Chapter 8. Kubernetes Building Blocks
Label Selectors
ReplicationControllers vs ReplicaSets
Deployments
Namespaces
Chapter 9. Authentication, Authorization, Admission Control
Authentication
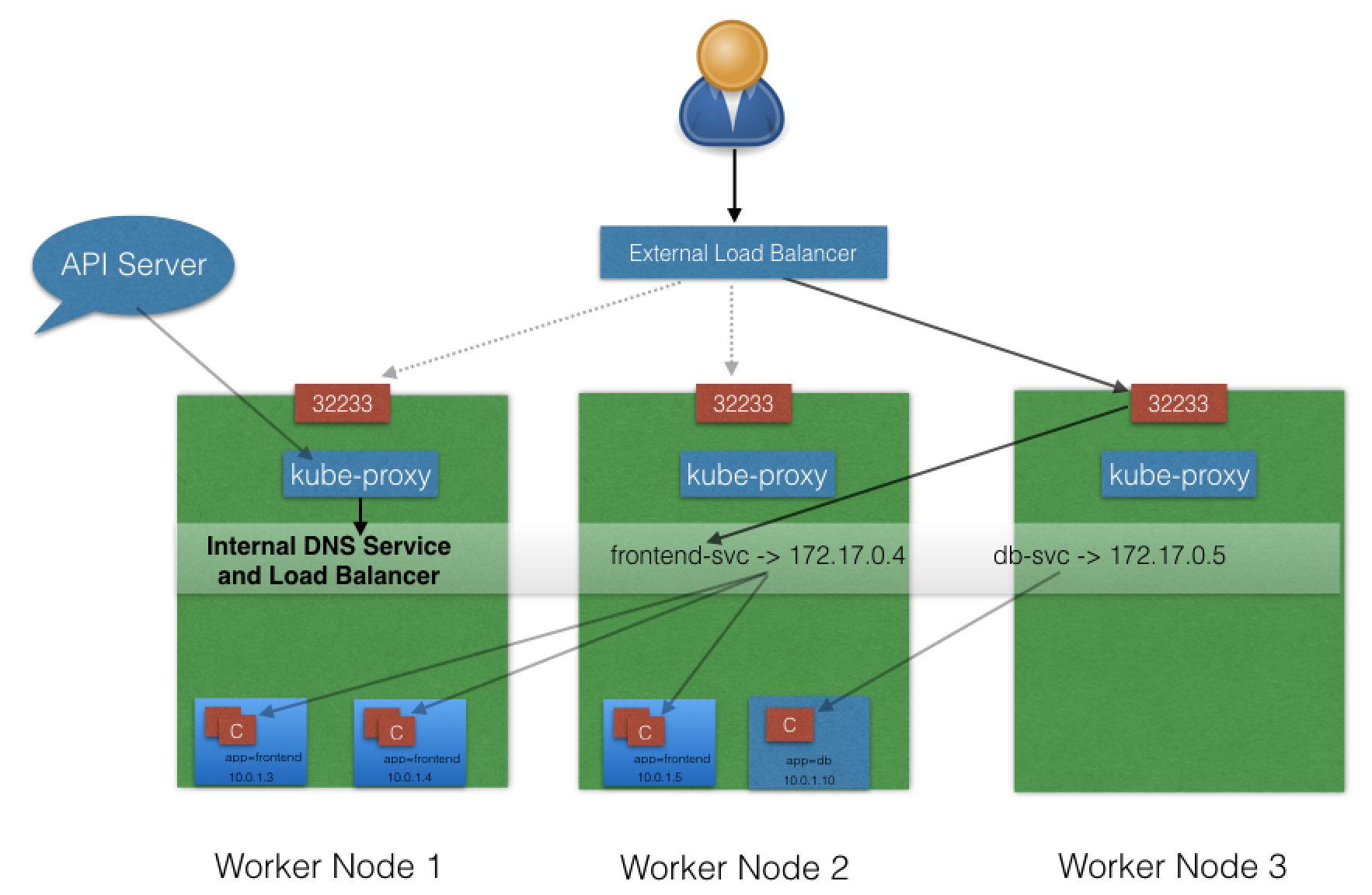
Chapter 10. Services
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: frontend-svc
spec:
selector:
app: frontend
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 5000 # 如果没有指定,则默认同 port
kube-proxy
Service Discovery
ServiceType: ClusterIP and NodePort
ServiceType: LoadBalancer
ServiceType: ExternalIP
ServiceType: ExternalName
Chapter 11. Deploying a Stand-Alone Application
Liveness and Readiness Probes
Chapter 12. Kubernetes Volume Management
PersistentVolume (PV) && PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC)
Container Storage Interface (CSI)
Chapter 13. ConfigMaps and Secrets
ConfigMaps
configmap/my-config createdapiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: customer1
data:
key1: value1
key2: value2
Use ConfigMaps Inside Pods
...
containers:
- name: myapp-full-container
image: myapp
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: full-config-map
...
...
containers:
- name: myapp-specific-container
image: myapp
env:
- name: SPECIFIC_ENV_VAR1
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: config-map-1
key: SPECIFIC_DATA
- name: SPECIFIC_ENV_VAR2
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: config-map-2
key: SPECIFIC_INFO
...
...
containers:
- name: myapp-vol-container
image: myapp
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: vol-config-map
...
Secrets
$ echo mysqlpassword | base64
bXlzcWxwYXNzd29yZAo=
$ echo -n ‘bXlzcWxwYXNzd29yZAo=‘ > password.txt
# Now we can create the Secret from the password.txt file:
$ kubectl create secret generic my-file-password --from-file=password.txt
secret/my-file-password created
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-password
type: Opaque
data:
password: bXlzcWxwYXNzd29yZAo=
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-password
type: Opaque
stringData:
password: mysqlpassword
Use Secrets Inside Pods
# Using Secrets as Environment Variables
....
spec:
containers:
- image: wordpress:4.7.3-apache
name: wordpress
env:
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: my-password
key: password
....
# Using Secrets as Files from a Pod
....
spec:
containers:
- image: wordpress:4.7.3-apache
name: wordpress
volumeMounts:
- name: secret-volume
mountPath: "/etc/secret-data"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: secret-volume
secret:
secretName: my-password
....
Chapter 14. Ingress
Ingress Controller
Chapter 15. Advanced Topics
Annotations
Jobs and CronJobs
Quota Management
Autoscaling
DaemonSets
StatefulSets
Network Policies
Monitoring and Logging
Chapter 16. Kubernetes Community
Final Exam
文章标题:02-Introduction to Kubernetes.md
文章链接:http://soscw.com/index.php/essay/67660.html