Spring 常用注解
2021-04-09 13:26
标签:set 两种 参考 结束 支持 base bean sharp target 1.组件注解 下面我们一个一个的详细说说以上注解怎么使用(请仔细阅读以下通俗语言归纳,句句“诛心”): 组件注解 : @Component(“xxx”) 用于标注类为spring容器bean的注解有四个,主要用于区别不同的组件类,提高代码的可读性。 对于上面四种注解的解析可能是相同的,尽量使用不同的注解提高代码可读性。 注解用于修饰类,当不写value属性值时,默认值为类名首字母小写。 @Scope(“prototype”) 该注解和 @Lazy(true) 指定bean是否延时初始化,相当于 注:此处初始化不是指不执行init-method,而是不创建bean实例和依赖注入。只有当该bean(被@Lazy修饰的类或方法)被其他bean引用(可以是自动注入的方式)或者执行getBean方法获取,才会真正的创建该bean实例,其实这也是BeanFactory的执行方式。 @DepondsOn({“aa”,“bb”}) 该注解也是配合 上面的代码指定,初始化bean “userAction"之前需要先初始化“aa”和“bb”两个bean,但是使用了@Lazy(true)所以spring容器初始化时不会初始化"userAction” bean。 @PostConstructor和@PreDestroy @PostConstructor和@PreDestroy这两个注解是jee规范下的注解。这两个注解用于修饰方法,spring用这两个注解管理容器中spring生命周期行为。 @Resource(name=“xx”)注意这个注解要导入相关jar,请自行百度 @Resource 可以修饰成员变量也可以修饰set方法。当修饰成员变量时可以不写set方法,此时spring会直接使用jee规范的Field注入。 如果没有写name属性值时 @Autowired(required=false) @Autowired可以修饰构造器,成员变量,set方法,普通方法。@Autowired默认使用byType方式自动装配。required标记该类型的bean是否时必须的,默认为必须存在(true)。 @Autowired会根据修饰的成员选取不同的类型 以下是个小DEMO 业务逻辑层 数据访问层 测试类 输出结果 可以看到虽然UserDao 使用@Lazy,但是还是在spring容器初始化的时候还是创建了UserDao实例。原因很简单,因为在UserService中需要注入UserDao,所以在此时创建的UserDao实例也属于延时初始化。 在上面我们还使用了两个接口InitializingBean 和DisposableBean,这两个接口用于管理singleton作用域的bean的生命周期,类似init-method和destroy-method。不同之处就是调用的循序不一致。 初始化调用顺序 @PostConstructor > InitializingBean > init-method 用于指定bean依赖注入后的行为, 该注解是AspectJ中的注解,并不是spring提供的,所以还需要导入aspectjweaver.jar,aspectjrt.jar,除此之外还需要依赖aopalliance.jar。 UserDao.java 配置文件 applicationContext.xml 测试类 @Aspect 修饰Java类,指定该类为切面类。当spring容器检测到某个bean被@Aspect修饰时,spring容器不会对该bean做增强处理(bean后处理器增强,代理增强) @Before 修饰方法,before增强处理。。用于对目标方法(切入点表达式表示方法)执行前做增强处理。可以用于权限检查,登陆检查 对com.example.aop 包下所有的类的所有方法做 before增强处理 结果: 如果同一条切入点表达式被使用多次,可以使用更友好的方式。定义一个切入点 增强方法可以接受一个JoinPoint 类型的参数,用于获取被执行目标方法的一下属性。 结果: @AfterReturning 常用属性 pointcut/value:指定切入点表达式 注意: 以上面的例子来说,目标方法返回结果类型应该满足下面的条件 修改返回值 可以看到 AfterReturning 修改了返回结果。 @AfterThrowing 常用属性 pointcut/value :指定切入点表达式 参数类型必须是 Throwable 的子类,同样也会有上面@AfterReturning 参数类型匹配的问题。 @After 修饰方法 ,after增强处理。无论方法是否正常结束,都会调用该增强处理(@After= @AfterReturning+@AfterThrowing)。 但是该增强方式无法获取目标方法的返回结果,也获取目标方法抛出的异常。所以一般用于进行释放资源,功能类似于 finally 常用属性 value :指定切入点表达式 结果: 从上面的结果来看 After 增加处理 ,因为不能接受返回结果作为参数,所以不能修改返回结果。 @Around 修饰方法, around增强处理。该处理可以目标方法执行之前和执行之后织入增强处理(@Before+@AfterReturning)。 常用属性 value :指定切入点表达式 小结: 使用Around 修改返回结果: 结果: 可以看到 around 和 afterReturning 都可以修改返回结果。不过两者的原理不同。 从此之外从输出结果来看,增强处理是有序的 小结: 只有 around 和 afterReturning 可以获取并修改返回结果。