Java String
2021-04-08 16:26
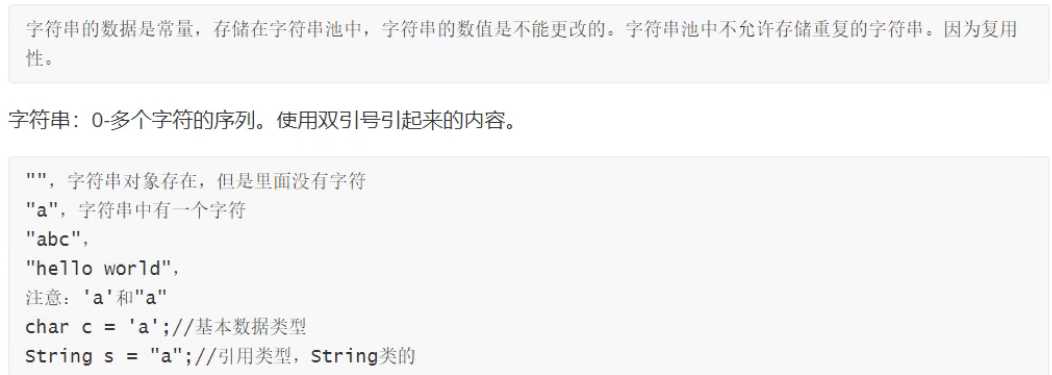
标签:als 判断字符串 内容 区分 的区别 相同 contains 根据 package Java String 标签:als 判断字符串 内容 区分 的区别 相同 contains 根据 package 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yzg-14/p/13377824.html1. 字符串常量
package com.qf.demo01string;
public class Test1String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.字符串常量:双引号引起来的字符串的内容
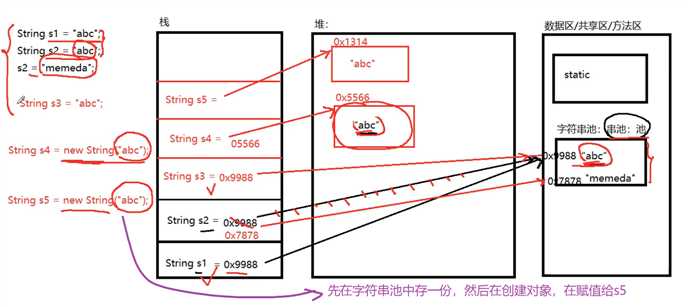
//2.直接声明一个字符串:字符串池中。相同内容的字符串,就一份。共享。
String s1 = "abc";//池中
System.out.println(s1);
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s1 == s2); //true
s2 = "memeda";
String s3 = "abc";//池中
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//2.通过new关键字,创建String对象。
String s4 = new String("abc");//因为有new,在堆中创建一个对象,保存在堆中
String s5 = new String("abc");//因为有new,重新创建对象,保存在堆中
String s6 = new String("haha");//因为有new,重新创建对象,
//地址的比较:==
System.out.println(s1 == s3);//true
System.out.println(s4 == s5);//false
System.out.println(s1 == s4);//false
//比较内容:equals,String类重写了equals,专门比较内容
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//true
System.out.println(s4.equals(s5));//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s4));//true
}
}
2. 字符串的创建
package com.qf.demo01string;
public class Test2CreateString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.null和""的区别:
String s1 = new String();//字符串对象存在,只是存储的字符没有,内容是空的。
System.out.println(s1);
String s3 = "";//""
System.out.println(s3);//""
String s2 = null;//字符串对象不存在,直接访问属性或方法,会空指针异常。
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s1.length());//该字符串的长度
// System.out.println(s2.length());//java.lang.NullPointerException
//2.使用字节数组构建一个字符串,IO流
/*
* String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的字节子阵列来构造新的 String
第一个参数:byte[] bytes,数据源
第二个参数:int offset,偏移量,从哪个下标开始的数据,构建字符串
第三个参数:int length,长度,获取的个数。
*/
byte[] b1 = {65,66,67,68,69};//ABCDE
String s4 = new String(b1);//使用b1这个数组中的数据,构建一个字符串
System.out.println(s4);
String s5 = new String(b1, 2, 3);
System.out.println(s5);
//3.通过字符数组,构建一个字符串
char[] c1 = {‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘,‘f‘};
String s6 = new String(c1);
System.out.println(s6);
String s7 = new String(c1, 1, 3);
System.out.println(s7);
}
}
3. String常用方法
package com.qf.demo01string;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test3StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "helloWorld";//10个字符
/*
* charAt(index)-->char,根据指定的下标获取对应的字符。要注意越界问题。StringIndexOutOfBoundsException。
* index的取值:从0开始,到长度减1。
*/
char c = s1.charAt(0);
System.out.println(c);
/*
* concat(String)-->String,字符串的拼接。效果同+起连接符作用一样的。
返回一个拼接之后的新的字符串
*/
String s2 = s1.concat("***");
System.out.println(s2);
/*
* contains()-->boolean判断字符串中,是否包含了指定的内容。
返回值是boolean,true,false。
*/
boolean b1 = s2.contains("***");
System.out.println(b1);
/*
* endsWith(String)--->boolean,判断指定的字符串,是否以某个后缀结尾。。
* startsWith(String)--->boolean,判断是否以指定的内容开头。
