数据结构与算法-绪论
2021-04-09 13:29
标签:return 问题 例子 可行性 滚动数组 斐波那契数 空间 str1 状态 算法:即是在特定计算模型下,旨在解决特定问题的指令序列 层级级别: 减而治之 分而治之 数组反向 改进1: 改进2: 相关链接 蛮力 递增 分治 减治 动态规划 情况分析 空间优化 递归版本(没写JAVA版的) 相关链接 数据结构与算法-绪论 标签:return 问题 例子 可行性 滚动数组 斐波那契数 空间 str1 状态 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/suit000001/p/13373802.html绪论
要保证正确性、确定性、可行性、有穷性
有穷性:例子1:HailStone序列

@Test
public void test1() {
int n = 7;
int length = 1;
while (n > 1) {
n = ((n % 2) > 0) ? 3 * n + 1 : n / 2;
length++;
}
System.out.println(length);
}
例子2:计算任意N个整数之和
@Test
public void test4() {
int[] A = {100, 836, 3236, 5, 16, 26, -3, 89, 69, 43};
long begintime = System.nanoTime();
/*int n = A.length;//简单递归
System.out.println(sum1(A,n));*/
int lo = 0;//二分递归
int hi = A.length - 1;
System.out.println(sum2(A, lo, hi));
long endtime = System.nanoTime();
long costTime = (endtime - begintime);
System.out.println(costTime);
}
public int sum1(int A[], int n) {
return (n 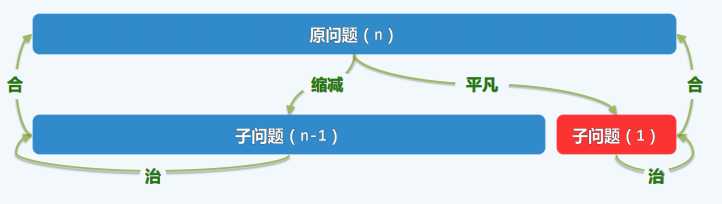
public int sum2(int A[], int lo, int hi) {
if (lo == hi) {
return A[lo];
}
int mi = (lo + hi) >> 1;
return sum2(A, lo, mi) + sum2(A, mi + 1, hi);
}
@Test
public void test5() {
int[] A = {100, 836, 3236, 5, 16, 26, -3, 89, 69, 43};
int lo = 0;
int hi = A.length - 1;
reverse(A, lo, hi);
}
public void reverse(int[] A, int lo, int hi) {
if (lo 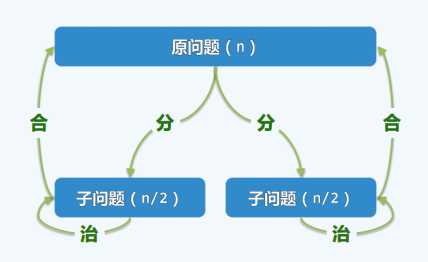
例子3:从数组区间中找出最大的两个整数元素
@Test
public void test6() {
int[] A = {100, 836, 3236, 5, 16, 26, -3, 89, 69, 43};
int lo = 0;
int hi = A.length - 1;
/*int[] int1 = max2(A, lo, hi);*/
/*int[] int2 = max02(A, lo, hi);*/
int[] int3 = max002(A, lo, hi);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(int3));
}
public int[] max2(int[] A, int lo, int hi) {
int x1 = lo;
int x2 = lo;
//扫描lo-hi,找到x1
for (int i = lo + 1; i public int[] max02(int[] A, int lo, int hi) {
int x1 = lo;
int x2 = lo + 1;