需要注意两种方式修改的区别。 around 需要线程安全 虽然增强处理都需要 切入点表达式,并不是都支持 pointcut 属性,所以最好都是用value 属性指定。当注解只需要value属性时,value可以省略 @Pointcut 修饰方法,定义一个切入点表达式用于被其他增强调用。使用该方式定义切入点方便管理,易复用。 切入点方法定义和测试方法定义类似,具有以下特点: 切入点表达式 切入点表达式可以通过 &&、 ||、 ! 连接 execution 表达式格式: 注:?表示出现一次或零次 使用通配符* ,表示任意一个参数类型。 2.within: 所以within可以看做execution的简写,不需要指定返回类型、方法名、参数 3. @annotation:匹配使用指定注解修饰的目标方法; 匹配使用@CustomAnnotation注解的目标方法。 4. @within: 用于匹配使用指定注解修饰的类下的所有方法 匹配使用@ResponseBody 注解的类 下的所有方法。 新增AOP 测试类: 自定义注解:方法注解 修改类UserDao 对listUsers 增加自定义方法注解。 输出结果: 可以看到不同的声明方式 顺序也是不同的。 AOP 小结: 增强方式的顺序: 切入点表达式不同声明方式的顺序: @Bean(name=“xxx”) 修饰方法,该方法的返回值为spring容器中管理的bean。当然该注解和上面的@Component效果一样,主要用于做区分 @Bean 通常使用在 @Configuration 修饰的配置类中,该注解功能相当于 常用的属性 @ConfigurationProperties 用于从属性文件中获取值 包含的属性: Mybatis属性配置 application.properties ConfigurationProperties 可以配置前缀,然后会根据实体的变量名拼接前缀,去配置文件中查询配置。 @Configuration 修饰一个Java类,被修饰的类相当于一个xml配置文件。功能类似于 可以发现 @Configuration使用了@Component 注解修饰。 配置 Mybatis 会话工厂 @Import 功能和 通常用于导入不在包扫描范围内的配置文件。可以被扫描的配置类可以直接访问,没有必要使用@Import 导入 比如 SpringBoot的启动类指定的包扫描路径为 com.example 数据库的配置文件在 com包下。 在MyBatisConfig 中引入 DataSourceConfig, 就会解析DataSourceConfig。将解析出的Bean交给容器管理 @ImportResource 修饰Java类,用于向类引入xml配置文件。 用于导入包含bean定义的配置文件,功能和 @Value("${expression}") 修饰成员变量或者 方法、构造器的参数,用于属性值注入(在配置文件中配置的值)。 注意: @PropertySource(value=“classpath:jdbc.properties”) 常用属性: 在 PropertySource 中可以指定多个路径,并且会将属性文件中的值加载到 Environment 中。 上面介绍一个加载配置文件的注解 在以往的开发中通常会将数据库连接信息存放在单独的属性文件中(jdbc.properties)。而在spring boot 中我们会将数据库的信息存放在配置文件中,这会极大便利开发工作。 jdbc.properties 可以通过 @Value 注解将配置文件的值注入到实体类中 也可以注入Environment ,通过Environment 获取值 @Value还能注入很多类型,字符串、系统变量等等,参考《JAVAee的颠覆者》 @ResponseBody 控制器方法返回值会使用 同样的 ResponseBodyAdvice: 针对所有以@ResponseBody的参数做处理。 @RestController @RequestBody 从Reuqest请求体中获取内容,绑定到方法的指定参数上。 SpringMVC 使用HttpMessageConverter 接口将请求体中的数据转化为方法参数类型。 SpringMVC 给用户对参数的处理提供了很大支配权。 我们可以使用 接口RequestBodyAdvice 来实现对参数进行拦截处理。 利用此功能我们可以做以下处理工作。 参数解密功能 IOUtils 依赖包: 定义一个注解。用来控制参数是否加密 @RequestBody 修饰参数的处理类 自定义 内容处理类 调用接口时对参数进行约定方式的加密处理。使用 application/json 等文本请求。 修改方法入参 很多操作可能需要记录,修改人、更新人。这样会导致重复代码比较多,那么我们可以在此处做增强处理。 当然我们也可以通过AOP 实现 @RequestParam 从Request请求中获取指定的参数 required : 默认为itrue 参数必须存在。参数不存在时抛出异常 有点乱~大家将就着看吧~嘿嘿 Spring 常用注解 标签:set 两种 参考 结束 支持 base bean sharp target 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/47Gamer/p/13355956.html
@Component("xxx")
@Scope("prototype")
@Lazy(true)
@DepondsOn({"aa","bb"})
@PostConstructor和@PreDestroy
@Resource(name="xx")
@Autowired(required=false)
2.Aop相关注解