*/
String s3 = "aa.jpeg";
if(s3.endsWith(".jpeg")){
System.out.println(s3+",是一张图片。。");
}
String s4 = "20200120记录.txt";
if(s4.startsWith("202001")){
System.out.println("是今年1月份的记录文件。。");
}
/*
* equals(Object obj)-->boolean,比较两个字符串的内容是否相等。""引起来的内容是否一致
* equalsIgnoreCase()-->boolean,比较两个字符串的内容, 忽略大小写。
*/
String s5 = "hello";
String s6 = "HeLLo";
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));//Object类,此处是重写:比较内容
System.out.println(s5.equalsIgnoreCase(s6));
/*
* getBytes()-->byte[]根据字符串,获取对应的字节数组。
* toCharArray()-->char[]
*/
//s1 = "helloWorld";//10个字符
byte[] bytes = s1.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
char[] array = s1.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
/*
* indexOf(int 字符)-->index,在字符串中,查找指定的参数的字符,
返回值是该字符在字符串中第一次出现的下标。如果没有该字符,返回-1。
*
* indexOf(String 子串)-->index,同上
*
* indexOf(int 字符,int fromIndex)-->index,表示在字符串中,
从fromIndex下标开始向后找指定的字符,如果有就返回下标,如果没有就-1。
*
* indexOf(String 子串,int fromIndex)-->同上
*
* lastIndexOf(int 字符)-->index,在指定的字符串中,搜索该字符,
最后一次出现的位置。理解为倒着搜。
*
* lastIndexOf(String 子串),同上
*
* lastIndexOf(int 字符,int fromIndex)-->index,在字符串中查找指定的内容,
从fromIndex,从后往前,倒着搜,第一次出现的位置。
*
* lastIndexOf(String ,int fromIndex)
*/
//s1 = "helloWorld";//10个字符
int i1 = s1.indexOf(‘x‘);//
System.out.println(i1);
int i2 = s1.indexOf("llo");
System.out.println(i2);
int i3 = s1.indexOf(‘W‘,5);
System.out.println(i3);
int i4 = s1.lastIndexOf(‘l‘);
System.out.println(i4);//8
int i5 = s1.lastIndexOf(‘l‘, 0);
System.out.println(i5);//3
/*
* length()-->int,字符串的长度,字符串中字符的个数。
* 同数组区分:
* length:属性
*
*/
System.out.println(s1.length());//10
System.out.println("abc".length());//3
/*
* replace(oldchar , newchar)-->String,替换指定的字符,获取新串
* replace(CharSequence,CharSequence)-->
*/
//s1 = "helloWorld";//10个字符
String s7 = s1.replace(‘l‘, ‘*‘);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s7);
String s8 = s1.replace("llo", "X");
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s8);
/*
* split(分隔符)-->String[] ,按照指定的内容,
将字符串进行分离(切割),得到一个数组。
*
* 注意点:分隔符,在开头,在中间,都起作用的。在末尾不起作用。
*/
String s9 = "鹅鹅a鹅,曲项,,向a天歌,拔毛加漂水,点火盖上锅,,,,,,,,,,";//""
System.out.println(s9);
String[] arr = s9.split(",");
System.out.println("--->"+arr.length);
for(int i =0;iString,从参数表示的下标开始,截取到末尾,
* substring(beginIndex,endIndex)-->String,
* [begin,end)
*/
//s1 = "helloWorld";//10个字符
String s10 = s1.substring(5); ///World
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s10);
String s11 = s1.substring(2, 6);//lloW,包含下标2,不包含6之间的字符
System.out.println(s11);
/*
* 转换大小写
* toLowerCase(),
* toUpperCase(),
*
*/
String s12 ="aBcD123**";
System.out.println(s12.toLowerCase());//abcd123**
System.out.println(s12.toUpperCase());//ABCD123**
/*
* trim()--》String,去除首尾的空格
*/
String s13 = " hello world ";//前2个空格,中间1个,末尾1个
System.out.println(s13.length());
String s14 = s13.trim();
System.out.println(s14.length());
}
}