标签:而且 pac show ica 多少 头文件 图表 int hdu
拓扑排序
在一个有向图中,对所有的节点进行排序,要求没有一个节点指向它前面的节点
具体实现
1
找到一个入度为0的点
2
把这个点删掉(放入ans中),把所有以他为起点的路断掉
3
重复 1 2 直到没有入度为0的点 如果还有点没有被删掉 那就是有环(所以还可以用来判断图里是否有环)
ans中的顺序就是拓扑排序后的顺序
下面这个图表现的更明显
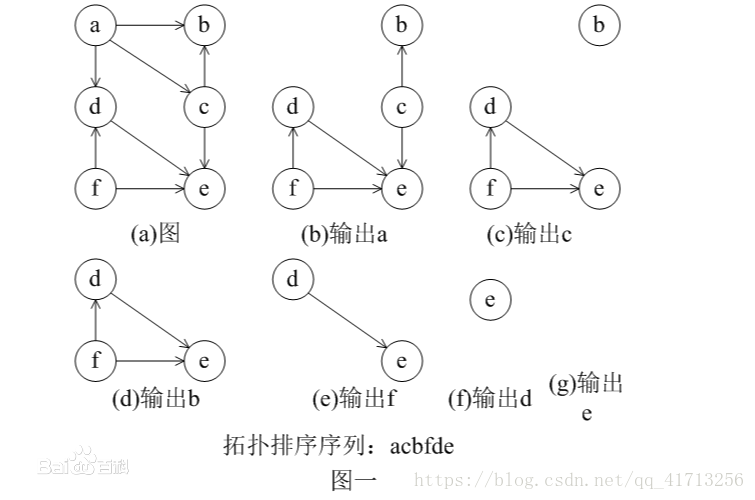
代码实现
1 首先看到“具体实现”我们先考虑模拟
好理解,好写,效率低
所以我们不写了
2 在搞完模板题后,看到正确的打开方式应该是 queue
模板题:HDU-1285
vector实现
因为是要求编号尽量从小到大,所以这里的queue要用优先队列
而且要用priority_queue, greater > q; 就要加一个头文件 #include
我们记下每个点的入度是多少,先找到一个入度为0的点,放入queue中,然后循环取top,把所有以他为起点的路断掉,终点入度-1,当前点放到ans中,如果这个点入度为0了,再扔进queue
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(a) ((a) & -(a))
#define clean(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 9;
int _;
//========================================================================
int vis[509];
priority_queue, greater > q;
vectorans;
vectoredge[509];
void topological_sort(int n)
{
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
ans.clear();
for(int i=1;i
链式前向星实现
(都差不多,但我很久没用链式前向星了,复习一下)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(a) ((a) & -(a))
#define clean(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 9;
int _;
//========================================================================
int vis[509];
priority_queue,greater > q;
vectorans;
struct edge
{
int to,cost,next;
}e[maxn];
int top,head[maxn];
void init()
{
top=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void insert_(int u,int v,int c)
{
e[top].to=v;
e[top].cost=c;
e[top].next=head[u];
head[u]=top++;
}
void topological_sort(int n)
{
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
ans.clear();
for(int i=1;i
[拓扑排序]
标签:而且 pac show ica 多少 头文件 图表 int hdu
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/YangKun-/p/13258426.html