@Aspect
@Before
@AfterReturning
@AfterThrowing
@After
@Around
@Pointcut
3.Java配置类相关注解
@Bean(name="xxx")
@ConfigurationProperties
@Configuration
@Import
@ImportResource
@Value("${expression}")
@PropertySource(value="classpath:jdbc.properties")
4.SpringMVC 相关注解
@ResponseBody
@RestController
@RequestBody
@RequestParam
指定某个类是容器的bean,@Component(value="xx")相当于
@Component这一类注解联合使用,用于标记该类的作用域,默认singleton。
也可以和@Bean一起使用,此时@Scope修饰一个方法。关于@Bean稍后有说明@Component这类注解使用,用于强制初始化其他bean@DepondsOn("other")
@Lazy(true)
@Controller
@Scope("prototype")
public class UserAction{
String wdnmd = "我带你们打";
}
@Resource有两个比较重要的属性,name和type
可以配合@Qualifier(value="xx"),实现按beanName注入。
//service层,业务逻辑
@Service
public class UserService{
@Resource(name="userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
//@Autowired
//@Qualifier("userDao")
//private IUserDao userDao;
//相对来说使用`@Resource`更简单一些
.......实际业务.............
}
//dao层,持久化
@Repository
@Lazy(true)
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserDao implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean{
public UserDao() {
System.out.println("constructor...................");
}
public List
//测试类
public class TestAnnotation{
@Test
public void test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext application=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//配置文件里只有一行就是开启自动扫描”
constructor...................
post_constructor.................
after_properties_set..............
--------获取bean-----------
com.dao.PersonManager@4872669f
pre_destroty.................
destry.............
pre_destroty.................
destry.............
销毁调用顺序 @PreDestroy > DisposableBean > destroy-method 用于定制bean销毁之前的行为。Aop相关注解:
package com.example.aop;
import com.example.domain.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public class UserDao {
public UserDao() {
System.out.println("constructor...................");
}
public List
public class TestAnnotation{
@Test
public void test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext application=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//配置文件里只有一行就是开启自动扫描”
package com.example.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class UserAdvice{
}
常用属性
@Before(value = "execution(* com.example.aop.*(..)))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("before 增强处理。。。。。。。。。。。。");
}
constructor…
before 增强处理。。。。。。。。。。。。
查询所有用户
返回结果: []
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.*(..)))")