if (A[x1] public int[] max002(int[] A, int lo, int hi) {
int x1 = 0;
int x2 = 0;
if (lo + 1 == hi){
if (A[x1 = lo] A[mid]) && (A[lo] > A[hi])){
x1 = lo;
x2 = (A[mid] > A[hi]) ? mid:hi;
}else if((A[lo] A[hi])){
x1 = mid;
x2 = (A[lo] > A[hi]) ? lo:hi;
}else{
x1 = hi;
x2 = (A[lo] > A[mid]) ? lo:mid;
}
return new int[]{x1,x2};
}
int mi = (lo + hi) / 2;
int[] L= max002(A, lo, mi);
int[] R = max002(A, mi+1, hi);
if (A[L[0]] > A[R[0]]){
x1 = L[0];
x2 = (A[L[1]] > A[R[0]]) ? L[1]:R[0];
}else{
x1 = R[0];
x2 = (A[L[0]] > A[R[1]]) ? L[0]:R[1];
}
return new int[]{x1,x2};
}
例子3.5:最大综合区间(还没写)




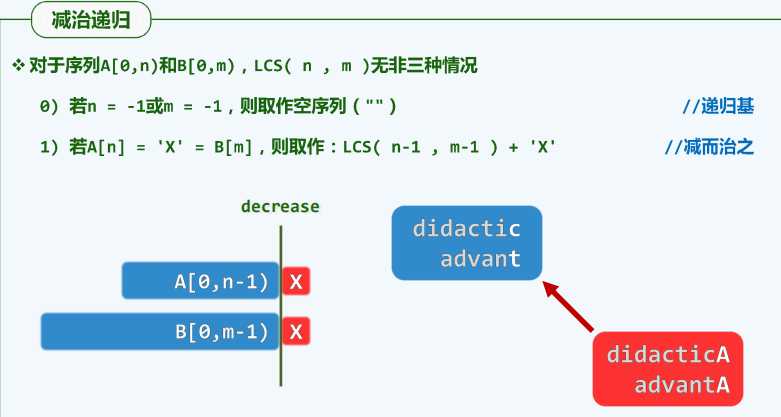
例子4:斐波那契数列
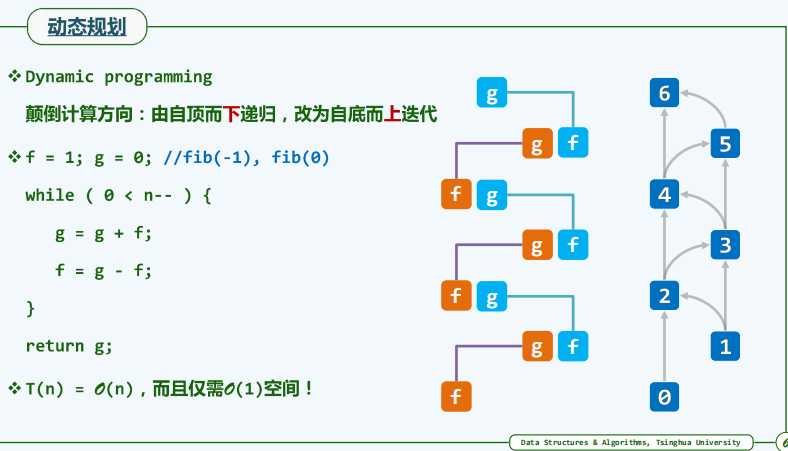
@Test
public void test7(){
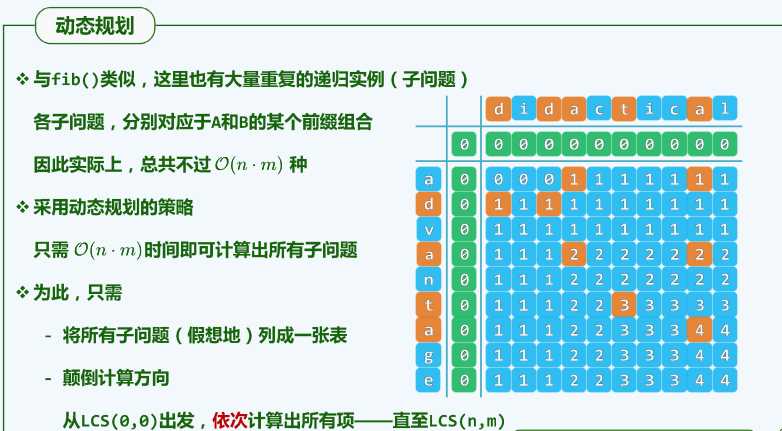
for (int i = 0;i 例子5:最长公共子序列
@Test
public void test8(){
char[] x = {‘A‘,‘B‘,‘C‘,‘B‘,‘D‘,‘A‘,‘B‘};
char[] y = {‘B‘,‘D‘,‘C‘,‘A‘,‘B‘,‘A‘};
int[][] b = new int[x.length+1][y.length+1];
int[][] c = lcsLength(x,y,b);
System.out.println(c[x.length][y.length]);
lcs(x.length,y.length,x,b);
}
//从[0][0]向[x.length+1][y.length+1]不断的得到1、共同序列个数 2、各种情况并作出标记
public int[][] lcsLength(char[] x,char[] y,int[][] b) {
//给第一行,第一列设置空序列
int[][] c = new int[x.length+1][y.length+1]; //0存空序列
for(int i=0;i/**
* 方法二、进行空间上的优化
* 通过状态方程可知,计算c[i][j]时只需知道c[i-1][j-1]、c[i-1][j]、c[i][j-1]就行了
* 那么就和斐波那契数列比较相似,可以利用滚动数组
*/
//从[0][0]向[x.length+1][y.length+1]不断的得到1、共同序列个数 2、各种情况并作出标记
public Setfunction LCS(str1, str2, a, b) {
if(a === void 0){
a = str1.length - 1
}
if(b === void 0){
b = str2.length - 1
}
if(a == -1 || b == -1){
return 0
}
if(str1[a] == str2[b]) {
return LCS(str1, str2, a-1, b-1)+1;
}
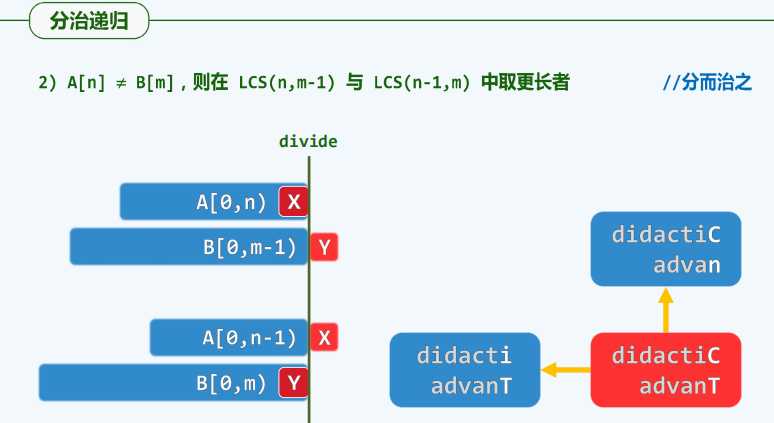
if(str1[a] != str2[b]) {
var x = LCS(str1, str2, a, b-1)
var y = LCS(str1, str2, a-1, b)
return x >= y ? x : y
}
}
例子6:就地循环位移(还没写)
例子7:就地随机置乱(还没写)
下一篇:tarjan 算法与图的连通性