public void addLog(){}
@Before(value = "addLog()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("before 增强处理。。。。。。。。。。。。");
}
@Before(value = "addLog()")
public void execute(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("before 增强处理。。。。。。。。。。。。");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
System.out.println(joinPoint.getKind());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getModifiers());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSourceLocation());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getTarget());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getThis());
}
constructor…
before 增强处理。。。。。。。。。。。。
[]
method-execution
listUsers
com.example.aop.UserDao
class com.example.aop.UserDao
1
org.springframework.aop.aspectj.MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint$SourceLocationImpl@15d49048
com.example.aop.UserDao@7098b907
com.example.aop.UserDao@7098b907
查询所有用户
修饰方法,afterreturning增强处理。目标方法正常结束后做增强处理。
returning:指定一个参数名,用于接受目标方法正常结束时返回的值。参数名称需要在增强方法中定义同名的参数。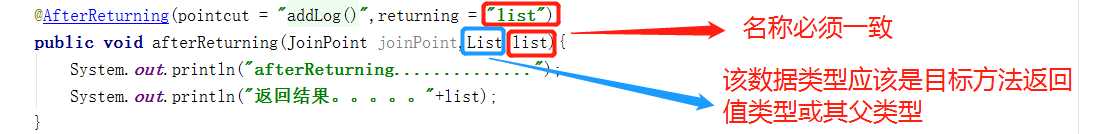
returnResult instanceof List
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "addLog()",returning = "list")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,List list){
System.out.println("afterReturning..............");
System.out.println("afterReturning 接收结果。。。。。" + list);
//修改返回结果
list.add(new User(3L, "afterReturning......"));
}
修饰方法,afterthrowing增强处理。当目标程序方法抛出 异常或者异常无法捕获时,做增强处理。
throwing:指定一个形参,在增强方法中定义同名形参,用于访问目标方法抛出的异常
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "addLog()",throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception e){
System.out.println("afterThrowing..............");
System.out.println("抛出异常。。。。。"+e);
}
@After("addLog()")
public Object after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("after..............");
//试图修改返回结果
List
constructor…
before 增强处理。。。。。。。。。。。。
查询所有用户
after…
afterReturning…
afterReturning 接收结果。。。。。[]
查询结果: [User{id=3, name=‘afterReturning…’}]
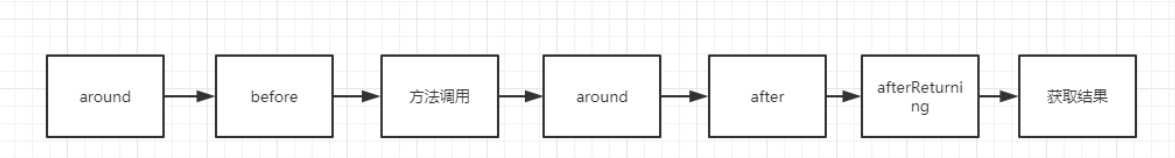
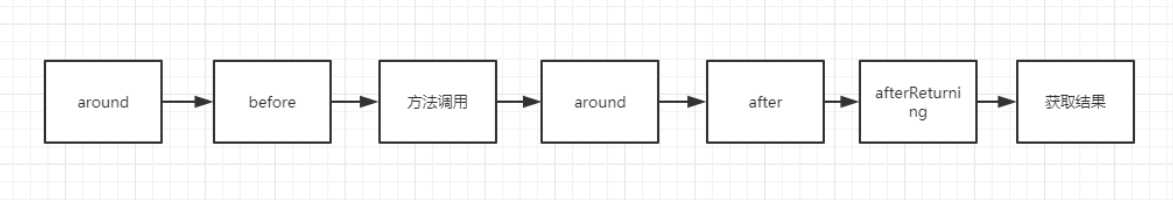
Around增强处理通常需要在线程安全的环境下使用,如果@Before和@AfterReturning可以处理就没必要使用@Around。
当定义一个Aound增前处理时,增强方法第一形参需要时ProceedingJoinPoint类型。ProceedingJoinPoint有一个Object proceed()方法,用于执行目标方法。当然也可以为目标方法传递数组参数,来修改目前方法的传入参数。public interface ProceedingJoinPoint extends JoinPoint {
void set$AroundClosure(AroundClosure var1);
Object proceed() throws Throwable;
/**
* 修改目标方法的传参
*/
Object proceed(Object[] var1) throws Throwable;
}
@Around(value= "addLog()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("around.....begin");
Object object=null;
try {
object = joinPoint.proceed();
//修改返回结果
List
constructor…
around…begin
before 增强处理。。。。。。。。。。。。
查询所有用户
around…end
after…
afterReturning…
afterReturning 接收结果。。。。。[User{id=4, name=‘around…’}]
查询结果: [User{id=4, name=‘around…’}, User{id=3, name=‘afterReturning…’}]
[User{id=4, name=‘around…’}, User{id=3, name=‘afterReturning…’}]
@Before(value = "execution(* com.example.aop.*(..)))")
@Before("execution(* com.example.aop.*(..)))")
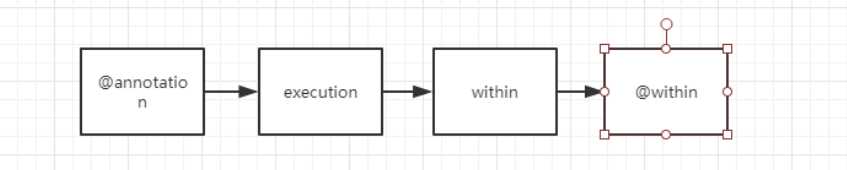
execution
@Pointcut("execution(* user*(..))")
//使用一个返回值为void,空方法体的方法命名切入点。
//public 为修饰符,跟方法的修饰符一致,public 可以在其他切面类中使用该切点,default在同一个包下的切面类中使用该切点
//返回值必须为void , 方法名就是定义的切点名称
public void userAdvice(){}
execution(modifiers-pattern? return-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern? method-name(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
使用通配符==…==,表示零个或多个任意类型的参数。
(*,String),匹配两个参数的方法。表示第一个参数类型任意,第二个必须为String类型。
(…),表示任意(个数、类型)参数
throws-pattern:方法抛出异常,可以省略execution(* *(..)) // 匹配所有包及其子包下所有类的所有方法
execution(* com..*(..)) // 匹配com包及其子包下所有类的所有方法
execution(* com.example..*(..)) // 匹配com.example包及其子包下所有类的所有方法
execution(* com.example..get*(..)) // 匹配com.example包及其子包下所有类的所有get方法
within(com.example..*) //匹配com.example包及其子包下所有类的所有方法
within(com.example.aop.UserDao) //匹配 UserDao类下的所有方法
within(com..*)
execution(* com.*(..))
@Before("@annotation(com.example.aop.CustomMethodAnnotation)")
within 作用范围是类,@within的作用范围与其一致。不同的是@within 指定的不是类而是注解@Before("@within(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody)")
package com.example.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class AdviceTest{
//execution
@Before("execution(* com.example..*(..))")
public void execution(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("execution..........");
}
//within
@Before("within(com.example..*)")
public void within(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("within..........");
}
//@within
@Before("@within(org.springframework.stereotype.Repository)")
public void withinAnnotation(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("withinAnnotation..........");
}
//@annotation
@Before("@annotation(com.example.aop.CustomMethodAnnotation)")
public void annotationAnnotation(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("annotationAnnotation..........");
}
}
package com.example.aop;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface CustomMethodAnnotation {
String value() default "";
}
@CustomMethodAnnotation
public List
constructor…
annotationAnnotation…
execution…
within…
withinAnnotation…
查询所有用户
[]
Java配置类相关注解
@Bean
public User user(){
return new User();
}
application.properties 或者 application.yml。当然了 如果在配置文件中引入其他配置文件,也可以获取到属性值。# 开发环境的配置文件 application-dev.properties
# 通常会配置三套, 生产,测试,本地
# 将通用部分配置存放在 application.yml,譬如 数据库连接等信息存放在application-xxx.yml中。这样不用每次都要繁琐的修改。
spring.profiles.active=dev
# 配置mybatis
mybatis.configuration.mapperLocations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
mybatis.configuration.typeAliasPackage=com.example.domain
mybatis.configuration.configLocation=classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="mybatis.configuration")
@Data
public class MybatisProperties {
private String configLocation ; //配置文件的路径等价于 @Value("mybatis.configuration.configLocation")
private String mapperLocations; //配置Mapper映射文件的路径
private String typeAliasPackage; //别名的实体路径
}
在springboot中大量使用了该注解,该注解提供了一种使用Java类方式配置bean。@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceConfig.class)
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
MybatisProperties mybatisProperties;
@Bean(name="sqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean=new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource); //配置数据源
factoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage(mybatisProperties.getTypeAliasPackage()); //实体类所在包
factoryBean.setConfigLocation(new DefaultResourceLoader().getResource(mybatisProperties.getConfigLocation()));// mapper配置文件
factoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mybatisProperties.getMapperLocations())); //Mapper实体类所在路径
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
// 事务管理器
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager getDatasourceManager(){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan("com.example")
@MapperScan("com.example.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
package com;
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Autowired
private JdbcProperties properties;
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
@Primary
public DataSource getSqlDataSource() throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource datasource=new DruidDataSource();
............................
return datasource;
}
}
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceConfig.class)
@Import(DataSourceConfig.class)
public class MyBatisConfig
@AliasFor("locations")
String[] value() default {};
@ImportResource({"classpath:config/beans.xml"})
该注解用来加载属性文件。
@ConfigurationProperties 。
它们的使用有一些差异:
#数据源配置
spring.datasource.url=xxxxxxxx
spring.datasource.username=xxxx
..............................
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Data
public class JdbcProperties {
@Value("${spring.datasource.maxActive}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.maxActive}")
private String type;
..............................
}
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class AppConfig {
@Autowired
Environment env;
@Bean
public User user() {
System.out.println(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url"));
return new User();
}
}
SpringMVC 相关注解
HttpMessageConverter 进行数据转化。通常会转化为JSON字符串@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody。
注意:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface SecurityParameter {
/**
* 入参是否解密,默认解密
*/
boolean inDecode() default true;
/**
* 出参是否加密,默认加密
*/
boolean outEncode() default true;
}
// 对com.demo.controller 包下的方法进行 处理
@ControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.demo.controller")
public class RequestParameterHandle implements RequestBodyAdvice {
private static final String ENCODING = "UTF-8";
//1. 控制该处理器是否支持对数据进行处理
// 主要用于判断该处理器是否对传入的数据类型支持
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Type type,
Class extends HttpMessageConverter>> aClass) {
return true;
}
//2. 当supports返回true ,执行该部分代码。在请求体被读取和转化之前执行
@Override
public HttpInputMessage beforeBodyRead(HttpInputMessage httpInputMessage,
MethodParameter methodParameter, Type type,
Class extends HttpMessageConverter>> aClass) throws
IOException {
//解码
boolean decoder = false;
//判断方法是否使用@SecurityParameter注解
if (methodParameter.getMethod().isAnnotationPresent(SecurityParameter.class)) {
//获取注解配置的包含和去除字段
SecurityParameter serializedField = methodParameter
.getMethodAnnotation(SecurityParameter.class);
//入参是否需要解密
decoder = serializedField.inDecode();
}
//自定义解码
if (decoder) {
return new CustomerHttpInputMessage(httpInputMessage);
} else {
return httpInputMessage;
}
}
@Override
public Object handleEmptyBody(Object o, HttpInputMessage
httpInputMessage, MethodParameter methodParameter, Type type,
Class extends HttpMessageConverter>> aClass) {
return o;
}
@Override
public Object afterBodyRead(Object o, HttpInputMessage httpInputMessage,
MethodParameter methodParameter, Type type,
Class extends HttpMessageConverter>> aClass) {
return o;
}
}
public class CustomerHttpInputMessage implements HttpInputMessage {
private HttpHeaders headers;
private InputStream body;
public CustomerHttpInputMessage(HttpInputMessage inputMessage) {
this.headers = inputMessage.getHeaders();
try {
//获取内容
String reqBody = IOUtils.toString(inputMessage.getBody(),
ENCODING);
//解析string为JSON
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(reqBody);
String reqData = jsonObject.getString("securityData");
//参数的解密处理
//.................
this.body = IOUtils.toInputStream(reqData, ENCODING);
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
@Override
public InputStream getBody() throws IOException {
return body;
}
@Override
public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
return headers;
}
}
/**
*
* 此方法返回结果就是 方法的入参
*/
public Object afterBodyRead(Object o, HttpInputMessage httpInputMessage,
MethodParameter methodParameter, Type type,
Class extends HttpMessageConverter>> aClass){
//获取当前的登录人
ServletRequestAttributes servletRequestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = servletRequestAttributes.getRequest();
User user = (User) httpServletRequest.getSession().getAttribute("userInfo");
// 参数类型是 Map,则使用put 方法添加
if(o instanceof Map){
Map targetMap = (Map) o;
targetMap.put("createUser",user.getName());
}else{
//其他类型
// type 通常是指方法的入参 参数类型
Class cls = (Class) type;
try {
Method method = cls.getMethod("setName",String.class);
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(o,user.getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
可以设置的属性
defaultValue :设置参数默认值。 只有在required 设置为false的情况下,才会生效 。
name | value 关联的参数名称。 request.getParameter(name);